The global market for Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Hydraulic Control Units (HCUs) is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing vehicle production, stringent safety regulations, and rising demand for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the ABS market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader automotive brake system market—of which ABS HCUs are a critical component—is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2030, fueled by enhanced focus on vehicle safety and the proliferation of electric vehicles. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and technological integration in HCU production. Here are the top 9 ABS Hydraulic Control Unit manufacturers shaping the future of automotive safety.
Top 9 Abs Hydraulic Control Unit Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Anti
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zf.com
Key Highlights: ZF offers a unique range of hydraulic ABS technology that integrates electronic stability control (ESC) for light- and medium-duty commercial vehicles. Helps to ……
#2 Antilock Braking Systems (ABS)/ESP and Stability
Domain Est. 1995
Website: bendix.com
Key Highlights: It’s the first widely available ABS-based truck stability system potentially capable of recognizing and assisting in under-steer and over-steer loss-of-control ……
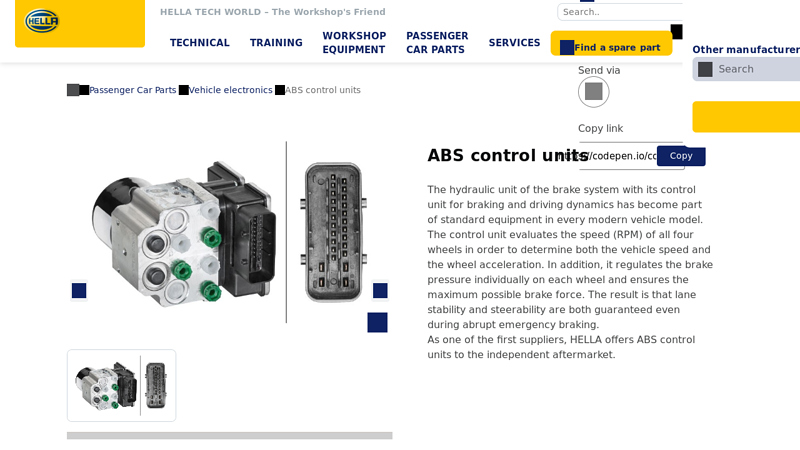
#3 ABS control units
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hella.com
Key Highlights: The control unit evaluates the speed (RPM) of all four wheels in order to determine both the vehicle speed and the wheel acceleration. In addition, it regulates ……
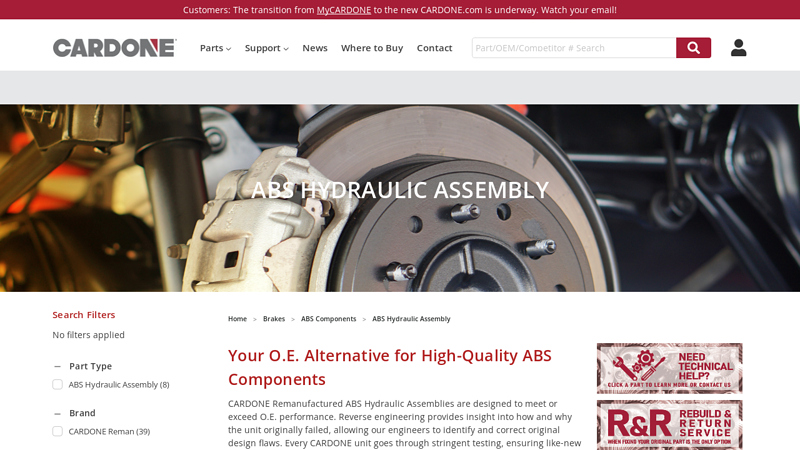
#4 ABS Hydraulic Assembly
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cardone.com
Key Highlights: CARDONE Remanufactured ABS Hydraulic Assemblies are engineered to improve O.E. design and stringently tested to ensure like-new performance….
