The global lithium battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by rising demand for energy storage solutions in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles (EVs), and off-grid applications. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global lithium-ion battery market size was valued at USD 73.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is further amplified by advancements in battery technology and decreasing production costs, making high-capacity solutions like 400Ah lithium batteries increasingly accessible. As industries and consumers alike seek reliable, long-lasting, and efficient energy storage, the demand for premium 400Ah lithium batteries has escalated. This growing need has propelled several manufacturers to the forefront of innovation, scalability, and quality. Based on current market trends and technological capabilities, the following nine companies have emerged as leading manufacturers of 400Ah lithium batteries, combining performance, durability, and global reach to meet evolving energy demands.
Top 9 400Ah Lithium Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 24V 400Ah Lithium Battery Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: dnkpower.com
Key Highlights: DNK Power is a custom Rechargeable 24V Lithium battery manufacturer based in China,We have In stock small and compact 24V Lithium battery pack….
#2 JM China Manufacturer 51.2V 400ah Lithium Ion Battery Pack Energy
Domain Est. 2022
Website: jmbatteries.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryJM China Manufacturer 51.2V/48V 400Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Ion Battery Pack – ideal for solar energy storage. Features 8000+ deep cycles, 10-year warranty, ……
#3 Quality Deep Cycle Batteries
Domain Est. 1997
Website: usbattery.com
Key Highlights: Reliable, deep cycle batteries from U.S. Battery Mfg Co. High-quality 6V, 8V, 12V, 24V, and 48V batteries deliver power you can depend on!…
#4 CALB CA400 3.2V 400Ah Lifepo4 battery cell
Domain Est. 2010
Website: evlithium.com
Key Highlights: CALB CA400 LiFePO4 Battery is one of best 400Ah lithium ion battery with high power energy.The weight is only 14kg.with brand new design….
#5 12V 400Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Domain Est. 2011
Website: manlybattery.com
Key Highlights: MANLY Battery offers 12V 400Ah LiFePO4 lithium battery with top-tier safety, long-lasting power, and customizable bulk ordering options for businesses….
#6 25.6V 400AH Lithium Ion Battery
Domain Est. 2014
Website: lithiumbatterycompany.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsExplore our 24V 400AH Lithium Ion Battery, the ultimate choice for reliable, long-lasting power. Ideal for anyone seeking a top-performing 400ah lithium…
#7 Battle Born Batteries
Domain Est. 2016
Website: battlebornbatteries.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery · 30-day returnsShop premium LiFePO4 lithium batteries from Battle Born for unmatched power, reliability, and a 10-year warranty. Get started today!…
#8 TBB M12 400Ah Lithium Battery with Heat
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fsi-sales.com
Key Highlights: In stock $86.29 deliveryThe TBB M12 400Ah Lithium Battery is compact, has a long cycle life, comes with heat, internal BMS, metal case, and can scale up to 8 modules….
#9 Ezeal: Shop Lead Acid Lithium Battery
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ezealco.com
Key Highlights: $59.96 delivery 14-day returnsLooking for a store you can buy lithium-ion batteries online from? Get in touch with the team at Ezeal now for custom-built batteries….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 400Ah Lithium Battery

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 400Ah Lithium Batteries
The global market for 400Ah lithium batteries is poised for substantial growth and transformation by 2026, driven by accelerating demand in energy storage, electric mobility, and renewable integration. As a high-capacity solution, the 400Ah lithium battery—typically based on lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) chemistry—has emerged as a preferred choice for industrial, commercial, and residential applications due to its balance of safety, longevity, and performance. Here are the key market trends expected to shape the 400Ah lithium battery sector in 2026:
1. Surge in Energy Storage Systems (ESS) Adoption
The deployment of residential, commercial, and utility-scale energy storage systems is a primary driver. With solar photovoltaic (PV) installations rising globally, especially in regions like North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, there is growing demand for high-capacity batteries to store excess energy. The 400Ah format offers optimal energy density and scalability for home and small commercial ESS, enabling longer backup times and greater energy independence. By 2026, the integration of AI-driven energy management systems will further increase the value proposition of these batteries.
