The global 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machine market has experienced steady momentum in recent years, driven by rising demand across personalized gifting, industrial marking, and artistic applications. According to Grand View Research, the global laser marking and engraving market was valued at USD 2.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by advancements in laser technology and increasing automation in manufacturing sectors. This growth is further supported by the rising consumer preference for customized and precision-etched products, particularly in high-margin industries like luxury goods, medical devices, and commemorative keepsakes. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront of innovation, offering advanced 3D subsurface laser systems capable of producing intricate, high-resolution engravings within transparent materials such as glass and crystal. These companies are distinguished by their technological precision, software integration, and scalability—key factors shaping the competitive landscape. Below is a data-informed overview of the top 9 manufacturers leading this specialized segment of the engraving industry.
Top 9 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 3D Glass Crystal Laser Engraving Machine Supplier in China …
Website: stnlaser.com
Key Highlights: Wuhan Syntony Laser Co., Ltd is a dedicated developer and manufacturer of 3D laser engraving products in China….
#2 Fiber Laser Engraving Machine
Website: haotianlasers.com
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer, not a reseller, we specialize in crafting high-quality CO2 laser engraving machines, UV laser marking machines, and fiber laser ……
#3 3D Subsurface Laser Engraving
Website: crystal-d.com
Key Highlights: Our 3D subsurface engraving process comes in, allowing us to recreate any image inside a crystal award or gift in two or three dimensions….
#4 ApexRay HD 3D Crystal Subsurface Laser Engraving Machine
#5 Master Sub
Website: heatsign.com
Key Highlights: The 3D Crystal Laser Engraving Machine from HeatSign is designed for creating stunning sub-surface engravings in crystal and glass….
#6 3D Crystal Laser Engraving Machine
Website: sismarlaser.com
Key Highlights: Start small, impress big. With the UV 3D Laser Engraving Machine, your startup can create both emotional 3D crystal keepsakes and surface-engraved products, ……
#7 ARGUS 2D/3D Green Laser Engraving Machine Crystal Laser for …
Website: arguslaser.net
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (79) Wide application range—an ideal model for all types of 2D/3D internal crystal engraving. This engraver is perfect for creating personalized crystal gifts and ……
#8 Perfect Laser 3D crystal engraving machine
Website: perfectlaser.net
Key Highlights: Perfect Laser offers 3D crystal engraving machine,widely used for 3D crystal engraving and 3D portraits for human image.affordable and easy-to-use….
#9 2D/3D Subsurface Laser Engraving
Website: crystalsensations.com
Key Highlights: Subsurface Laser Engraving enables us to create stunning awards containing 2D and 3D artwork that appears to float gracefully inside solid crystal shapes….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machines
The global market for 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machines is projected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and rising consumer demand for personalized products. This section explores key market trends expected to shape the industry landscape in 2026.
1. Growth in Personalized and Customized Products
A major driver for the 3D subsurface laser engraving market is the increasing consumer preference for bespoke and personalized items. By 2026, the demand for custom awards, corporate gifts, wedding memorabilia, and artistic décor is expected to surge, particularly in e-commerce and retail sectors. Laser engraving machines capable of producing high-precision, three-dimensional internal engravings in glass and crystal will be in high demand to meet this need.
2. Advancements in Laser Technology and Automation
Technological innovation is accelerating the capabilities of 3D subsurface engraving systems. By 2026, expect wider adoption of ultrafast lasers (e.g., femtosecond lasers) that enable finer detail, reduced thermal damage, and faster processing speeds. Integration with AI-driven design software and automated workflows will enhance precision and scalability, making these systems more accessible to small businesses and creative entrepreneurs.
3. Expansion into New Industries
Beyond traditional uses in giftware and awards, 3D laser engraving is penetrating new verticals such as medical devices (for marking surgical tools), security (embedding tamper-proof serial numbers), and architectural glass (decorative interior elements). The ability to create permanent, subsurface engravings without compromising material integrity makes this technology ideal for high-value and regulated industries.
4. Rising Demand in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are expected to see accelerated market growth by 2026 due to increasing disposable incomes, digitalization of manufacturing, and growing awareness of laser engraving capabilities. Local manufacturers in countries like China, India, and Brazil are investing in domestic production of engraving machines, reducing costs and improving accessibility.
5. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient laser systems and recyclable crystal materials. By 2026, eco-certified machines and sustainable production practices are likely to become competitive differentiators, influencing purchasing decisions among environmentally conscious businesses and consumers.
