The global market for automotive adhesives is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight vehicle construction, enhanced fuel efficiency, and improved structural integrity in auto body assembly. According to Grand View Research, the global automotive adhesives market size was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of structural adhesives in place of traditional mechanical fastening methods, especially in electric and high-performance vehicles. As automakers prioritize crash safety, noise reduction, and design flexibility, advanced adhesives have become critical in bonding auto body panels made from mixed materials such as aluminum, composites, and high-strength steel. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, innovating with high-strength, durable, and temperature-resistant adhesive solutions tailored for modern automotive manufacturing. Below are the top seven adhesive manufacturers shaping the future of auto body panel assembly.
Top 7 Adhesive For Auto Body Panels Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Automotive Structural Adhesives – OEM & Tier
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: 3M’s liquid and tape automotive structural adhesives are made for semi-automated or manual applications to provide strength and protection to your vehicles….
#2 Sika Adhesive Solutions for Vehicle Assembly
Domain Est. 1995
Website: industry.sika.com
Key Highlights: Sikaflex® 500 Series panel adhesives have a proven track record in all kinds of adhesive bonding and sealing applications in industrial manufacturing….
#3 Adhesives
Domain Est. 1999
Website: semproducts.com
Key Highlights: Repair Adhesives · Dual-Mix™ Forever Warranty · OEM recommended · Superior impact and peel strength · Excellent corrosion resistance · 60 minute working ……
#4 Henkel Adhesives:
Domain Est. 2000
Website: next.henkel-adhesives.com
Key Highlights: Henkel Adhesive Technologies is the world’s number one producer in adhesives, sealants, and functional coatings….
#5 UNITECH, Korean Adhesive Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2011
Website: unitechcorp.com
Key Highlights: UNITECH values customer safety before all. Body shop adhesives produced by UNITECH provides the best performance for improving the vehicle strength which ……
#6 Aftermarket Solutions
Domain Est. 1987
Website: dupont.com
Key Highlights: Adhesive formulations enable the repair of metal, plastic, and composite body panels and joints to keep cars looking and performing in top shape. Learn more ……
#7 Quality automotive body panel adhesives for industry
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tesa.com
Key Highlights: Use tesa® automotive body panel adhesives for reliable results, even in demanding car body applications. Masking, protection &security. Discover more here….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Adhesive For Auto Body Panels

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Adhesives in Auto Body Panels
The global market for adhesives used in auto body panels is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive manufacturing, a growing emphasis on lightweighting, and the rise of electric vehicles (EVs). As automakers strive to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance vehicle performance, structural and semi-structural adhesives are increasingly replacing traditional mechanical fastening methods such as spot welding and riveting.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the shift toward multi-material vehicle design. Modern auto body panels often combine high-strength steel, aluminum, magnesium, and composites—materials that are difficult to join using conventional techniques. Adhesives provide superior bonding strength across dissimilar materials, reduce stress concentrations, and improve overall structural integrity. This trend is particularly pronounced in premium and electric vehicle segments, where manufacturers like Tesla, BMW, and Rivian are leveraging adhesive technologies to achieve sleek designs and improved crash performance.
Another critical driver is the expansion of the electric vehicle market. EVs demand lightweight construction to maximize battery range, and adhesives contribute significantly to weight reduction. Moreover, adhesives help dampen vibrations and reduce noise—important factors in the quieter cabin environment of EVs. By 2026, the integration of adhesives in battery enclosures and body-in-white (BIW) assemblies is expected to become standard in EV manufacturing, further boosting demand.
Technological innovation is also accelerating. Leading chemical companies such as Henkel, 3M, and Sika are developing next-generation adhesives with faster cure times, enhanced durability under extreme conditions, and improved sustainability profiles. Reactive acrylics, epoxies, and polyurethanes dominate the market, but water-based and bio-based formulations are gaining traction as automakers respond to environmental regulations and consumer demand for greener production.
Additionally, automation and digitalization in automotive assembly lines are influencing adhesive application processes. By 2026, precision robotic dispensing systems integrated with real-time monitoring and quality control will become more widespread, ensuring consistent bond quality and reducing material waste.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is expected to lead market growth due to robust automotive production and aggressive EV adoption policies. North America and Europe will follow closely, supported by stringent CO₂ emission standards and investments in advanced manufacturing.
