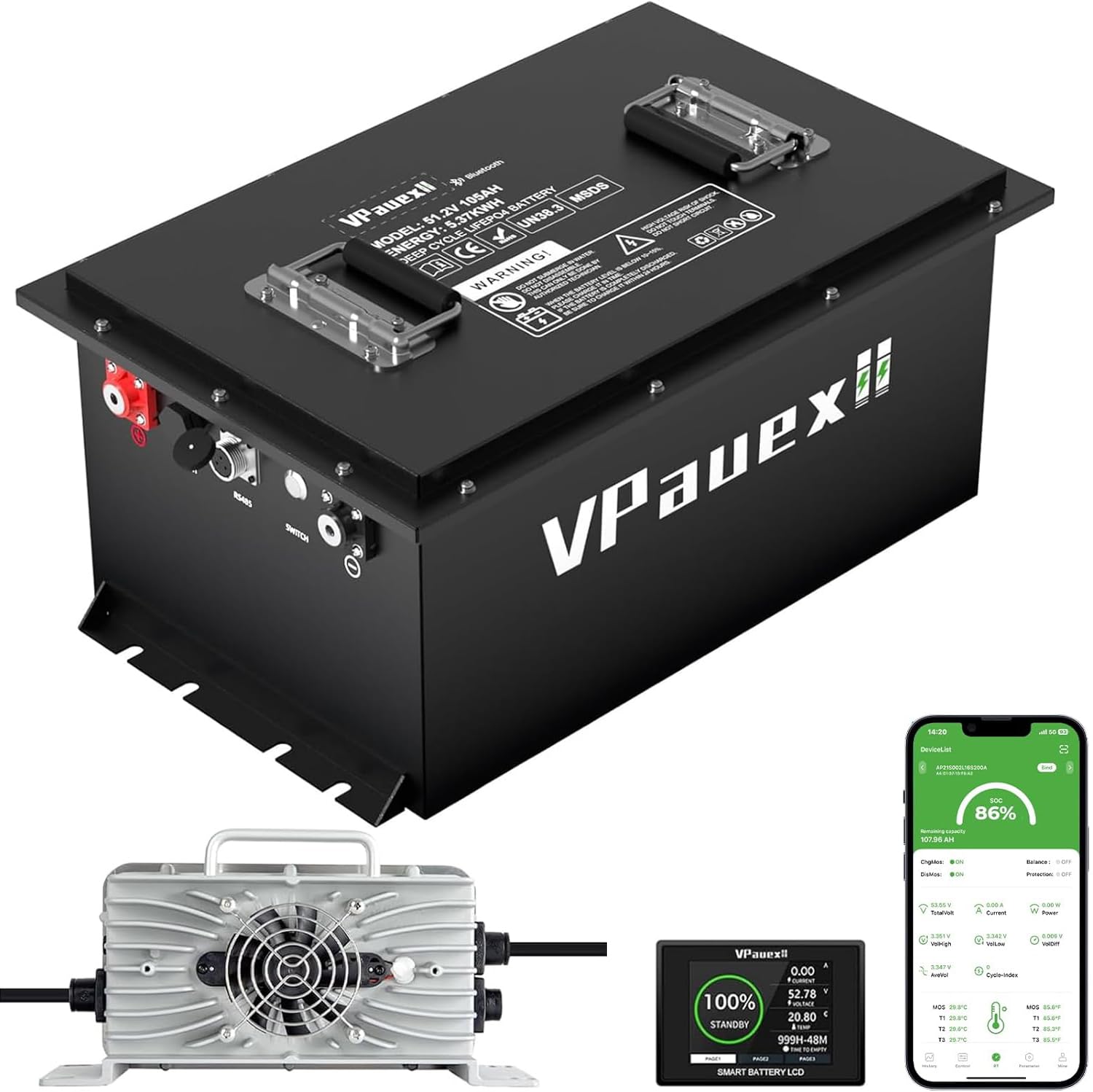
The global golf cart battery market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the rising demand for efficient, durable, and eco-friendly power solutions. With the shift from traditional lead-acid to advanced lithium-ion technology, 48V lithium batteries have emerged as the preferred choice for modern golf carts, offering longer life cycles, faster charging, and superior energy density. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global golf cart market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2023 to 2028, with electrification trends and increasing adoption in residential, commercial, and utility applications fueling demand for high-performance batteries. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader lithium-ion battery market will expand at a CAGR of 14.3% from 2023 to 2030, underpinned by advancements in battery technology and growing investments in sustainable mobility. As OEMs and fleet operators increasingly prioritize reliability and total cost of ownership, leading manufacturers are scaling production and innovation in the 48V lithium space. This list highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping the future of golf cart energy systems, evaluated on technology, market presence, product performance, and customer feedback.
