The global acrylic fiber market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for affordable, durable, and lightweight textile alternatives in apparel and home furnishings. According to Grand View Research, the global acrylic fiber market size was valued at USD 5.4 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by rising consumer preference for synthetic fibers that offer wool-like properties at a lower cost—making acrylic sweaters a popular choice in fast fashion and budget-friendly clothing lines. As sustainability and performance standards evolve, manufacturers are investing in advanced polymerization techniques and recycled content integration. Against this backdrop, a select group of material producers has emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and quality in acrylic sweater production. Based on market presence, production capacity, and technological advancement, the following eight manufacturers represent the top players shaping the future of acrylic knitwear materials worldwide.
Top 8 Acrylic Sweater Material Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Vardhman
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vardhman.com
Key Highlights: Acrylic Fibers. Marketed under the brand name ‘VARLAN®’, Vardhman has a capacity to manufacture 22,000 tons per annum of Acrylic Staple Fibre and Tow….
#2 Garg Acrylics Limited
Domain Est. 2002
Website: gargltd.com
Key Highlights: Garg Acrylics Ltd. are one of the leading manufacturers, suppliers & exporters of basic yarns, specialty yarn & garments. Yarns is our largest business with ……
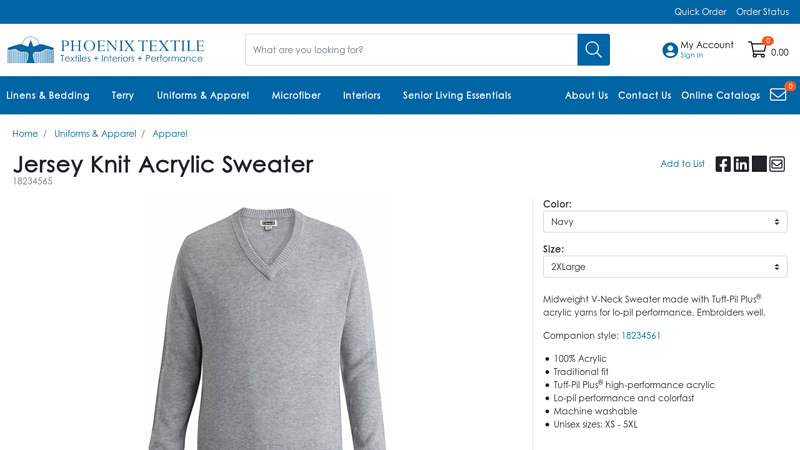
#3 Jersey Knit Acrylic Sweater
Domain Est. 2021
Website: pyphoenixtextile.com
Key Highlights: Style: Sweater · Fit: Unisex · Color(s): Black, Grey, Heather Grey, Navy · Fabric Blend: 100% Acrylic · Sleeve Length: Long Sleeve · Manufacturer: Edwards Garment ……
#4 TORAYLON™ Acrylic Fiber
Domain Est. 1995
Website: toray.com
Key Highlights: Acrylic Fiber. With excellent bulkiness, colorability, adaptability with other fibers, soft feel and elasticity, TORAYLON™ is perfectly suited to a wide variety ……
#5 What Is Acrylic Fabric?
Domain Est. 1998
Website: swavelle.com
Key Highlights: Acrylic is a synthetic fabric originally developed as a wool alternative. It’s a popular material worldwide due to its ease of care, durability and comfort….
#6 Custom Apparel Made from Acrylic Fabrics
Domain Est. 2013
Website: merchology.com
Key Highlights: 4.5 540 The sweaters, cardigans, and pull-overs featured within the acrylic fabrics collection are easy to wear and easy to care for, meaning they’ll look stylish ……
#7 Acrylic Fabric
Domain Est. 2024
Website: gnbgarments.com
Key Highlights: Acrylic fabric, a synthetic textile like wool, offers durability and vibrant paint applications for US B2B apparel and upholstery….
