The global stainless steel market, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, construction, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% from 2024 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With Type 304 stainless steel accounting for nearly 50% of total stainless steel consumption worldwide—owing to its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability—the demand for high-quality 304 SS composition manufacturers has intensified. As of 2023, the Asia Pacific region alone dominated over 55% of global production, led by China and India’s expanding industrial infrastructure. Companies seeking reliable supply chains are increasingly prioritizing manufacturers with consistent material traceability, ISO certifications, and advanced metallurgical capabilities. In this competitive landscape, identifying the top 304 stainless steel producers is crucial for ensuring performance and compliance across high-stakes applications.
Top 7 304 Ss Composition Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Grade 304 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: azom.com
Key Highlights: Stainless steel types 1.4301 and 1.4307 are also known as grades 304 and 304L respectively. Type 304 is the most versatile and widely used stainless steel….
#2 Stainless Steel Grades
Domain Est. 1999
Website: jindalstainless.com
Key Highlights: Stainless Steel 304 is a versatile austenitic alloy renowned for its remarkable corrosion resistance and durability. Its versatility shines in applications ……
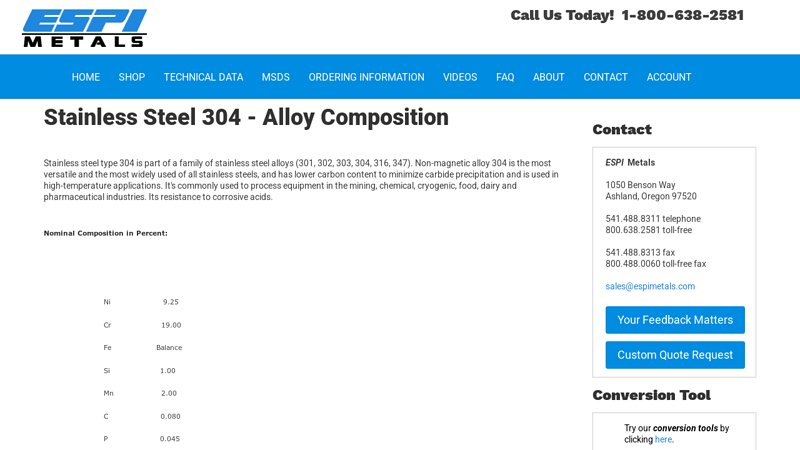
#3 Stainless Steel 304
Domain Est. 2000
Website: espimetals.com
Key Highlights: Non-magnetic alloy 304 is the most versatile and the most widely used of all stainless steels, and has lower carbon content to minimize carbide precipitation ……
#4 Stainless Steel Grades and Families: Explained
Domain Est. 2002
Website: unifiedalloys.com
Key Highlights: You’ll find various grades that help to describe specific properties of the alloy such as toughness, magnetism, corrosion resistance and alloy composition….
#5 AISI 304
Domain Est. 2007
Website: stahlportal.com
Key Highlights: The stainless steel alloys AISI 304 and AISI 304L are the best known and most widely used chromium-nickel steels. Their excellent corrosion resistance, high ……
#6 304 Stainless Steel, AISI 304, EN 1.4301, S30400 …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: neonalloys.com
Key Highlights: 304 stainless steel is the most commonly use austenite steel. 304 SS usually contains 18% chromium, 8% nickel. 304 stainless steel has a very good resistance….