Top 10 48V Lithium Golf Cart Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Olelon Energy
Domain Est. 2023
Website: olelonenergy.com
Key Highlights: Olelon Energy: LiFePO4 battery manufacturer specializing in 36V, 48V, 72V solutions for golf carts and low-speed vehicles, features proprietary BMS and ……
#2 US 48V105 Lithium-Ion Battery
Domain Est. 1997
Website: usbattery.com
Key Highlights: Upgrade your golf cart with our Essential Li US48V105 48V Li-ion battery. Superior performance and reliability for carts, EVs & more….
#3 Golf Cart & Utility Vehicle Batteries
Domain Est. 1999
Website: trojanbattery.com
Key Highlights: OnePack 48V 105Ah Lithium Battery Pack … Simons Island, Georgia, upgraded their official 2018 Ryder Cup golf cart with three 48V GC2 Trojan Lithium batteries….
#4 Eco Battery: Lithium Golf Cart Batteries
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ecobattery.com
Key Highlights: Eco Battery offers high-quality lithium batteries for golf carts & LSVs. We offer replacement options for your traditional lead acid batteries at an ……
#5 ROYPOW: Battery Energy Storage System
Domain Est. 2010
Website: roypow.com
Key Highlights: Motive Power Systems · Golf Lithium Golf Cart Batteries. 36V Golf Cart Battery · 48V Golf Bart Battery · 72V Golf Cart Battery….
#6 Lithium Golf Cart Batteries
Domain Est. 2014
#7 Lithium
Domain Est. 2016
Website: evolutionelectricvehicle.com
Key Highlights: Lithium golf cart batteries are much lighter. This makes your golf cart easier to maneuver and helps you reach a comfortable speed faster. As an added bonus, ……
#8 Lithium Golf Cart Batteries (36V/48V) – Long‑Life LiFePO4
Domain Est. 2020
Website: epochbatteries.com
Key Highlights: Upgrade to 36V/48V LiFePO4 golf cart batteries—fast charge, 5000+ cycles, lighter weight, advanced BMS. See kits, specs & dealer options….
#9 Vatrer Lithium Batteries
Domain Est. 2021
Website: vatrerpower.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsVatrer Power delivers high-quality lithium batteries for golf carts, RVs, solar systems and marine trolling motors, ensuring safe, sustainable energy….
#10 Bolt Energy USA
Domain Est. 2021
Website: boltenergyusa.com
Key Highlights: At Bolt Energy USA, we specialize in high-performance lithium golf cart batteries designed to enhance efficiency and reliability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 48V Lithium Golf Cart Battery

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 48V Lithium Golf Cart Battery
The market for 48V lithium golf cart batteries is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in battery technology, rising demand for sustainable transportation, and the broader electrification of recreational and utility vehicles. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the 48V lithium golf cart battery sector in 2026 across technology, demand drivers, regional growth, and competitive dynamics.
1. Shift from Lead-Acid to Lithium-Ion Dominance
By 2026, lithium-ion batteries—particularly 48V systems—are expected to dominate the golf cart battery market, overtaking traditional lead-acid batteries. This transition is fueled by lithium’s superior energy density, longer cycle life (2,000–5,000 cycles vs. 300–500 for lead-acid), faster charging, and lower maintenance requirements. The total cost of ownership (TCO) advantage of lithium batteries continues to widen, making them increasingly attractive to both private owners and fleet operators.
2. Growth in Non-Golf Applications
While initially developed for golf carts, 48V lithium batteries are increasingly being adopted in adjacent markets such as:
– Community electric vehicles (CEVs)
– Resort and campus shuttles
– Last-mile delivery carts
– Warehouse and industrial utility vehicles
This diversification is expanding the addressable market beyond golf courses, contributing to projected compound annual growth rates (CAGR) of 12–15% for 48V lithium battery systems through 2026.
3. Advancements in Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Chemistry
LiFePO4 remains the preferred chemistry for 48V golf cart batteries due to its thermal stability, safety, and long cycle life. By 2026, improvements in manufacturing efficiency and raw material sourcing are expected to further reduce LiFePO4 battery costs—projected to fall below $100/kWh at the pack level—making them more accessible to mid-tier consumers and emerging markets.