#8 Best Acrylic Fabric Manufacturers of 2025
Website: szoneierfabrics.com
Key Highlights: Discover the top 20 acrylic fabric manufacturers in 2025, offering high-quality, sustainable fabrics and custom solutions for various ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Acrylic Sweater Material
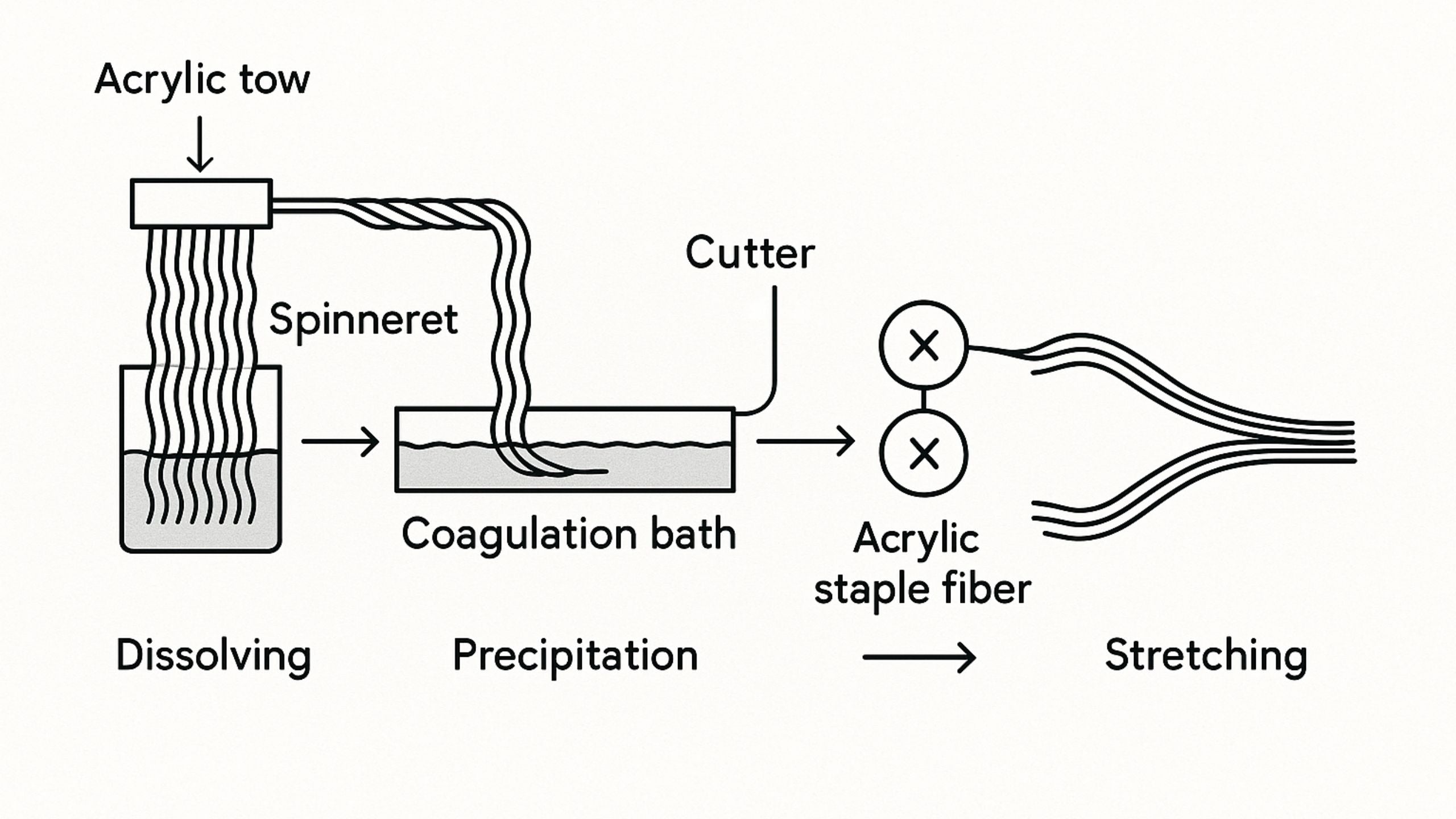
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Acrylic Sweater Material
The global market for acrylic sweater material is expected to undergo significant shifts by 2026, shaped by evolving consumer preferences, sustainability concerns, technological advancements, and competitive dynamics with natural and alternative synthetic fibers. Below is an analysis of the key trends expected to influence the acrylic sweater material market in 2026:
-
Declining Demand Due to Sustainability Pressures
By 2026, demand for traditional acrylic sweater material is anticipated to face downward pressure due to growing environmental awareness. Acrylic, being a petroleum-based synthetic fiber, contributes to microplastic pollution and has a high carbon footprint during production. As consumers and brands prioritize eco-friendly materials, many are shifting toward biodegradable or recycled alternatives. This trend is particularly strong in North America and Western Europe, where sustainability regulations and green certifications are tightening. -
Rise of Modified and Recycled Acrylic Fibers
In response to environmental concerns, fiber manufacturers are investing in modified acrylic variants and recycled acrylic solutions. By 2026, expect increased availability of “eco-acrylic” fibers—acrylic blends incorporating recycled content or produced using lower-energy processes. These innovations aim to retain acrylic’s desirable qualities (softness, warmth, color retention) while reducing ecological impact, potentially stabilizing market share in mid-tier apparel segments. -
Price Competitiveness Keeping Acrylic Relevant in Emerging Markets
Despite sustainability challenges, acrylic will maintain a foothold in price-sensitive markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa. Its low cost compared to wool, cashmere, or even cotton makes it a preferred choice for budget-friendly winter wear. By 2026, rising disposable incomes in these regions may boost volume demand for acrylic sweaters, especially in mass-market retail and private-label brands. -
Competition from Bio-Based and Plant-Derived Alternatives
The emergence of bio-based synthetics—such as polylactic acid (PLA) fibers and castor bean-based nylons—will challenge acrylic’s dominance in the synthetic sweater segment. Brands aiming for circularity and lower environmental impact are increasingly experimenting with these next-generation materials. By 2026, such alternatives could capture a growing share of the mid-to-premium sweater market, particularly among eco-conscious millennial and Gen Z consumers. -
Technological Improvements in Fiber Performance
Ongoing R&D is expected to yield acrylic fibers with enhanced breathability, reduced pilling, and better moisture management. These performance upgrades may help acrylic regain appeal in activewear-inspired knitwear and lightweight sweaters. Additionally, anti-static and odor-resistant treatments could broaden its application beyond traditional casual wear. -
Impact of Fast Fashion and Seasonal Trends
Fast fashion brands continue to rely on acrylic for its versatility and low production cost. However, increasing scrutiny on overproduction and waste may force these brands to reduce acrylic usage by 2026. Instead, some may adopt blended fabrics (e.g., acrylic-organic cotton or acrylic-recycled polyester) to balance cost, performance, and sustainability. -