6. Integration with Digital Platforms and On-Demand Services
The rise of online customization platforms—where users upload designs for instant engraving—will fuel demand for network-connected, cloud-integrated laser engraving machines. By 2026, seamless integration with e-commerce systems, mobile apps, and AI-based design tools will enable real-time order fulfillment and mass customization at scale.
7. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is expected to see increased competition among established players (e.g., Trotec, Epilog Laser) and emerging tech startups. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and product diversification will be common as companies aim to capture niche segments. Additionally, open-source firmware and modular machine designs may democratize access, fostering innovation.
In summary, the 2026 market for 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machines will be shaped by personalization trends, technological innovation, industry diversification, and global expansion. Businesses that leverage automation, sustainability, and digital integration will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machine (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machine involves significant investment and technical complexity. Falling into common pitfalls can lead to poor quality output, legal risks, and operational inefficiencies. Below are key areas to watch for, focusing on quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost machines, particularly from less-regulated suppliers, use substandard components that compromise performance and longevity. Look out for cheap lasers with unstable output, imprecise galvanometer scanners, or low-resolution controllers. These directly affect engraving accuracy, clarity, and consistency. Poorly assembled optical systems can lead to beam misalignment, resulting in blurry or distorted 3D images. Always request third-party quality certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) and inspect build materials and workmanship before purchasing.
Inaccurate or Exaggerated Technical Specifications
Suppliers may inflate laser power, engraving speed, or resolution metrics to appear competitive. For example, advertising a “5W laser” when the actual effective power for crystal engraving is much lower can mislead buyers. Similarly, claimed engraving depths or dot positioning accuracy may not reflect real-world performance. Always request sample engravings on your preferred crystal type and verify specs through independent testing or trusted reviews.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection and Risk of Infringement
Some machines, especially those from certain regions, may incorporate cloned firmware, copied software interfaces, or unauthorized laser drivers that infringe on patented technologies. Using such equipment exposes your business to legal liability, including cease-and-desist orders or customs seizures. Ensure the supplier can provide proof of IP compliance and original software licensing. Avoid machines with generic or unbranded control systems, which are often red flags for IP violations.
Inadequate Software and Limited Customization
The software driving the engraving process is critical for design flexibility and precision. Low-quality machines often come with proprietary software that lacks features, has a poor user interface, or does not support common file formats. Worse, some software may contain malware or hidden backdoors. Confirm that the software is reputable, regularly updated, and allows full control over voxel placement, depth mapping, and image rendering. Open SDKs or API access can be a strong indicator of legitimate development.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and troubleshooting. Sourcing from suppliers with poor customer support, incomplete manuals, or no local service network can result in extended downtime. Verify the availability of technical documentation, training resources, and responsive support channels. Lack of IP-compliant firmware updates can also leave you vulnerable to future legal or security issues.
Hidden Costs from Non-Standard Consumables or Repairs
Some machines are designed to work only with proprietary crystals or lenses, locking you into expensive consumables. Others may use non-standard laser components that are difficult or costly to replace. These practices often stem from attempts to circumvent IP-protected technologies through closed ecosystems. Opt for machines using industry-standard parts and open compatibility to avoid long-term vendor lock-in and inflated maintenance costs.
