The global solid-state drive (SSD) market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-speed data storage across consumer electronics, enterprise servers, and data centers. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global SSD market size was valued at USD 43.7 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.5% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the transition from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to faster, more reliable SSDs, particularly in portable and high-performance computing applications. As 3.5-inch form factor SSDs gain traction in enterprise environments for their balance of capacity, performance, and rack integration, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation and market share. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and revenue performance, the following nine companies represent the forefront of 3.5-inch SSD manufacturing in today’s data-centric landscape.
Top 9 3.5 Solid State Hard Drive Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SSSTC|Industrial|Enterprise|Solid State Drives|SATA、Nvme
Domain Est. 2013
Website: ssstc.com
Key Highlights: We are a global leader in the design, development and manufacturing of Solid-State Drives (SSDs) for Enterprise/Data Center, Cloud Computing, Personal computers ……
#2 Internal SSDs
Domain Est. 1992
Website: seagate.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsInternal Solid-State Drives (SSDs). Step into the future of storage with Seagate Internal SSDs, designed to deliver exceptional performance and reliabil…
#3 Solid State Drives (SSDs) for Laptops, Desktop PCs, and Servers
Domain Est. 1993
Website: kingston.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $70 30-day returnsSSDs can extend the lifecycle and dramatically improve the performance of a PC with higher speeds, greater durability and legendary Kingston re…
#4 Internal Drives
Domain Est. 1995
#5 Shop Hard Drives
Domain Est. 1998
Website: westerndigital.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $299 Free 30-day returnsBrowse our catalog of internal, external, and portable HDDs to simplify data transfer in the office, your gaming rig, at home, or on the …
#6 Sabrent
Domain Est. 2002
Website: sabrent.com
Key Highlights: Rocket Enterprise PCIe 4.0 U.2 NVMe SSD Hgh-endurance storage solution for demanding enterprise workloads Shop Now Learn More decorative Sabrent Rocket ……
#7 MS30 M.2 2280 SATA SSD 512GB
Domain Est. 2013
Website: teamgroupinc.com
Key Highlights: MS30 is a M.2 high speed solid state drive of the latest generation. It has the latest SATA III 6Gb/s transfer interface and offers excellent transfer ……
#8 KIOXIA SSD (Solid State Drive)
Domain Est. 2018
Website: apac.kioxia.com
Key Highlights: Upgrading from a hard drive or SATA SSD should be easy and affordable and that’s where EXCERIA SSDs come in. KIOXIA EXCERIA SSD Series is built to boost your ……
#9 SATA
Domain Est. 2019
Website: serverdiskdrives.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsExplore our collection of SATA SSD 3.5″ drives. Perfect for server upgrades, business storage, and enterprise applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3.5 Solid State Hard Drive

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for 3.5-Inch Solid State Drives
As of 2026, the market for 3.5-inch solid state drives (SSDs) is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by advancements in data center infrastructure, enterprise storage demands, and evolving form factor standards. While traditional 3.5-inch drives have long been associated with hard disk drives (HDDs), the adoption of 3.5-inch SSDs is gaining momentum in specific high-performance, high-capacity applications—particularly in enterprise and hyperscale data center environments.
-
Enterprise Adoption in Data Centers
The 3.5-inch SSD form factor is increasingly being leveraged in enterprise storage systems where physical space, power efficiency, and thermal management are optimized for high-density deployments. Unlike smaller M.2 or 2.5-inch SSDs, the 3.5-inch size allows for improved heat dissipation and greater NAND flash integration, making it ideal for all-flash arrays and storage appliances requiring multi-terabyte to petabyte-scale capacity. In 2026, major vendors such as Dell, HPE, and NetApp are incorporating 3.5-inch SSDs into their next-generation storage platforms, especially for AI/ML workloads and real-time analytics. -
Capacity and Performance Enhancements
By 2026, 3.5-inch SSDs are expected to offer capacities exceeding 60TB per drive, thanks to advances in quad-level cell (QLC) and 3D NAND stacking technologies. These drives provide a compelling alternative to HDDs in capacity-sensitive environments where performance must still surpass traditional spinning media. NVMe-over-Fabrics (NVMe-oF) support is becoming standard, enabling ultra-low latency and high throughput, aligning with the needs of modern cloud-native applications. -
Hybrid Use in Edge and Industrial Applications
Beyond data centers, 3.5-inch SSDs are finding niche applications in edge computing and industrial systems where ruggedness, large form factor compatibility, and sustained write performance are required. Their larger PCB and enhanced cooling options make them suitable for harsh environments where smaller drives may fail under thermal stress. -
Competition and Market Challenges
Despite these advantages, the 3.5-inch SSD faces stiff competition from 2.5-inch U.2 and E1.S form factors, which are more power-efficient and better suited for scale-out architectures. As a result, 3.5-inch SSDs are not expected to dominate the broader SSD market but will occupy a specialized segment focused on high-capacity, high-reliability storage solutions. -
Sustainability and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Enterprises are increasingly evaluating TCO and environmental impact. 3.5-inch SSDs, while consuming more power than smaller NVMe drives, offer better longevity and endurance per terabyte, reducing replacement frequency and e-waste. Vendors are responding with energy-efficient controllers and smarter wear-leveling algorithms, enhancing their appeal in green data center initiatives.