#7 Stainless Steel 304
Domain Est. 2017
Website: thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk
Key Highlights: Stainless steel 304 and stainless steel 304L are also known as 1.4301 and 1.4307 respectively. Type 304 is the most versatile and widely used stainless steel. ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 304 Ss Composition
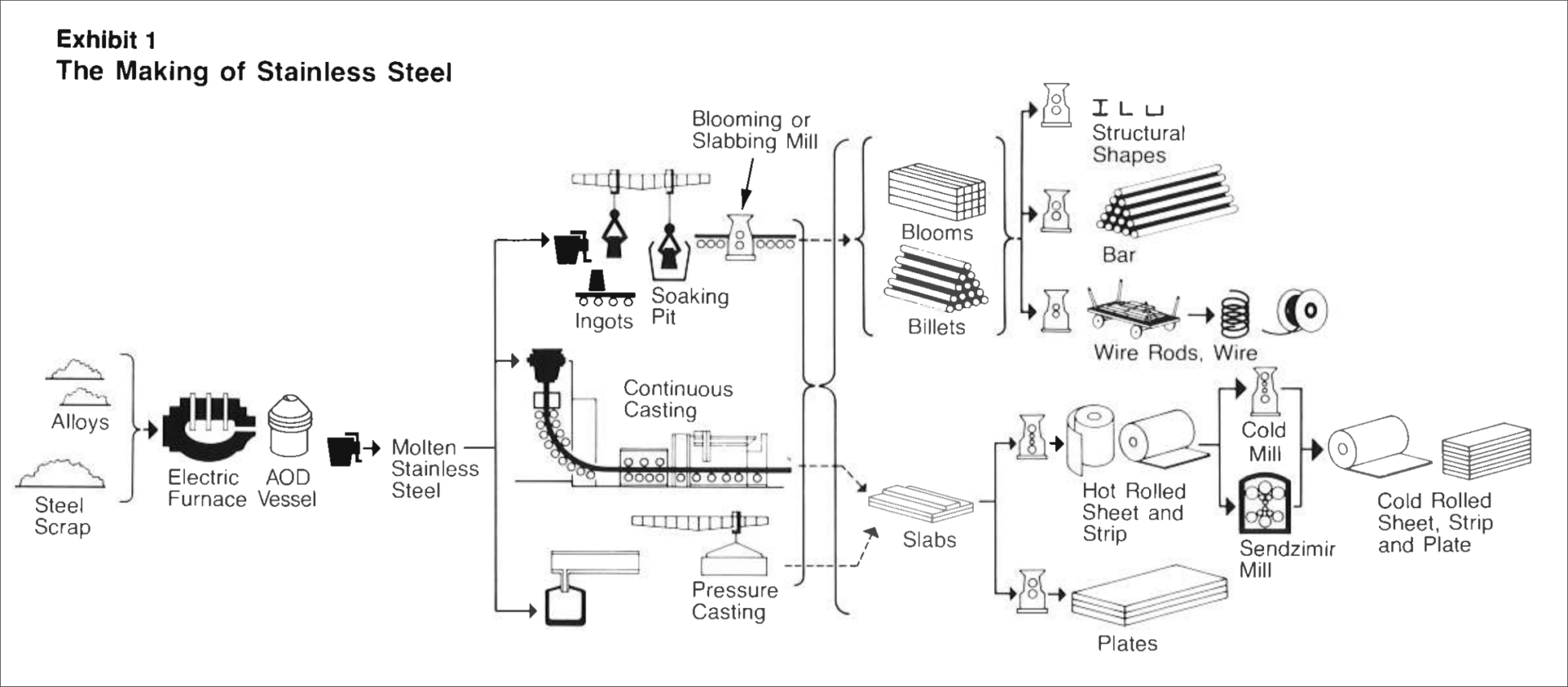
H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for 304 Stainless Steel Composition
The global market for 304 stainless steel (SS), one of the most widely used austenitic stainless steels, is poised for significant shifts by 2026. Driven by evolving industrial demands, sustainability imperatives, and raw material dynamics, the composition and application of 304 SS are expected to adapt in response to both technological advancements and macroeconomic trends.
1. Stable Core Composition with Minor Adjustments
The fundamental composition of 304 SS—18% chromium, 8% nickel, and a maximum of 0.08% carbon—remains unchanged due to its optimal balance of corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability. However, by 2026, minor compositional tweaks are anticipated to enhance performance under specific conditions. For instance, tighter control over trace elements like sulfur and selenium may improve machinability without compromising corrosion resistance, especially in precision engineering sectors.
2. Rising Demand in Green and Construction Sectors
The construction, architecture, and renewable energy sectors are projected to be primary drivers of 304 SS demand in 2026. The push for sustainable infrastructure and durable building materials supports the use of 304 SS in facades, roofing, and water treatment systems. Its recyclability and long lifecycle align with global ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals, reinforcing its market position.
3. Nickel Price Volatility and Cost Mitigation Strategies
Nickel, a key component of 304 SS, continues to face price volatility due to geopolitical factors and supply chain constraints, particularly from Indonesia and the Philippines. In response, some manufacturers may explore low-nickel alternatives or adopt more efficient recycling practices to stabilize input costs. However, 304 SS is expected to maintain its dominance in applications where performance cannot be compromised.