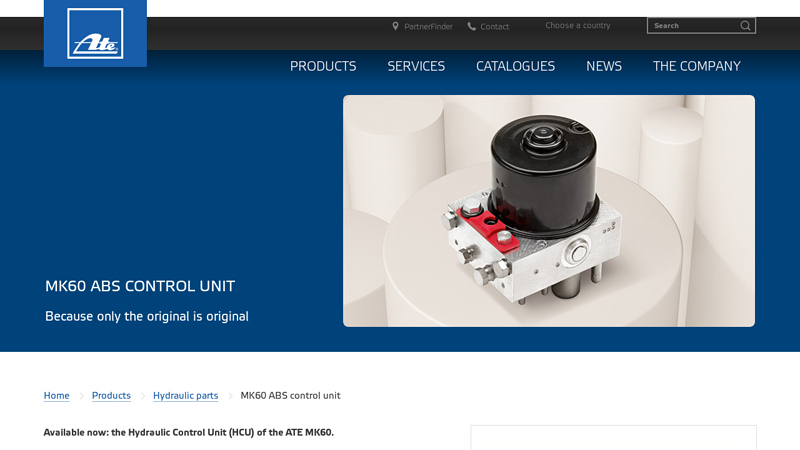
#5 MK60 ABS control unit
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ate-brakes.com
Key Highlights: Now available as an original part: the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) for the ATE MK60, including accessories. Precise braking when you need it. Reliable braking ……
#6 ABS Pump, module and hydraulic units combined
Domain Est. 2006
Website: ecutesting.com
Key Highlights: Common faults for ABS pump, ABS hydraulic unit and ABS pump motor combined, how to test and repair along with descriptions for each parts function….
#7 Antilock braking system
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bosch-mobility.com
Key Highlights: The antilock braking system (ABS) from Bosch prevents the wheels from locking and enables safe braking up to 40 times a second….
#8 Mopar ABS Hydraulic Control Unit HCU, 68143491AB
Domain Est. 2013
Website: moparonlineperformance.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsRam Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU). Same as production for 2012-2018 Ram 2500/3500 trucks. OE (Original Equipment) Mopar parts….
#9 ABS System Package
Domain Est. 2019
Website: wabco-customercentre.com
Key Highlights: ABS System Package with a material number 4005000880 is available. Interested in another ABS Electronic Control Unit (ECU)? See more on new Inform….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Abs Hydraulic Control Unit

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for ABS Hydraulic Control Units
The market for Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Hydraulic Control Units (HCUs) is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and shifting automotive landscapes. Here’s an analysis of the key H2-level trends shaping this market:
1. H2: Accelerated Integration with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and Autonomous Driving
* Trend: The HCU is transitioning from a standalone safety component to a critical actuator within the broader ADAS and vehicle dynamics control ecosystem. By 2026, integration with Electronic Stability Control (ESC), Traction Control (TCS), Automated Emergency Braking (AEB), and higher levels of autonomous driving (L2+/L3) will be paramount.
* Impact: This demands HCUs with faster response times, higher precision control (requiring more solenoid valves and sophisticated algorithms), enhanced communication capabilities (high-speed CAN FD, Ethernet), and robust functional safety (ISO 26262 ASIL D compliance). Suppliers will focus on developing integrated “Brake Control Modules” rather than just HCUs.
2. H2: Electrification Driving Demand for Brake-by-Wire (BbW) Solutions
* Trend: The rapid growth of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs) is a primary catalyst. Traditional vacuum-assisted braking is incompatible with EVs (no engine vacuum). This necessitates the adoption of Brake-by-Wire systems, where the HCU is the core actuator.
* Impact: The market for BbW HCUs (specifically Electro-Hydraulic Brake – EHB or Electro-Mechanical Brake – EMB variants, though EMB faces challenges) will see explosive growth by 2026. This requires HCUs with integrated electric pumps, pressure sensors, and fail-operational redundancy designs. Suppliers are investing heavily in scalable BbW HCU platforms.
3. H2: Consolidation and Platform Standardization Among Suppliers
* Trend: Facing intense cost pressure, the need for economies of scale, and complex integration requirements, Tier 1 suppliers are consolidating and developing highly modular, scalable HCU platforms.
* Impact: Expect fewer, but larger, players dominating the market (e.g., Bosch, Continental, ZF, Nissin Kogyo, Akebono). These standardized platforms will offer different performance levels (valve count, pump power) on the same core architecture, reducing development costs for OEMs and improving time-to-market. Regional suppliers (especially in China) will also gain significant share.
4. H2: Focus on Lightweighting, Miniaturization, and Cost Optimization
* Trend: Despite technological complexity, relentless cost pressure from OEMs and competition, especially in high-volume segments, will drive innovation in materials, design, and manufacturing.
* Impact: Increased use of lightweight alloys (aluminum, magnesium), optimized hydraulic circuit designs, integration of components (e.g., combining valve block and reservoir), and advanced manufacturing techniques (e.g., 3D printing for prototypes, high-pressure die casting) will be key. The focus will be on reducing size, weight, and Bill of Materials (BoM) cost without compromising safety or performance.