4. Integration with Smart Technologies
48V lithium batteries in 2026 are increasingly integrated with Battery Management Systems (BMS) and IoT-enabled monitoring platforms. These smart systems provide real-time data on state of charge, health, temperature, and usage patterns. Fleet managers use this data for predictive maintenance and energy optimization, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
5. Regional Market Expansion
- North America: The U.S. remains the largest market, driven by high golf participation rates, aging lead-acid fleets, and strong aftermarket demand.
- Europe: Growth is fueled by sustainability mandates and the rise of eco-resorts and green communities.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization, expanding middle class, and government support for electrification in countries like China and India are creating new opportunities.
- Latin America & Middle East: Emerging tourism infrastructure and golf course development are driving incremental demand.
6. Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices. By 2026, closed-loop recycling programs for lithium batteries are expected to become more prevalent, reducing environmental impact and supporting ESG goals. Second-life applications—reusing retired golf cart batteries for energy storage—are also gaining traction.
7. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing consolidation as major battery manufacturers (e.g., CATL, LG Energy Solution, and RELiON) expand into the 48V golf and light EV segment. Simultaneously, specialized players are differentiating through modular designs, drop-in replacement solutions, and enhanced warranties (often 5–10 years). Price competition is intensifying, but premium brands maintain margins through reliability and service offerings.
8. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical concerns and supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional battery production. By 2026, North American and European manufacturers are increasingly sourcing cells and components locally to reduce dependency on Asia and comply with trade regulations.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 48V lithium golf cart battery market will be characterized by technological maturity, cost competitiveness, and expanded applications. The convergence of performance, sustainability, and smart integration will solidify lithium’s position as the battery of choice, with LiFePO4 leading the segment. Stakeholders who invest in innovation, sustainability, and customer-centric solutions will be best positioned to capture value in this rapidly evolving market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 48V Lithium Golf Cart Batteries (Quality & IP Protection)
Sourcing a 48V lithium golf cart battery can significantly improve performance and longevity compared to traditional lead-acid options. However, the market is rife with potential pitfalls, especially concerning battery quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings. Avoiding these common mistakes ensures safety, reliability, and optimal value.
Poor Cell Quality and Sourcing
One of the most critical yet hidden pitfalls is the use of low-grade or inconsistent lithium cells. Reputable manufacturers use high-quality lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) cells from established suppliers like CATL, EVE, or CALB. In contrast, lower-cost alternatives often source cells from unknown or inconsistent manufacturers, leading to:
- Reduced Cycle Life: Inferior cells degrade faster, cutting usable lifespan by 50% or more.
- Inconsistent Performance: Mismatched cells within a pack cause imbalances, reducing capacity and efficiency.
- Safety Risks: Poor thermal stability increases risks of overheating, swelling, or thermal runaway.
Always verify the cell brand and request certification data (e.g., UN38.3, MSDS) before purchase.
Lack of Proper Battery Management System (BMS)
A high-quality BMS is essential for safety and longevity. Many low-cost batteries use under-specified or poorly programmed BMS units that fail to provide:
- Cell Balancing: Prevents individual cells from overcharging or deep discharging.
- Overcurrent/Overvoltage Protection: Critical for preventing damage during charging or high-load operation.
- Temperature Monitoring: Shuts down the system if cells overheat.
Without a robust BMS, even premium cells can be compromised, leading to premature failure or hazardous conditions.
Misleading or Absent IP Ratings
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings indicate resistance to dust and water, crucial for golf carts exposed to rain, mud, and humidity. Common pitfalls include:
- Falsified or Inflated IP Ratings: Some suppliers claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP67) without independent certification.
- Incomplete Sealing: Poor gasket design, unsealed terminals, or cable entry points create vulnerabilities.
- Lack of Environmental Testing: No evidence of salt mist, vibration, or thermal cycling tests.
An IP65 rating (dust-tight and protected against low-pressure water jets) is recommended; IP67 (immersion up to 1m) is ideal for harsh conditions. Always request test reports or third-party verification.
Inadequate Mechanical Design and Build Quality
Beyond electronics, physical construction matters. Watch for:
- Flimsy Casings: Thin aluminum or plastic housings that crack under vibration.
- Poor Wiring and Connectors: Undersized cables or loose terminals increase resistance and fire risk.
- Lack of Vibration Resistance: Golf carts experience constant shaking; poorly secured cells or components can fail prematurely.