2. Advancements in LiFePO₄ Technology
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) remains the dominant chemistry for 400Ah batteries due to its thermal stability, long cycle life (often exceeding 6,000 cycles), and lower risk of thermal runaway. Ongoing R&D efforts are enhancing energy density and reducing manufacturing costs. Innovations such as cell-to-pack (CTP) designs and improved battery management systems (BMS) will allow 400Ah units to deliver higher efficiency and better performance in extreme temperatures, broadening their usability.
3. Declining Battery Costs and Economies of Scale
Lithium battery prices have continued to decline due to improvements in production efficiency, raw material sourcing, and increased manufacturing scale—particularly in China, where most 400Ah LiFePO₄ cells are produced. By 2026, average prices for 400Ah units are projected to fall below $0.10 per Wh, making them increasingly accessible for off-grid and backup power applications. This cost reduction is expected to stimulate demand in emerging markets.
4. Expansion in Electric Mobility and Micro-Mobility
Beyond stationary storage, 400Ah lithium batteries are finding use in electric buses, marine applications, and heavy-duty off-road vehicles. Their high capacity and reliability make them suitable for fleets requiring extended operational cycles. Additionally, industrial equipment such as electric forklifts and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are increasingly adopting 400Ah modules for longer uptime and reduced charging frequency.
5. Regulatory Support and Incentives
Government policies promoting clean energy and carbon neutrality—such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), EU Green Deal, and China’s dual carbon goals—are accelerating adoption. Tax credits, rebates, and subsidies for energy storage systems directly benefit consumers and businesses investing in 400Ah battery solutions. By 2026, stricter emissions standards and grid modernization initiatives will further incentivize deployment.
6. Growth in Off-Grid and Remote Applications
In rural and underserved regions, 400Ah lithium batteries are playing a critical role in off-grid power systems, telecom towers, and emergency backup infrastructure. Their durability and low maintenance requirements make them ideal for harsh environments. With rising investments in decentralized energy access, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia, demand is expected to grow significantly.
7. Increased Competition and Product Differentiation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established players (e.g., CATL, BYD, LG Energy Solution) and emerging brands offering 400Ah products. Differentiation is occurring through features such as Bluetooth-enabled monitoring, modular designs, and extended warranties (up to 10 years). Consumer focus on brand reliability, safety certifications (e.g., UL, IEC), and service networks will shape purchasing decisions.
8. Sustainability and Second-Life Applications
As environmental concerns grow, the lifecycle management of lithium batteries is gaining attention. By 2026, the reuse of degraded 400Ah batteries in less demanding applications (e.g., secondary storage, street lighting) will become more common. Additionally, recycling technologies are improving, supporting circular economy models and reducing dependency on raw materials.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 400Ah lithium battery market will be characterized by robust growth, technological refinement, and expanding applications across energy, transportation, and industrial sectors. With continued cost declines, supportive policies, and rising energy resilience needs, the 400Ah format is expected to solidify its position as a cornerstone of modern energy storage solutions. Stakeholders should focus on innovation, sustainability, and customer-centric design to capitalize on these evolving trends.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing 400Ah Lithium Batteries: Quality & IP Risks (H2)
Sourcing 400Ah lithium batteries requires careful due diligence due to significant risks related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Falling into these pitfalls can lead to safety hazards, performance failures, project delays, and legal liability.
Quality Pitfalls: Beyond the Spec Sheet
- Inflated Capacity & False Ratings: The most common deception. Suppliers may label batteries as “400Ah” based on unrealistic discharge rates (e.g., C/100) or brief peak outputs, not usable capacity under standard conditions (e.g., C/20). Consequence: Significantly shorter runtime, system failure under load.
- Substandard Cell Quality & Origin:
- Unknown/Unverified Cell Brand: Suppliers may claim “Grade A” cells from reputable brands (e.g., CATL, EVE, LFP) but use counterfeit, recycled, or low-tier cells (often unmarked or rebranded “white-label”).
- Mixing Cell Bins: Using cells from different manufacturing batches, grades, or even chemistries within a single battery pack, leading to imbalance, reduced lifespan, and safety risks.