5. H2: Regional Market Divergence and Emerging Market Growth
* Trend: Regulatory mandates (e.g., UN R13-H, NCAP requirements) are becoming global, but adoption pace varies. Mature markets (North America, Europe, Japan, South Korea) will see near-universal ABS/ESC adoption and rapid BbW adoption in EVs. Emerging markets (India, Southeast Asia, Latin America) will experience significant volume growth driven by new safety regulations but will initially focus on cost-effective, basic ABS/ESC HCUs.
* Impact: Suppliers will need dual strategies: high-tech, high-performance HCUs for premium/EV segments in mature markets, and robust, low-cost platforms for volume segments globally. China, as the world’s largest EV market, will be a critical battleground for both volume and technology leadership.
6. H2: Enhanced Focus on Cybersecurity and Software-Defined Functionality
* Trend: As HCUs become more connected and software-dependent (part of the vehicle’s software-defined architecture), their vulnerability to cyberattacks increases. Simultaneously, software enables features like predictive maintenance, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and customizable braking feel.
* Impact: By 2026, HCUs will incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures (secure boot, intrusion detection). The software stack within the HCU’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU) will become a key differentiator, enabling new safety and performance features that can be updated post-production, moving towards a software-defined braking experience.
In conclusion, the 2026 ABS HCU market will be defined by its role as an intelligent actuator within electrified, connected, and increasingly automated vehicles. Success will depend on suppliers’ ability to deliver integrated, safe, cost-effective, and software-rich solutions that meet the diverse demands of a rapidly transforming automotive industry.
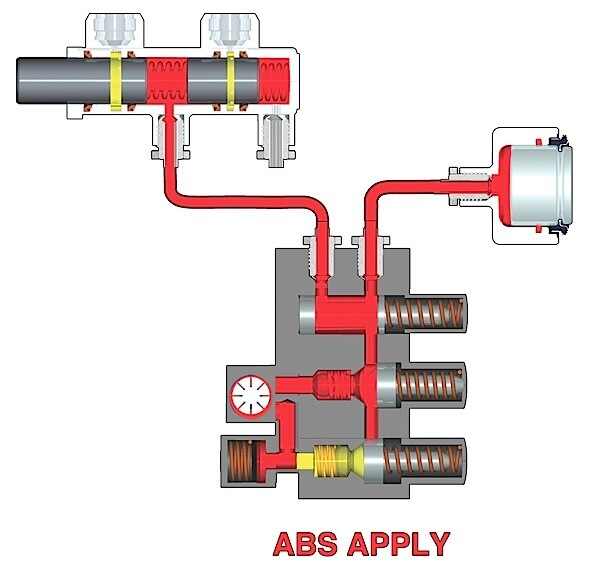
Common Pitfalls Sourcing ABS Hydraulic Control Unit (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ABS Hydraulic Control Units (HCU) involves significant technical and commercial risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to production delays, safety recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls:
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Validation
- Insufficient Supplier Qualification: Selecting suppliers based solely on cost without rigorous audits of their manufacturing processes, quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949 certification), and track record in automotive safety components.
- Lack of Robust Testing Protocols: Failing to mandate comprehensive performance, environmental, and durability testing (e.g., pressure cycling, thermal shock, corrosion resistance) that meets OEM specifications and international standards (e.g., ISO 11451, ISO 11452).
- Inconsistent Production Quality: Absence of strict incoming inspection, in-process controls, and statistical process control (SPC) at the supplier’s facility, leading to batch-to-batch variations and potential field failures.
- Poor Traceability and Documentation: Suppliers not maintaining full traceability of components and materials (e.g., casting batches, solenoid valves), making root cause analysis and recalls extremely difficult.
Intellectual Property (IP) Vulnerabilities
- Weak or Ambiguous IP Clauses: Contracts lacking clear definitions of ownership for design specifications, software algorithms, calibration data, and tooling developed during the sourcing process.
- Inadequate Protection of Sensitive Information: Failure to implement robust NDAs and data security measures, risking exposure of proprietary control logic, valve timing maps, and diagnostic routines.
- Unauthorized Reverse Engineering: Suppliers using the sourced HCU to develop competing products or supply clones to third parties, especially in regions with lax IP enforcement.