Opaque Warranty and Support
Many budget batteries offer “lifetime” warranties with vague terms or no local support. Key red flags include:
- No Clear Cycle Warranty: e.g., “3000 cycles at 80% capacity.”
- Restocking Fees or Return Hurdles: Makes valid claims difficult to process.
- No Technical Support: Lack of access to troubleshooting or firmware updates.
Choose suppliers with transparent, written warranties and accessible customer service.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, prioritize suppliers that provide detailed specifications, certified cell information, verifiable IP ratings, and robust BMS features. Investing in a quality 48V lithium golf cart battery—backed by solid engineering and support—ensures long-term reliability, safety, and performance on the course.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 48V Lithium Golf Cart Battery (Using UN Hazard Class 2 Classification Framework)
Note: While lithium batteries are primarily regulated under Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods), this guide interprets “Use H2” as a directive to apply hazard assessment principles analogous to Class 2 (Gases) for enhanced safety awareness—especially regarding thermal runaway risks resembling pressurized gas hazards. This approach supports rigorous handling, storage, and transport protocols.
1. Product Overview
- Battery Type: 48V Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Golf Cart Battery
- Chemistry: Typically Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄) or NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt)
- Nominal Voltage: 48 volts
- Capacity Range: 100–200 Ah (typical)
- Weight: 50–90 lbs (23–41 kg)
- UN Number: UN 3480 (Lithium-ion batteries, packed separately)
- Proper Shipping Name: “Lithium ion batteries, not contained in or packed with equipment”
- Primary Hazard Class: Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods
- Secondary Hazard Analogy (H2 Framework): Thermal runaway risk compared to Class 2 – Gases due to potential for pressurized gas release, fire, and explosion under fault conditions.
2. Regulatory Framework (Globally Aligned)
A. Transportation Regulations
- IMDG Code (Maritime): Applies when shipping by sea
- IATA DGR (Air): Strict rules for air transport; often prohibited or limited unless under Special Provision A154/A48
- 49 CFR (U.S. DOT): Governs domestic ground transport
- ADR (Europe): Road transport in Europe
B. Hazard Classification (H2 Analogy)
Although lithium batteries are Class 9, applying Class 2 (Gases) thinking enhances safety:
– Thermal runaway can produce flammable and toxic gases (e.g., CO, H₂, HF).
– Internal pressure buildup may lead to rupture/explosion—similar to pressurized gas containers.
– Venting events mimic gas release; require ventilation and explosion-proof zones.
🛠️ Best Practice: Treat lithium batteries as dual-hazard items—Class 9 primary, Class 2 secondary risk.
3. Packaging Requirements
A. Primary Packaging
- Use rigid, non-conductive outer casing.
- Terminals must be insulated (e.g., caps or tape) to prevent short circuits.
- Individual cells/modules protected against physical damage.
B. Secondary Packaging (Shipping)
- Strong outer container (e.g., double-wall corrugated or wooden crate).
- Cushioning material to prevent movement.
- Flame-resistant lining recommended.
- Ventilation: Include vents if large batteries (analogous to gas cylinder venting).
C. Marking & Labeling (Per Class 9 + H2 Analogy)
- Class 9 Hazard Label (Black 7-striped diamond)
- UN 3480 clearly marked
- Lithium Battery Handling Mark (IATA/IMDG compliant)
- “CAUTION: Risk of Gas Emission if Damaged” (H2-inspired advisory)
- Orientation arrows (if required by volume/weight)
4. Storage Guidelines (H2-Inspired Safety)
A. Facility Requirements
- Ventilation: Well-ventilated, preferably with exhaust systems (like gas storage).
- Fire Suppression: Class D fire extinguishers (lithium fires); water mist systems acceptable for LiFePO₄.
- Separation: Store away from flammables, oxidizers, and high-traffic areas.
- Temperature Control: 0°C to 25°C (32°F to 77°F); avoid direct sunlight (like propane tanks).
B. Storage Position
- Upright, on non-conductive racks.
- Spaced to allow airflow (min. 1 inch between units).
- No stacking unless designed for it (risk of pressure/short circuit).
C. Charge State
- Ship and store at 30–50% state of charge to reduce thermal risk (like minimizing gas cylinder pressure).
5. Transportation Protocols
A. Ground Transport (49 CFR / ADR)
- Vehicles must be non-leaking, non-sparking.
- Batteries secured to prevent movement.