In summary, the 2026 market for adhesives in auto body panels will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and integration with next-generation vehicle platforms. As adhesives evolve from auxiliary materials to critical structural components, their role in shaping the future of automotive design and manufacturing will become increasingly indispensable.
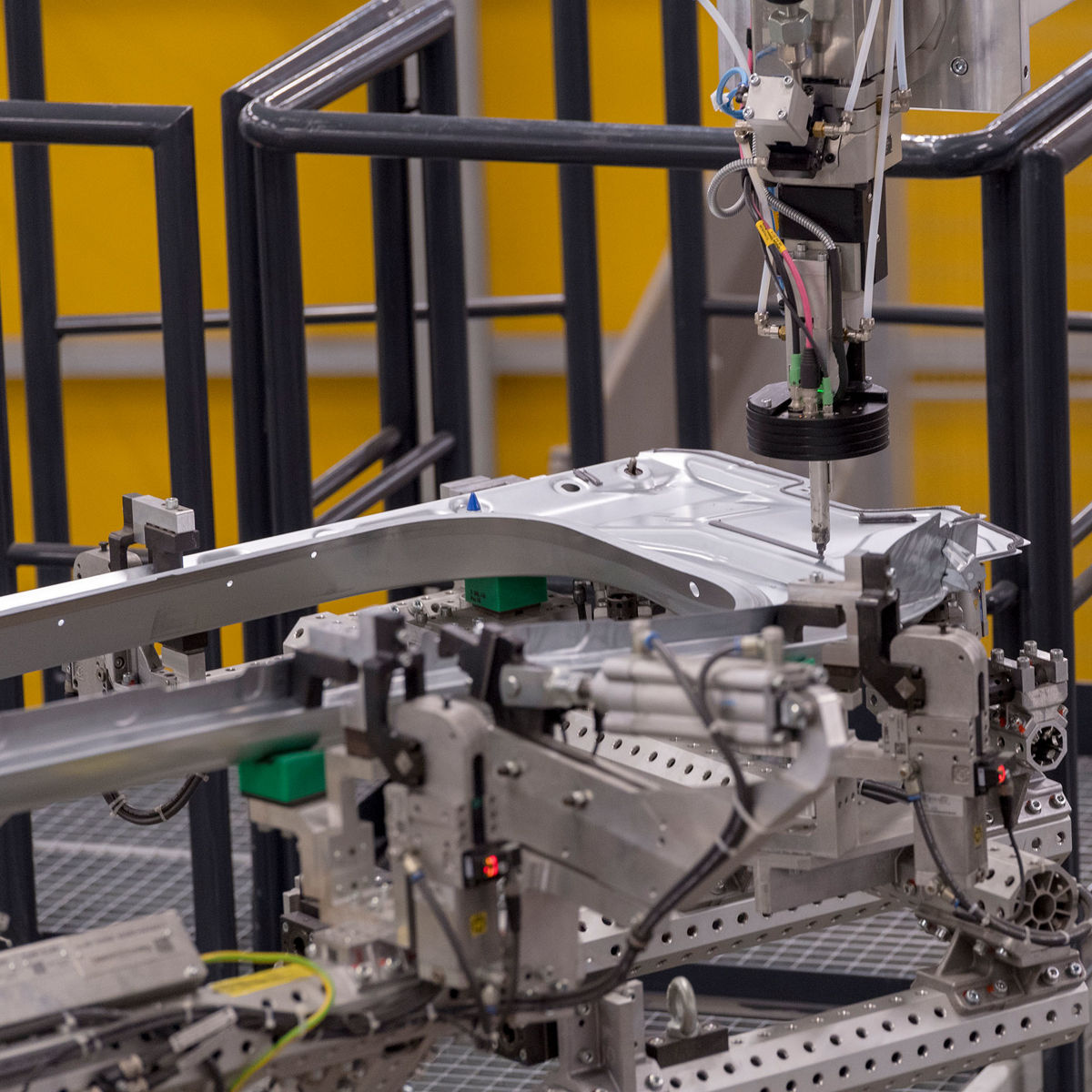

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Adhesive for Auto Body Panels (Quality, IP)
When sourcing adhesives for auto body panels, manufacturers and suppliers must navigate several critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, legal complications, and reputational damage. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Compromising on Adhesive Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting adhesives based solely on cost, which can lead to subpar performance. Low-quality adhesives may fail under environmental stress, such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, or vibration, compromising the structural integrity of the vehicle.