- Consequence: Rapid capacity fade, thermal runaway risk, inconsistent performance, premature failure.
- Poor BMS (Battery Management System):
- Inadequate Protection: BMS lacking essential protections (over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, short-circuit, high/low temperature, cell balancing) or with poorly calibrated thresholds.
- Ineffective Balancing: Passive balancing only, slow balancing speed, or no balancing, causing cell divergence and capacity loss.
- Poor Communication & Monitoring: Inaccurate state-of-charge (SOC) reporting, unreliable communication protocols (RS485, CAN), or lack of diagnostic data.
- Consequence: Safety hazards, reduced cycle life, inaccurate system monitoring, difficult troubleshooting.
- Inferior Materials & Construction:
- Thin Busbars & Connectors: Undersized copper or aluminum busbars and connectors cause excessive heat under high current (common with 400Ah), leading to voltage drops, efficiency loss, and fire risk.
- Poor Welding: Weak or inconsistent spot welding on cell terminals increases resistance and creates hotspots.
- Inadequate Insulation & Housing: Flimsy, non-flame-retardant materials or poor internal layout increasing short-circuit risk.
- Consequence: Overheating, voltage instability, catastrophic failure, safety incidents.
- Lack of Authentic Testing & Certification:
- Fake or Misrepresented Certificates: Suppliers may present fake UL, UN38.3, IEC, or CE certificates, or certificates for different models.
- No Independent Validation: Absence of test reports (cycle life, capacity, safety tests like nail penetration, crush) from reputable 3rd party labs.
- Consequence: Unknown safety profile, non-compliance with regulations, inability to verify performance claims.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls: Risking Your Reputation & Legality
- Counterfeit Branding & Logos:
- Direct Cloning: Batteries physically and visually identical to well-known brands (e.g., Victron, Pylontech, EG4) with logos, model numbers, and packaging copied exactly. This is blatant trademark infringement.
- “Inspired By” Designs: Close visual mimics using slightly altered names/logos (e.g., “EGG4”, “PyloTech”) to confuse buyers and trade on brand reputation.
- Consequence: Legal liability for importing/selling counterfeit goods, seizure by customs, lawsuits, reputational damage, voided warranties on integrated systems.
- Copied Firmware & Software:
- Reverse-Engineered BMS Code: BMS firmware cloned or heavily modified from open-source projects (e.g., DIY-BMS, Venus OS) or proprietary systems without proper licensing or attribution, violating software copyrights.
- Consequence: Potential legal action from copyright holders, security vulnerabilities, lack of updates/support, instability.
- Stolen Design & Circuitry:
- PCB Copying: Reverse engineering and copying the physical circuit board (PCB) layout and design of a competitor’s BMS or battery management module.
- Consequence: Patent or design right infringement, legal challenges, potential product recalls.
- Misrepresentation of Compatibility & Protocols:
- “Drop-in Replacement” Claims: Marketing batteries as compatible with specific systems (e.g., “Works with Victron”) by cloning communication protocols (CAN, RS485) without proper authorization or thorough validation, potentially causing system errors or damage.
- Consequence: Integration failures, damage to other system components, voided warranties on the host equipment, misleading marketing.
Mitigation Strategies (H2)
- Demand Transparency: Require detailed cell specifications (manufacturer, model number, datasheet), BMS model/firmware details, and full bill of materials (BOM).
- Verify Certifications & Test Reports: Insist on valid, current, model-specific certificates from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek) and independent cycle life/safety test reports. Verify certificate authenticity directly with the issuing body.
- Conduct Physical & Functional Inspection: Perform incoming inspection: check build quality, materials, welding, labeling. Test capacity, voltage, and BMS functions rigorously under load.
- Audit the Supplier: If possible, conduct factory audits or use reputable 3rd party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) before large orders.
- Prioritize Reputable Suppliers: Work with established, known manufacturers or distributors with verifiable track records and clear IP ownership policies. Be wary of extremely low prices.
- Legal Due Diligence: Consult legal counsel regarding IP risks, especially if branding, compatibility claims, or software are involved. Ensure contracts include warranties against IP infringement.