Regulatory and Supply Chain Influences
Global regulations targeting single-use plastics and microfiber shedding may extend to textile production, affecting acrylic manufacturing. By 2026, compliance with stricter chemical usage and emissions standards could increase production costs, potentially reducing profit margins for acrylic producers unless offset by innovation or scale efficiencies.
Conclusion:
The acrylic sweater material market in 2026 will likely be characterized by transition rather than growth. While traditional virgin acrylic may decline in high-income markets due to environmental concerns, modified, recycled, and blended versions could sustain relevance in value segments and developing economies. Success for acrylic will depend on the industry’s ability to innovate sustainably while maintaining affordability and performance.
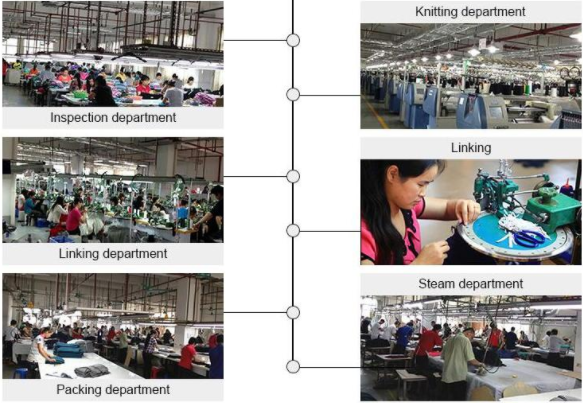

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Acrylic Sweater Material (Quality, IP)
When sourcing acrylic sweater material, businesses must navigate several challenges related to both quality control and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to substandard products, legal disputes, or reputational damage. Below are key issues to watch for:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Fiber Composition
Not all acrylic fibers are created equal. Suppliers may offer materials labeled as “acrylic” that contain blends with lower-cost fibers (e.g., polyester or recycled acrylic) without clear disclosure. This affects softness, durability, pilling resistance, and color retention.
Poor Dye Fastness and Color Consistency
Low-quality acrylic yarns often suffer from poor dye absorption, leading to fading after washing or exposure to sunlight. Batch-to-batch color variation is common with less-reputable suppliers, making it difficult to maintain consistent product lines.
Pilling and Abrasion Resistance
Inferior acrylic fibers tend to pill quickly due to shorter fiber lengths and lower tenacity. Buyers may receive material that looks premium initially but degrades after minimal use.
Lack of Testing and Certification
Many suppliers, especially in emerging markets, may not provide third-party test reports (e.g., for Oeko-Tex, REACH, or ISO standards). Without verifiable data, ensuring material safety and performance becomes risky.
Inadequate Lot Traceability
Poor batch tracking can make it difficult to identify the source of quality issues, especially when problems arise post-production or during customer use.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Use of Branded or Patented Yarns
Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” versions of proprietary acrylic fibers (e.g., modacrylic blends or anti-pilling technologies) that infringe on patents held by companies like Dralon, Courtelle, or Zeflan. Using such materials can expose buyers to legal liability.
Counterfeit Certifications and Misleading Claims
Suppliers may falsely claim their acrylic yarn is certified by recognized bodies or is a specific branded fiber. This misrepresentation not only affects quality but may also constitute trademark or IP infringement.
Design and Texture Copying
Sweater knit patterns or finishes may mimic protected designs. Sourcing fabric with such features—without proper licensing—can lead to IP disputes, especially when selling in regulated markets like the EU or U.S.
Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts
Many supply agreements fail to include clear IP indemnification clauses. Without these, buyers may bear the legal and financial burden if the material is found to violate third-party rights.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify fiber content through independent lab testing.
- Request full documentation, including test reports and chain-of-custody records.
- Work with reputable suppliers who openly disclose fiber sources and IP status.
- Include IP warranties and indemnification in procurement contracts.
- Conduct due diligence on patented fiber technologies and avoid “too good to be true” alternatives.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, businesses can ensure reliable sourcing of acrylic sweater material while minimizing legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Acrylic Sweater Material
Material Overview
Acrylic is a synthetic fiber derived from acrylonitrile, a petrochemical-based polymer. Widely used in sweater manufacturing, acrylic offers wool-like warmth, softness, color retention, and resistance to moths and mildew. It is lightweight, easy to care for, and cost-effective. However, its synthetic nature requires specific considerations in logistics, environmental compliance, and international trade.
Classification & Tariff Codes
Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance and duty assessment:
– HS Code (Harmonized System): Typically 5501.30 (acrylic staple fibers) or 6110.30 (sweaters, pullovers, etc., of synthetic fibers).
– Country-Specific Codes: Consult local tariff databases (e.g., HTSUS in the U.S., TARIC in the EU).
– Textile Category: Often falls under Category 6 (synthetic fiber apparel) for quota monitoring in some regions.
International Shipping & Packaging
- Packaging Standards: Use moisture-resistant polybags to prevent mildew during transit. Consolidate units in sturdy corrugated cartons with internal dividers to avoid compression damage.
- Marking Requirements: Clearly label packages with product description, fiber content (e.g., “100% Acrylic”), country of origin, care instructions, and safety warnings.
- Shipping Modes: Ocean freight is common for bulk shipments; air freight for urgent or high-value consignments. Ensure proper stacking and humidity control in containers.
Environmental & Chemical Compliance
- REACH (EU): Comply with registration, evaluation, and restriction of chemicals. Acrylonitrile monomer residuals must be below regulated thresholds.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Acrylonitrile is listed as a carcinogen. Provide clear warnings if applicable.
- OEKO-TEX® Standard 100: Recommended certification to ensure absence of harmful substances in textile products.
- PFAS & Azo Dyes: Ensure dyes and finishing agents are free of banned substances per global textile regulations.
Sustainability & Waste Management
- Recycling Challenges: Acrylic is not readily biodegradable and difficult to recycle. Encourage take-back programs or mechanical recycling where available.
- Microplastic Shedding: Educate consumers on laundry practices (e.g., use of microfiber filters) to reduce environmental impact.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Monitor evolving EPR laws in target markets requiring brands to manage end-of-life textiles.
Import/Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail fiber content, value, origin, and HS code.
- Packing List: Itemize quantities, weights, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements.
- Textile Declaration: Mandatory in many countries (e.g., EU, U.S. FTC) stating fiber composition.
Labeling & Consumer Information
- Fiber Content Label: Clearly state “100% Acrylic” or blend percentages as per FTC (U.S.) or EU Textile Regulation (EU No 1007/2011).
- Care Instructions: Include washing, drying, and ironing symbols per ISO 3758.
- Country of Origin: Legally required in most markets; must be accurate and permanent.
Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Supplier Audits: Verify raw material sourcing and manufacturing compliance.
- Testing Protocols: Conduct third-party testing for flammability (e.g., 16 CFR 1610 in the U.S.), color fastness, and chemical content.
- Incoterms® Usage: Clearly define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, CIF) to avoid disputes.
- Insurance: Cover risks such as water damage, contamination, or customs delays.
Regulatory Updates & Monitoring
Stay informed on evolving standards:
– EU Green Deal & Strategy for Sustainable Textiles: Anticipate stricter eco-design, labeling, and recycling rules.
– CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism): Future carbon costs may affect synthetic fiber imports.
– National Bans on Single-Use Plastics: May indirectly influence packaging materials used in logistics.
Adhering to this guide ensures efficient, compliant, and sustainable movement of acrylic sweater materials across global supply chains.
In conclusion, sourcing acrylic sweater material offers a cost-effective, durable, and versatile solution for manufacturers and fashion brands seeking affordable and low-maintenance knitwear. Acrylic fibers provide excellent softness, color retention, and resistance to shrinking and pilling, making them ideal for everyday garments. Additionally, the availability of recycled and sustainable acrylic options supports growing environmental concerns within the textile industry. While acrylic lacks the natural breathability of wool, ongoing advancements in fiber technology continue to improve its performance and eco-profile. By partnering with reliable suppliers, verifying quality certifications, and considering environmentally responsible alternatives, businesses can effectively balance cost, quality, and sustainability in their acrylic sweater material sourcing strategy.