- Inadequate Bond Strength: Poor adhesives may not provide sufficient adhesion between dissimilar materials (e.g., steel, aluminum, composites), leading to delamination or failure in crash scenarios.
- Lack of Durability: Inferior formulations may degrade over time, reducing service life and increasing warranty claims.
- Inconsistent Curing: Non-uniform curing behavior can lead to weak bonds or production delays.
2. Ignoring Industry Standards and Certifications
Failing to verify that the adhesive meets automotive industry standards (e.g., ISO 10140, ASTM D3163, OEM-specific specs like Ford WSB-M4-D120-A1) is a major oversight. Adhesives used in auto body applications must undergo rigorous testing for safety, durability, and compatibility.
- Non-compliance Risks: Using uncertified adhesives may lead to regulatory issues or rejection by OEMs.
- OEM Approval Gaps: Many vehicle manufacturers require adhesives to be pre-approved. Sourcing unapproved products can disrupt supply chains.
3. Overlooking Material Compatibility
Auto body panels often use mixed materials (e.g., high-strength steel, aluminum, carbon fiber). Not all adhesives bond effectively across these substrates.
- Chemical Incompatibility: Some adhesives react negatively with surface treatments or coatings (e.g., e-coats, primers).
- Thermal Expansion Mismatch: Adhesives must accommodate differences in thermal expansion between materials to prevent stress-induced failure.
4. Underestimating Environmental and Processing Conditions
Adhesives must perform under real-world conditions during both application and vehicle operation.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Adhesives that cure or perform poorly in cold or hot environments can lead to manufacturing defects.
- Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: Poor resistance can result in long-term corrosion at the bond line, especially in underbody or coastal applications.
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing adhesives from unauthorized or unverified suppliers can expose companies to IP infringement.
- Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products: Some suppliers may offer “compatible” adhesives that infringe on patented formulations or trademarks.
- Lack of Licensing: Using proprietary adhesive technologies without proper licensing agreements can result in legal action and financial penalties.
- Trade Secret Exposure: Poor supplier vetting may lead to unintentional disclosure of internal bonding processes or formulations.
6. Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Choosing suppliers based on price alone without evaluating their technical capability, quality control systems, or track record is risky.
- Limited Technical Support: Reputable suppliers offer formulation expertise, application guidance, and troubleshooting.
- Inconsistent Batch Quality: Poor manufacturing controls can result in variability between adhesive batches, affecting performance and process reliability.
7. Failure to Secure Long-Term Supply Agreements
Auto manufacturing requires continuity. Sourcing adhesives from suppliers without stable production capacity or raw material access can disrupt operations.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Geopolitical issues or raw material shortages can halt production if alternative sources aren’t vetted.
- Formulation Changes Without Notice: Suppliers may alter adhesive formulations without informing customers, impacting performance or compliance.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, procurement teams should conduct thorough due diligence, prioritize certified and OEM-approved adhesives, verify IP legitimacy, and build relationships with reputable, technically capable suppliers. Investing in quality and compliance upfront minimizes risks and ensures the safety, durability, and legality of automotive assemblies.
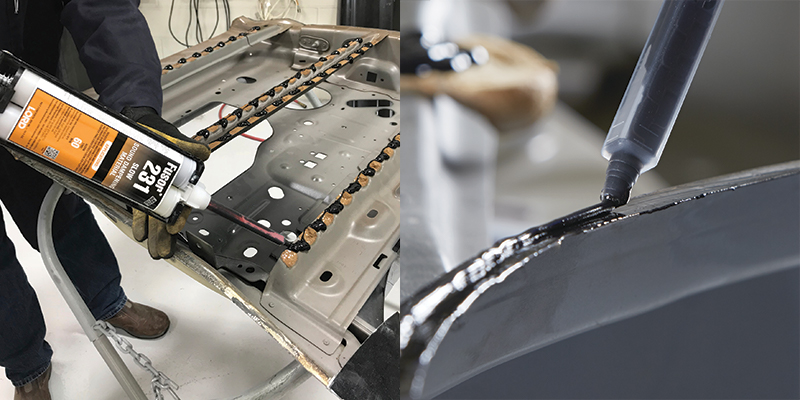

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Adhesive For Auto Body Panels
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Adhesives used for automotive body panels are subject to various international, national, and industry-specific regulations. These products are typically classified under chemical safety, transportation, and environmental compliance frameworks. Key regulatory systems include REACH (EU), TSCA (USA), GHS (Globally Harmonized System), and specific automotive OEM standards (e.g., Ford, GM, BMW). Proper classification ensures safe handling, storage, and transport across supply chains.