4. Growth in Asian Manufacturing and Urbanization
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will remain central to 304 SS consumption in 2026. Rapid urbanization, industrialization, and government infrastructure initiatives are increasing demand for stainless steel in household appliances, transportation, and water management systems. Domestic production in these regions is also rising, reducing import dependency and influencing global supply dynamics.
5. Technological Integration and Quality Control
By 2026, digitalization and Industry 4.0 technologies are expected to enhance the consistency and traceability of 304 SS composition. Advanced analytics, AI-driven process control, and blockchain for material certification will ensure precise alloy composition and improve product reliability—critical for aerospace, medical, and high-end automotive applications.
6. Recycling and Circular Economy Influence
With growing emphasis on circular economy models, the use of recycled stainless steel is expected to rise. 304 SS, being highly recyclable, benefits from closed-loop recycling systems. By 2026, a larger share of production may incorporate scrap-based feedstock, slightly altering trace element profiles but maintaining standard specifications through improved refining techniques.
Conclusion
In summary, while the core composition of 304 stainless steel will remain stable through 2026, market trends indicate increased scrutiny on cost-efficiency, sustainability, and performance optimization. Innovation in production, coupled with rising demand from emerging economies and green technologies, will sustain 304 SS as a cornerstone material in global industry. Strategic adaptations in sourcing, recycling, and manufacturing will be essential for stakeholders to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 304 Stainless Steel Composition (Quality and Material Integrity)
Sourcing 304 stainless steel requires careful attention to ensure the material meets required specifications, particularly regarding chemical composition, mechanical properties, and overall quality. Overlooking key aspects can lead to performance failures, compliance issues, and increased costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Verification of Chemical Composition
Suppliers may provide mill test reports (MTRs) that appear legitimate but lack third-party verification. Relying solely on supplier documentation without independent testing (e.g., via handheld XRF or lab analysis) risks receiving material with out-of-spec levels of key elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum—potentially compromising corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Accepting Non-Compliant or Marginal Grades
Some sourced material may fall within broad “304-type” ranges but does not meet ASTM, AISI, or ISO standards for 304 SS. For example, low nickel content (below 8%) or high carbon (approaching 0.08%) can degrade performance. Always confirm compliance with specific standards such as ASTM A240 or A276.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Material
Illegitimate suppliers may label substandard or recycled stainless steel as genuine 304. This includes material sourced from unverified mills or black-market supply chains. Without proper traceability (heat number, MTRs), verifying authenticity becomes nearly impossible.
Insufficient Quality Assurance Protocols
Procurement processes that skip incoming inspection or material testing expose buyers to risk. Implementing protocols such as positive material identification (PMI) at receiving ensures the material matches specifications before use in production.
Overlooking Surface and Structural Defects
Even with correct composition, poor manufacturing practices can introduce surface cracks, inclusions, or inconsistent grain structure. Visual inspection and non-destructive testing (NDT) may be necessary to detect flaws that impact performance, especially in high-stress or corrosive environments.
Ignoring Supply Chain Transparency
Lack of visibility into the supply chain increases the risk of receiving material that has been diverted, re-labeled, or blended. Work with trusted suppliers who provide full traceability from melt shop to final product to ensure integrity.
Assuming All 304 Is Equal
Not all 304 stainless steel performs the same. Variations in processing (e.g., annealing, cold work) affect mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Ensure material condition (e.g., 304L, 304H, annealed, as-rolled) matches application requirements.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous testing, supplier vetting, and clear specifications—buyers can ensure they receive genuine, high-quality 304 stainless steel that meets performance and regulatory standards.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 304 Stainless Steel Composition
Overview of 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steels. Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability, it contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel (18/8 stainless), along with iron and trace elements such as carbon, manganese, silicon, and phosphorus. Its chemical composition adheres to ASTM A240/A240M and UNS S30400 standards, making it suitable for a variety of industrial, food processing, and architectural applications.
Chemical Composition Requirements
To ensure compliance, the chemical composition of 304 stainless steel must conform to the following limits (by weight %):
- Chromium (Cr): 18.0 – 20.0%
- Nickel (Ni): 8.0 – 10.5%
- Carbon (C): ≤ 0.08%
- Manganese (Mn): ≤ 2.0%
- Silicon (Si): ≤ 1.0%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤ 0.045%
- Sulfur (S): ≤ 0.030%
- Iron (Fe): Balance
Material test reports (MTRs) must be provided by suppliers to verify conformance to these specifications.