In summary, the 3.5-inch SSD market in 2026 is characterized by niche but strategic growth. While not replacing smaller form factors, it fills a critical role in high-capacity enterprise storage, where performance, reliability, and serviceability are paramount. Continued innovation in NAND technology and thermal design will determine its long-term viability in an increasingly compact and efficient storage landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 3.5″ Solid State Hard Drive (SSD) – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
When sourcing 3.5-inch solid state drives (SSDs), despite their growing adoption in enterprise and industrial applications, several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can compromise performance, reliability, and legal compliance. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
1. Misunderstanding Form Factor and Technology Compatibility
A common misconception is equating 3.5-inch SSDs with traditional 3.5-inch hard disk drives (HDDs). While they share the same form factor, 3.5-inch SSDs are less common and often designed for niche applications such as industrial systems or legacy hardware upgrades. Buyers may inadvertently source drives that do not meet performance expectations or lack proper SATA/SAS interface compatibility, leading to integration issues.
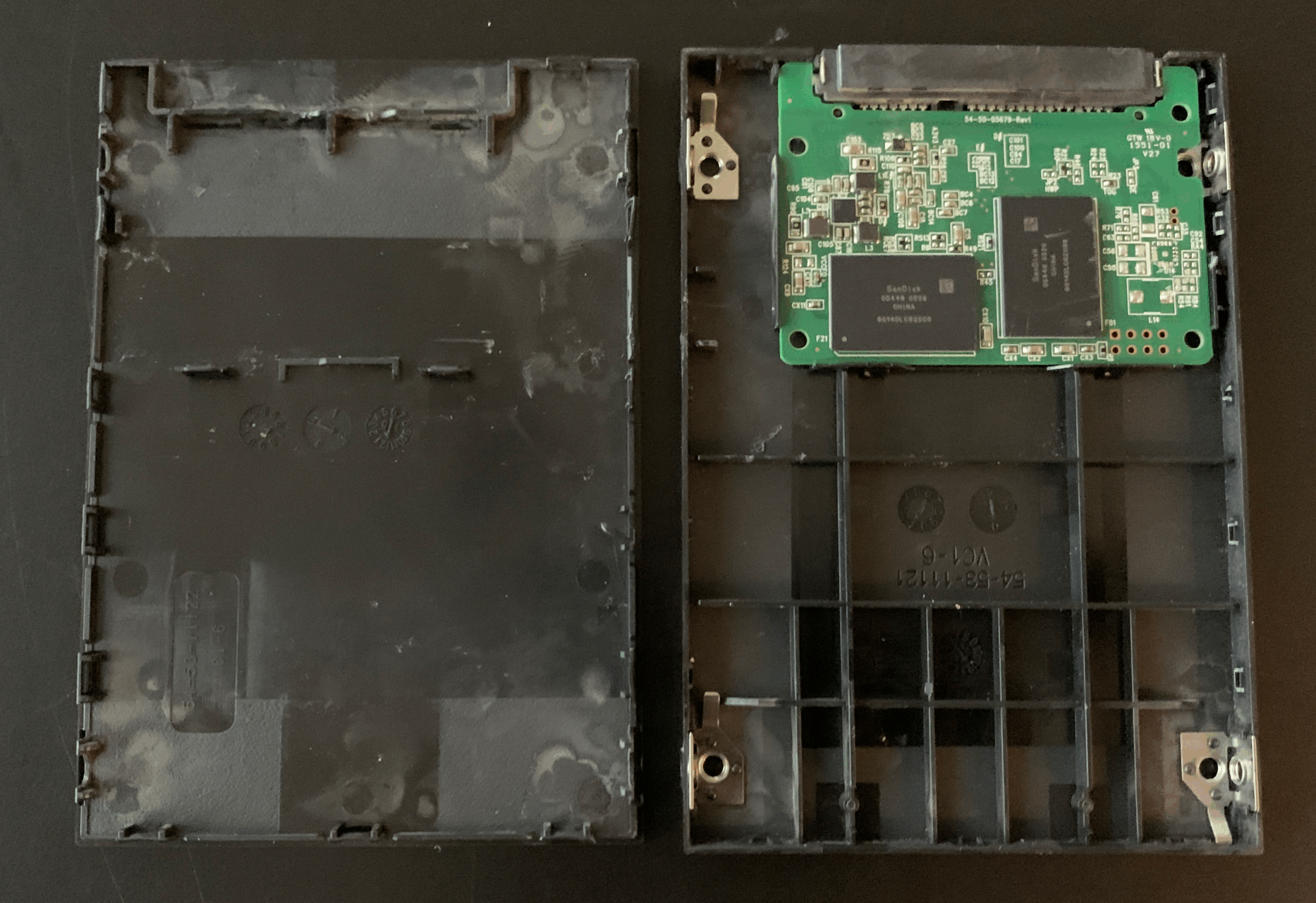
2. Compromised Component Quality
Lower-tier manufacturers may use substandard NAND flash memory, controllers, or power management components to cut costs. This compromises drive endurance, data retention, and thermal stability—especially critical in 24/7 operational environments. Be wary of drives lacking clear specifications on TBW (Terabytes Written), MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures), or industrial temperature ranges.
3. Lack of Firmware Transparency and Updates
Many budget SSDs come with proprietary firmware that is not regularly updated or lacks detailed documentation. Poor firmware can lead to data corruption, reduced lifespan, or vulnerability to exploits. Additionally, the absence of secure firmware updates raises concerns about long-term support and cybersecurity.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Manufacturing