Hazard Communication and Labeling
All adhesive products must comply with GHS labeling requirements, including hazard pictograms, signal words (e.g., “Danger” or “Warning”), hazard statements, and precautionary measures. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be up to date (version 16 or later as applicable) and provided to all downstream users. Labels must include product identifiers, manufacturer information, and batch numbers for traceability.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
Adhesives for auto body panels are often classified as hazardous materials due to flammability, toxicity, or reactivity. Ground, air, and sea shipments must comply with:
– ADR/RID (Europe – road/rail)
– IMDG Code (maritime transport)
– IATA DGR (air freight)
Packaging must be UN-certified, leak-proof, and compatible with adhesive chemistry. Proper hazard class (typically Class 3 Flammable Liquids or Class 8 Corrosive, depending on formulation) and packing group must be declared on shipping documents.
Storage and Handling Protocols
Store adhesives in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources (typically 10–25°C). Keep containers tightly sealed and segregated from incompatible materials (e.g., oxidizers, strong acids/bases). Use appropriate PPE (gloves, goggles, respirators) during handling. Implement spill containment systems and ensure emergency equipment (eyewash stations, fire extinguishers) is accessible.
Environmental and Waste Disposal Compliance
Spent containers, unused product, and cleanup materials are considered hazardous waste in many jurisdictions. Follow local regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., Environment Agency in the UK) for disposal. Never pour adhesives into drains or soil. Use licensed waste handlers and maintain disposal records. Consider recycling programs for empty adhesive drums where available.
Import and Export Documentation
Cross-border shipments require accurate documentation including:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– SDS and Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Regulatory Compliance Certifications (e.g., REACH SVHC declaration, TSCA compliance statement)
Ensure Harmonized System (HS) codes are correctly applied (e.g., 3506.91 or similar, depending on composition).
OEM and Industry Standards Compliance
Automotive adhesives must often meet OEM-specific technical and compliance standards such as:
– ISO 10360 (adhesive testing)
– VW 50180, GM 6258M, Ford WSS-M4D685-A1
– Resistance to temperature, vibration, and chemical exposure
Suppliers must provide test reports and material certifications upon request. Regular audits may be required to maintain approval status.
Supply Chain Traceability and Recordkeeping
Maintain full traceability from raw material sourcing to final delivery. Keep records of:
– Batch numbers and expiration dates
– SDS revisions and compliance updates
– Shipping manifests and customs documentation
– Quality control test results
Records should be retained for a minimum of 5–10 years, depending on jurisdiction.
Emergency Response and Incident Reporting
Develop and communicate an emergency response plan for spills, fires, or exposure incidents. Train personnel on first aid procedures and reporting protocols. Report significant incidents to relevant authorities (e.g., CHEMTREC in North America, SEVESO sites in EU) as required. Conduct regular drills and review procedures annually.
Sustainability and Future Compliance Trends
Monitor evolving regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), restricted substances (e.g., phthalates, heavy metals), and circular economy mandates. Invest in low-VOC, bio-based, or recyclable adhesive formulations where feasible. Prepare for Digital Product Passports (EU) and increased supply chain transparency requirements.
Conclusion:
Sourcing the right adhesive for auto body panels is a critical decision that directly impacts the structural integrity, durability, safety, and aesthetics of the vehicle. As automotive manufacturing continues to evolve with increased use of lightweight and mixed materials—such as aluminum, high-strength steel, and composites—traditional joining methods like spot welding are being supplemented or replaced by advanced structural adhesives.
When selecting an adhesive, key factors must be considered, including bonding strength, flexibility, resistance to environmental conditions (such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and UV exposure), cure time, compatibility with substrates, and ease of application. Additionally, compliance with industry standards and OEM specifications is essential to ensure long-term performance and warranty compliance.
The sourcing process should involve collaboration with reputable adhesive suppliers offering technical support, testing data, and proven track records in automotive applications. Prioritizing adhesives with high fatigue resistance and energy absorption characteristics enhances vehicle safety and crash performance.
In conclusion, a well-informed adhesive sourcing strategy—balancing performance, cost, manufacturability, and regulatory requirements—plays a vital role in achieving high-quality, reliable, and efficient auto body assembly. Investing in the right adhesive solution not only improves product performance but also supports innovation in vehicle design and sustainability.