International Standards and Certifications
304 stainless steel must comply with recognized international standards to ensure quality and regulatory acceptance:
- ASTM A240/A240M: Standard specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip.
- UNS S30400: Unified Numbering System designation.
- EN 1.4301: European equivalent standard.
- JIS SUS304: Japanese Industrial Standard.
Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 17025 (testing laboratories) enhance credibility and compliance across global supply chains.
Material Traceability and Documentation
Proper traceability is critical for logistics and regulatory compliance:
- Each shipment must include a Mill Test Certificate (MTC) or Material Test Report (MTR) that confirms chemical composition and mechanical properties.
- Heat or batch numbers must be clearly marked on packaging and documented throughout the supply chain.
- Digital tracking systems (e.g., blockchain or ERP integration) are recommended for audit trails and customs clearance.
Import/Export Compliance
When transporting 304 stainless steel across borders, adhere to the following:
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Typically 7219.32 (stainless steel flat-rolled products, not further worked than cold-rolled, with a width ≥ 600 mm).
- Export Controls: Verify if any dual-use or strategic metal regulations apply (e.g., U.S. EAR, EU Dual-Use Regulation).
- Customs Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin.
- Duty and Tariff Considerations: Check for trade agreements or sanctions that may affect tariffs (e.g., Section 232 steel tariffs in the U.S.).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
To maintain material integrity during transit:
- Use moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper) to prevent corrosion.
- Secure bundles on wooden pallets with steel strapping to avoid shifting.
- Label packages clearly with alloy type, heat number, dimensions, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Protect from Moisture”).
- Avoid contact with carbon steel during storage and transport to prevent cross-contamination and rust transfer.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Ensure adherence to environmental and occupational health standards:
- REACH (EU): Confirm that the material does not contain substances of very high concern (SVHC) above thresholds.
- RoHS (EU): Although primarily for electronics, applicable if used in electrical components.
- OSHA (U.S.): Follow safe handling practices when cutting or grinding; use appropriate PPE to avoid metal fume exposure.
- Waste Disposal: Recycle scrap in accordance with local environmental regulations; stainless steel is fully recyclable.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Prior to shipment or use, conduct the following quality checks:
- Spectrometric Analysis: Confirm chemical composition using OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry) or XRF.
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation must meet ASTM A240 requirements.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Perform visual, ultrasonic, or eddy current testing for surface and subsurface defects.
- Third-Party Inspection: Recommended for high-value or regulated applications (e.g., ASME, API).
Supplier Qualification and Audits
Select suppliers based on:
- Valid certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14001).
- Consistent production quality and traceability systems.
- Audit history (e.g., SABER, CE marking, TÜV).
- Ability to provide full compliance documentation upon request.
Regular supplier audits enhance supply chain reliability and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Compliance and efficient logistics for 304 stainless steel require strict adherence to material specifications, documentation standards, and international regulations. By ensuring proper traceability, packaging, and quality verification, businesses can mitigate risks, avoid customs delays, and maintain product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion: Sourcing 304 Stainless Steel Composition
Based on the analysis and evaluation of sourcing 304 stainless steel (SS), it is evident that this austenitic stainless steel remains one of the most reliable and widely used materials across various industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability. The standard composition of 304 SS—typically 18% chromium and 8% nickel (18/8)—provides a balanced combination of performance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for applications ranging from food processing and pharmaceuticals to construction and consumer goods.
When sourcing 304 stainless steel, it is crucial to ensure that the material complies with international standards such as ASTM A240, AISI 304, or EN 1.4301. Verification through mill test certificates (MTCs) and third-party material testing helps guarantee the correct chemical composition and mechanical properties. Additionally, factors such as supplier reliability, traceability, and consistent quality control are essential to avoid material substitution or substandard products.
While alternative grades (such as 304L for enhanced weldability or 316 for superior corrosion resistance) may be considered in specific environments, 304 SS continues to be the optimal choice for general-purpose applications. In summary, successful sourcing of 304 stainless steel hinges on due diligence in supplier selection, adherence to material specifications, and ongoing quality assurance—ensuring long-term performance and reliability in end-use applications.