- Test for Authenticity: For brand-name cells, use known verification methods (if available) or compare physical characteristics and performance against genuine samples.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, you can significantly reduce the risk of sourcing unreliable, unsafe, or legally problematic 400Ah lithium batteries and ensure the long-term success and safety of your application.
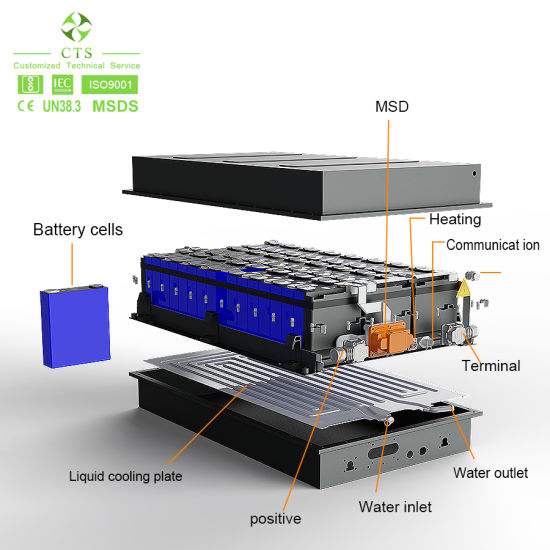
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 400Ah Lithium-Ion Batteries
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 400Ah Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries, including high-capacity units such as 400Ah models, are classified as hazardous materials for transport due to their potential to overheat, ignite, or release hazardous gases under certain conditions. This guide outlines the essential logistics and regulatory compliance requirements for the safe and legal shipment of 400Ah lithium-ion batteries across air, sea, road, and rail.
1. Regulatory Frameworks
Compliance with international and regional regulations is mandatory:
- UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (UN Model Regulations)
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) – For air transport
- IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code) – For sea transport
- ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road)
- 49 CFR (U.S. Department of Transportation – Hazardous Materials Regulations) – For domestic U.S. transport
- Local regulations (e.g., Transport Canada, ADR/RID in Europe)
Note: A 400Ah lithium-ion battery typically exceeds the 100Wh threshold and may be subject to full dangerous goods regulations.
2. Classification & Identification
- Proper Shipping Name (PSN):
Lithium ion batteries, UN 3480 - UN Number:
UN 3480 - Class:
Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods - Packing Group:
Not assigned (all lithium-ion batteries under UN 3480 are PG II by default) - Hazard Label:
Class 9 hazard label (black and white striped) must be affixed - Lithium Battery Mark:
Required for all shipments (see below)
3. Packaging Requirements
- Strong, Rigid Outer Packaging:
Must withstand stacking, drops, and vibrations. Use UN-certified packaging tested to 1.2-meter drop and stack tests. - Internal Protection:
Batteries must be protected against short circuits (e.g., terminals insulated, individually wrapped or separated). - Prevention of Movement:
Secure batteries to prevent shifting during transit. - Ventilation (if required):
For large battery systems or enclosed systems, ensure adequate ventilation per IATA/IMDG.
Note: Batteries shipped “on equipment” (e.g., in a solar system) may have different requirements than standalone batteries.
4. State of Charge (SoC)
- IATA and IMDG recommend shipping at not more than 30% State of Charge for standalone batteries unless excepted.
- This reduces thermal runaway risk during transport.
- Document SoC if required by carrier or country.
5. Lithium Battery Mark (Mandatory)
All packages containing lithium-ion batteries must display the Lithium Battery Mark:
- Diamond-shaped Class 9 hazard label
- “UN 3480” and proper shipping name
- Battery type: “Lithium ion”
- Phone number of responsible party
- 4-digit UN number (UN 3480)
- Mark must be at least 120 x 110 mm in size
Exception: Small batteries (e.g., under 2.7 Wh) or consumer-sized cells may be excepted under certain conditions.
6. Documentation
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (DGD):
Required for air and sea shipments of quantities exceeding exceptions. - Safety Data Sheet (SDS):
Provide under GHS regulations. - Air Waybill / Bill of Lading:
Must include proper class, UN number, PSN, and hazard labels. - Packing Certificate:
Confirming compliance with UN packaging standards.