- Driver trained in hazardous materials (HazMat certification).
- Emergency response guide (ERG 2024) on board (reference Guide 147 for Class 9).
B. Air Transport (IATA DGR)
- Prohibited unless:
- Battery < 20 Wh (rare for 48V systems)
- Or compliant with Special Provision A154 (tested per UN 38.3, SOC ≤ 30%)
- Typically not allowed for full 48V golf cart batteries on passenger aircraft.
- Cargo aircraft only, with approval.
C. Marine Transport (IMDG Code)
- Properly declared in transport documents.
- Stowed away from heat sources and living quarters.
- Ventilated hold or deck storage preferred.
6. Handling & Worker Safety (H2-Inspired Precautions)
A. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Insulated gloves (Class 0, 1000V rated)
- Safety goggles
- Flame-resistant (FR) clothing (especially during charging/repair)
- Face shield when servicing
B. Handling Procedures
- No dropping or impact (risk of internal short = thermal event)
- Use mechanical aids (dollies, forklifts with non-sparking tines)
- No metal tools near terminals (short circuit = arc flash, like igniting gas)
- Pre-shipment inspection for damage, leaks, or swelling
7. Incident Response (Thermal Runaway = Gas Explosion Analogy)
| Hazard | Response (H2-Inspired) |
|——-|————————|
| Smoking/Bulging Battery | Evacuate area, isolate 15 ft (5 m), monitor remotely |
| Venting (Hissing Sound) | Treat as gas leak: ventilate, do not inhale fumes |
| Fire | Use copious water to cool; Class D extinguisher if available. Do NOT use CO₂ (ineffective for deep cell fire) |
| Exposure to Gases | Evacuate upwind; medical attention if inhaled (HF risk) |
🆘 Emergency Info: Include 24/7 contact for manufacturer and SDS (Safety Data Sheet) with every shipment.
8. Documentation & Compliance
Required Documents:
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – Section 14: Transport Information
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (air/marine)
- Battery Test Summary (UN 38.3 test results)
- Origin & Destination Compliance Certificates (e.g., FCC, CE, if applicable)
9. End-of-Life & Recycling
- Do NOT dispose in landfill (fire hazard, environmental risk).
- Use certified lithium battery recyclers (e.g., Call2Recycle, Li-Cycle).
- Transport used batteries as hazardous waste (UN 3480).
- Label as “Used Lithium Batteries – Potential for Thermal Event.”
10. Checklist for Compliance (Quick Reference)
✅ UN 3480 Class 9 labeling
✅ Terminals insulated
✅ Packaged in rigid, non-conductive container
✅ State of charge ≤ 50% (ideally 30%)
✅ Ventilated storage (H2-inspired)
✅ SDS and shipping docs available
✅ Fire suppression and PPE on site
✅ Trained personnel for handling and emergencies
Conclusion
While 48V lithium golf cart batteries are officially Class 9, applying H2 (gas hazard) thinking strengthens safety culture by emphasizing venting, pressure, flammability, and explosion risks. This proactive approach aligns with best practices in high-risk battery logistics and ensures robust compliance across air, sea, and ground transport.
ℹ️ Always consult latest IATA, IMDG, ADR, and 49 CFR editions for updates. Regulations evolve rapidly.
Prepared by: Logistics & Compliance Team
Date: April 2025
For internal use – Not a substitute for official regulatory guidance.
Conclusion: Sourcing a 48V Lithium Golf Cart Battery
Sourcing a 48V lithium golf cart battery represents a smart, long-term investment that offers superior performance, longevity, and efficiency compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. With benefits including faster charging, deeper depth of discharge, lower maintenance requirements, and a significantly longer lifespan, lithium batteries enhance the overall reliability and usability of golf carts—whether for recreational, residential, or commercial applications.
When sourcing these batteries, it’s essential to consider key factors such as battery chemistry (e.g., LiFePO₄ for safety and cycle life), brand reputation, warranty coverage, BMS (Battery Management System) quality, and compatibility with your existing cart model. Purchasing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers ensures product authenticity, safety compliance, and access to technical support.
While the upfront cost of lithium batteries is higher, the total cost of ownership is often lower due to reduced replacement frequency and energy savings. Additionally, many suppliers now offer financing, leasing options, or bulk discounts, making lithium conversion more accessible.
In conclusion, upgrading to a 48V lithium battery improves performance and sustainability, and careful sourcing ensures a reliable, safe, and cost-effective solution for all golf cart power needs.