Some 3.5-inch SSDs—particularly from unknown or offshore suppliers—may incorporate cloned or reverse-engineered controllers and firmware. This raises significant IP infringement risks, potentially exposing buyers to legal liability, especially in regulated industries or international markets. Procuring from vendors without verifiable IP ownership or proper licensing agreements increases exposure.
5. Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reputable SSDs undergo rigorous testing for reliability, endurance, and compatibility. However, some suppliers skip or falsify certifications such as ISO 9001, IEC 60068 (environmental testing), or UN 38.3 (for shipping). Without these, there’s no assurance of consistent quality or safety, particularly in mission-critical applications.
6. Opaque Supply Chain and Traceability
A lack of supply chain transparency makes it difficult to verify the origin of components. This increases the risk of counterfeit parts, unauthorized resellers, or dual-use technology that may violate export controls or sanctions. Buyers should require full traceability and audit rights when sourcing such components.
7. Absence of Long-Term Availability and Lifecycle Support
Many 3.5-inch SSDs are produced in limited runs or for specific OEMs. Sourcing drives without guaranteed long-term availability can disrupt production or maintenance cycles. Lack of lifecycle management support (e.g., end-of-life notifications) further complicates inventory planning.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should prioritize suppliers with proven track records, transparent manufacturing practices, documented IP rights, and compliance with industry standards. Conducting supplier audits, requesting sample testing, and including IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts are effective strategies for ensuring quality and legal safety.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3.5″ Solid State Hard Drive
Product Overview
The 3.5″ Solid State Hard Drive (SSD) is a high-performance storage device designed for enterprise, data center, and industrial applications. Unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), this SSD utilizes NAND flash memory for faster data access, improved reliability, and lower power consumption. Its 3.5″ form factor ensures compatibility with standard drive bays and enclosures.
Packaging & Handling
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use anti-static bubble wrap or foam-lined packaging to protect against electrostatic discharge (ESD) and physical shock.