Note: For small quantities or “excepted” shipments (e.g., under IATA PI 965 Section IB), a DGD may not be required, but labeling is still mandatory.
7. Quantity Limits & Exceptions
- IATA PI 965 (Lithium ion batteries alone):
- Section IA: >100 Wh per battery – Full regulation (DGD, Class 9 label)
- Section IB: ≤100 Wh per battery, or limited SoC – May qualify for reduced requirements
- A 400Ah battery at 3.2V = ~1,280 Wh (well above 100 Wh), thus Section IA applies.
- Maximum Net Quantity per Package:
Typically 30 kg for cargo aircraft; lower for passenger aircraft.
8. Carrier & Mode-Specific Rules
| Mode | Key Requirements |
|——|——————|
| Air | IATA DGR applies. Prior notification to carrier. No more than 2 passengers per flight may carry such batteries unless shipped as cargo. |
| Sea | IMDG Code. Stowage away from heat sources. Ventilation required in enclosed spaces. |
| Road (ADR) | Class 9 label, transport document, driver training, placarding for large quantities. |
| Rail | ADR principles generally apply. Check carrier-specific rules. |
9. Training & Certification
- Personnel involved in handling, packing, labeling, or shipping must be dangerous goods trained and certified.
- Training must be refreshed every 2 years (IATA/IMDG/ADR requirements).
10. Emergency Response
- Provide 24-hour emergency contact number on shipping documents.
- Include spill response, fire procedures, and first aid measures in SDS.
- Equip transport vehicles with fire extinguishers (Class D or lithium-specific recommended).
11. Storage & Handling
- Store in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from flammable materials.
- Avoid stacking unless packaging is rated for it.
- Prevent mechanical damage, short circuits, and exposure to water.
12. Import/Export Compliance
- Verify destination country regulations (e.g., China, India, EU may have additional requirements).
- Ensure batteries meet UN 38.3 testing:
- Altitude simulation
- Thermal cycling
- Vibration, shock, impact, overcharge, forced discharge
- Certificate of Compliance with UN 38.3 must be available.
13. Environmental & End-of-Life Considerations
- Comply with WEEE Directive (EU) or equivalent for disposal/recycling.
- Label batteries with recycling symbols (e.g., crossed-out wheelie bin).
- Use authorized recyclers for end-of-life units.
Summary Checklist
✅ UN 3480 classification
✅ Class 9 hazard label + Lithium Battery Mark
✅ UN-certified packaging
✅ Terminals protected from short circuit
✅ Shipped at ≤30% SoC (recommended)
✅ Shipper’s Declaration (if required)
✅ Training certification for personnel
✅ UN 38.3 test summary on file
✅ Emergency contact on documentation
✅ Carrier notification and approval
Disclaimer: Regulations change frequently. Always consult the latest edition of IATA DGR, IMDG Code, ADR, or 49 CFR, and confirm requirements with your carrier before shipment.
For high-volume or international shipments, consider engaging a certified dangerous goods safety advisor (DGSA).
Prepared in accordance with global standards as of 2024.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 400Ah Lithium Battery
After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term performance, sourcing a 400Ah lithium battery is a strategic decision that supports high-capacity energy storage needs across various applications such as off-grid solar systems, electric vehicles, marine use, and backup power solutions. The shift from traditional lead-acid batteries to lithium technology offers significant advantages, including longer cycle life, higher energy density, faster charging, and lower maintenance requirements.
Key considerations in the sourcing process—such as battery chemistry (e.g., LiFePO4 for safety and longevity), certifications (UL, CE, UN38.3), thermal management, warranty terms, and after-sales support—must be prioritized to ensure quality and safety. Working with reputable manufacturers or suppliers, ideally with proven track records and transparent supply chains, minimizes risks associated with performance inconsistencies or reliability issues.
In conclusion, sourcing a 400Ah lithium battery delivers substantial operational and economic benefits over time. A well-vetted supplier offering a balanced combination of quality, service, and competitive pricing will ensure optimal return on investment, system reliability, and sustainability in energy storage solutions.