- Tooling and Fixture Ownership Disputes: Unclear agreements on ownership of molds, jigs, and test equipment paid for by the buyer, potentially leading to production lock-in or costly retooling.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, strong contractual safeguards, continuous supplier monitoring, and active IP management throughout the sourcing lifecycle.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for ABS Hydraulic Control Unit
Product Classification and Identification
The ABS Hydraulic Control Unit (Anti-lock Braking System Hydraulic Control Unit) is classified as an automotive safety component under HS Code 8708.39.00 (parts and accessories for braking systems of motor vehicles). Proper identification is essential for customs clearance, import/export compliance, and regulatory tracking. Each unit must bear a unique serial number, manufacturer part number, and relevant certification marks (e.g., E-Mark, DOT, ISO/TS 16949).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
ABS Hydraulic Control Units must be packaged in ESD-safe (electrostatic discharge) materials to prevent damage to electronic components. Units should be sealed in moisture-resistant, shock-absorbent packaging with internal cushioning to prevent movement during transit. Each package must be labeled with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Avoid stacking more than two layers in storage or transport unless using reinforced pallets.
Transportation and Shipping Regulations
Shipments must comply with international ground and air transport standards (e.g., IATA, ADR, IMDG as applicable). While the unit does not contain hazardous materials under normal conditions, residual brake fluid (if pre-filled) could trigger hazardous classification; confirm fluid status with the manufacturer. Use temperature-controlled transport when ambient temperatures are expected to exceed -40°C to +85°C. Maintain a clean, dry transport environment to prevent contamination.
Import/Export Compliance
Exporters must ensure compliance with destination country regulations. Key requirements include:
– U.S. (DOT/ FMVSS 105, 121): Certification of compliance with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
– European Union (ECE R13-H): E-Mark certification and inclusion in the vehicle type-approval documentation.
– China (CCC Mark): Compulsory Certification for automotive parts.
– Other Regions: Verify local type-approval and homologation requirements.
Complete export documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin, must be accurate and consistent.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
The ABS Hydraulic Control Unit must comply with the following standards:
– ISO 26262: Functional safety for road vehicles (ASIL-D compliance often required).
– ISO 16750: Environmental and electrical testing (vibration, humidity, thermal cycling).
– AEC-Q100: Stress test qualification for automotive ICs (if applicable).
– REACH & RoHS: Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical components.
Maintain up-to-date technical files and test reports for audit purposes.
Inventory and Traceability Management
Implement a traceability system (e.g., barcode or RFID) to track each unit from manufacturing through distribution. Retain records for a minimum of 15 years to support product recalls, warranty claims, and compliance audits. Conduct regular cycle counts and reconcile physical inventory with digital records to ensure accuracy.
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Return shipments must follow a controlled process. Returned units should be quarantined, inspected for damage or tampering, and documented with a return material authorization (RMA) number. Reconditioned or repaired units must undergo full functional testing and recalibration before re-entry into inventory or resale. Dispose of non-repairable units in compliance with WEEE and local e-waste regulations.
Certifications and Documentation Retention
Maintain copies of the following documents for each production batch:
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– Test reports (EMC, environmental, functional)
– ISO/TS 16949 or IATF 16949 certification
– Material declarations (REACH, RoHS)
– E-Mark or DOT certification documentation
Store digital and physical records securely with access restricted to authorized personnel.
Emergency and Incident Response
In the event of shipping damage, contamination, or non-compliance discovery, initiate a corrective action report (CAR) immediately. Notify relevant regulatory bodies if safety-critical defects are identified. Implement containment measures (e.g., hold shipments, recall notices) in accordance with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 procedures. Conduct root cause analysis and update logistics controls as needed.
Conclusion for Sourcing ABS Hydraulic Control Unit:
After a comprehensive evaluation of potential suppliers, technical specifications, cost considerations, and quality requirements, sourcing the ABS Hydraulic Control Unit should be approached with a strategic balance between reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency. It is recommended to partner with suppliers that demonstrate proven experience in automotive braking systems, adherence to international quality standards (such as ISO/TS 16949 and compliance with ISO 11452 and ISO 11451 for electromagnetic compatibility), and strong after-sales support.
Prioritizing suppliers with established testing protocols, robust supply chain resilience, and the ability to scale production will ensure long-term stability and minimize disruption risks. Additionally, considering both OEM and reputable aftermarket options can provide flexibility without compromising on safety and performance, as the ABS Hydraulic Control Unit is a critical component for vehicle safety.
Ultimately, the selected sourcing strategy should support regulatory compliance, integration compatibility with existing braking systems, and deliver optimal value across the product lifecycle. Continuous supplier performance monitoring and ongoing quality audits are essential to maintain the highest standards in vehicle safety and reliability.