- Include a static-shielding bag (e.g., metallized shielding bag per ANSI/ESD S541) for each unit.
-
Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “Electrostatic Sensitive Device,” and orientation arrows.
-
Handling Procedures:
- Personnel must wear ESD wrist straps when handling units outside of protective packaging.
- Avoid direct contact with connector pins and circuitry.
- Store and transport in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (see Storage Conditions below).
Shipping & Transportation
- Domestic & International Shipping:
- Compliant with IATA Packing Instruction 967 for lithium-containing electronic devices (if applicable, based on onboard backup power).
- No hazardous materials classification required for standard SSDs without integrated batteries.
-
Use UN-certified packaging for air freight when required.
-
Temperature & Humidity:
- Transit temperature range: –25°C to 70°C (–13°F to 158°F).
- Relative humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing.
- Monitor environmental conditions during shipment using data loggers for high-value or sensitive consignments.
Storage Conditions
- Long-Term Storage:
- Temperature: 0°C to 35°C (32°F to 95°F).
- Relative humidity: 20% to 50%.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, corrosive gases, or high electromagnetic fields.
- Recommended maximum storage duration without power: 12 months. Re-energize and validate data integrity periodically.
Regulatory Compliance
- Environmental & Safety Standards:
- RoHS 3 (EU Directive 2015/863): Compliant with restrictions on hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.).
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
-
WEEE (2012/19/EU): Marked with the crossed-out wheelie bin symbol; ensure proper end-of-life recycling.
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
- FCC Part 15 Class B (USA): Meets radiated and conducted emissions limits.
-
CE Marking (EMC Directive 2014/30/EU): Ensures electromagnetic compatibility in the EU.
-
Product Safety:
- UL 62368-1 / IEC 62368-1: Audio/Video, Information, and Communication Technology Equipment – Safety Requirements.
Import & Export Controls
- Export Compliance:
- ECCN (Export Control Classification Number): Typically 3A991.b.4 (solid-state storage not specially designed for military use).
- Subject to EAR (Export Administration Regulations) but generally eligible for license exception NLR (No License Required) for most destinations.
-
Verify destination country restrictions; certain regions may require authorization.
-
Customs Documentation:
- Provide commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
- Include HS Code: 8471.80 (Solid-state non-volatile storage devices).
End-of-Life & Recycling
- Disposal Guidelines:
- Do not dispose of in regular trash.
- Recycle through certified e-waste handlers compliant with local regulations (e.g., R2, WEEELABEX).
-
Data sanitization must be performed prior to recycling (use secure erase or cryptographic erase per NIST SP 800-88).
-
Take-Back Programs:
- Participate in manufacturer or regional take-back initiatives for responsible end-of-life management.
Documentation & Labeling
- Required labels on device or packaging:
- Manufacturer name and model number
- CE, FCC, UL, and RoHS compliance marks
- WEEE symbol
- Serial number and date code
- Input voltage and power requirements (if applicable)
Ensure all technical documentation, including user manuals and safety data sheets (SDS), are available in local languages for target markets.
Note: Always consult the latest regulatory updates and manufacturer specifications for application-specific compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 3.5″ Solid State Drive:
While 3.5″ solid state drives (SSDs) are not as common as their 2.5″ counterparts or M.2 variants, sourcing a 3.5″ SSD is feasible for applications requiring high performance, reliability, and compatibility with existing 3.5″ drive bays—particularly in enterprise storage systems, servers, and industrial environments. These drives typically come in the form of SSDs mounted in 3.5″ form factor converters or are purpose-built high-capacity SAS/SATA SSDs designed for data centers.
Key considerations when sourcing include interface type (SATA or SAS), performance requirements (read/write speeds, endurance), capacity, and compatibility with existing hardware. Major manufacturers such as Samsung, Seagate, Western Digital, and Kingston offer solutions either directly or through adapter trays. Additionally, cost-effectiveness should be evaluated, as 3.5″ SSDs may carry a premium due to niche demand and specialized use cases.
In conclusion, while the traditional 3.5″ SSD market remains limited, suitable options are available for specific high-performance or legacy system integration needs. Careful evaluation of technical specifications and vendor support ensures a successful implementation, balancing speed, durability, and scalability for modern storage demands.