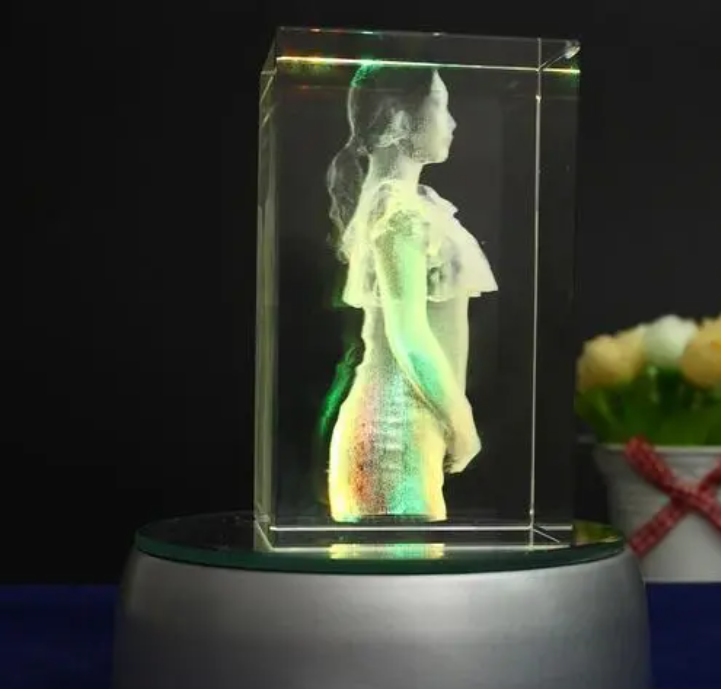

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machine
Shipping and Handling
Proper shipping and handling are crucial to ensure the 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machine arrives undamaged and functions as intended. Use only reputable freight carriers experienced in handling precision equipment. The machine must be securely crated with shock-absorbing materials such as foam inserts or custom wooden cases to prevent movement during transit. Always follow the manufacturer’s packing instructions. Clearly label the crate with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. For international shipments, ensure all handling personnel are aware of the equipment’s sensitivity to vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Import/Export Regulations
Compliance with international trade laws is essential when transporting the engraving machine across borders. Verify the Harmonized System (HS) code—typically under 8456.20 (Laser Engraving Machines)—with your local customs authority. Obtain necessary export licenses if required by the country of origin, especially if the laser exceeds certain power thresholds (e.g., Class 4 lasers may require an export control license under ITAR or EAR in the U.S.). Ensure all documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin, is accurate and complete. Be aware of import restrictions or tariffs in the destination country, and consider using a customs broker to streamline clearance.
Electrical and Safety Compliance
The machine must comply with electrical safety standards in the destination country. Confirm voltage (e.g., 110V or 220–240V), frequency (50/60 Hz), and plug type compatibility. Use appropriate power converters or transformers if needed. The device should meet recognized safety certifications such as CE (Europe), UL/CSA (North America), or PSE (Japan). Ensure the laser system complies with IEC 60825-1 for laser safety, including proper labeling of the laser class (usually Class 1 or Class 4 depending on enclosure). Provide users with safety interlocks, emergency stop mechanisms, and protective enclosures as required.
Laser Safety and Regulatory Approvals
Laser-based equipment is subject to stringent safety regulations. In the U.S., the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) requires compliance with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11, including product reporting and certification. In the EU, the machine must meet the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the Laser Products standard EN 60825-1. Provide users with a laser safety manual, proper warning labels, and training documentation. Confirm that the equipment includes safety features such as key-controlled operation, beam shutters, and interlocks to prevent accidental exposure during maintenance or operation.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Ensure the engraving machine complies with environmental directives such as the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive 2011/65/EU, which limits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electrical equipment. Provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and, if requested, a bill of materials (BOM) confirming RoHS compliance. For disposal or end-of-life handling, follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) guidelines to promote proper recycling. Avoid shipping to countries without adequate e-waste management infrastructure unless proper take-back programs are in place.
Warranty and After-Sales Support Logistics
Clearly define warranty terms, including duration, coverage, and service response times. Ship spare parts such as focusing lenses, laser diodes, or power supplies to regional service centers in advance to minimize downtime. Provide multilingual user manuals, technical documentation, and online support portals. For international customers, establish local service partners or train onsite technicians to perform basic maintenance and troubleshooting. Maintain an inventory tracking system to manage parts logistics and ensure compliance with product registration requirements in each market.
Conclusion: Sourcing a 3D Subsurface Laser Crystal Engraving Machine
After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, vendor capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term operational requirements, sourcing a 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machine represents a strategic investment in precision, customization, and value-added manufacturing. These advanced systems enable the creation of intricate, three-dimensional designs inside crystals and glass, offering unique applications in personalized gifts, corporate awards, medical devices, and high-tech optics.
Key findings from the sourcing process indicate that selecting a machine with high beam quality (typically involving Nd:YAG or fiber lasers), precise galvanometric scanning, and robust software integration is critical for achieving consistent, high-resolution engravings. Additionally, considerations such as after-sales support, training, warranty, and scalability are vital for ensuring uninterrupted operations and future growth.
While initial costs may be substantial, the versatility, durability, and premium market appeal of laser-engraved crystal products justify the investment. Sourcing from reputable suppliers with proven track records and technological expertise ensures reliability, compliance with safety standards, and access to ongoing innovation.
In conclusion, procuring a 3D subsurface laser crystal engraving machine enhances production capabilities, opens new revenue streams, and positions the business at the forefront of customized precision engraving—making it a sound and forward-looking decision for both commercial and industrial applications.