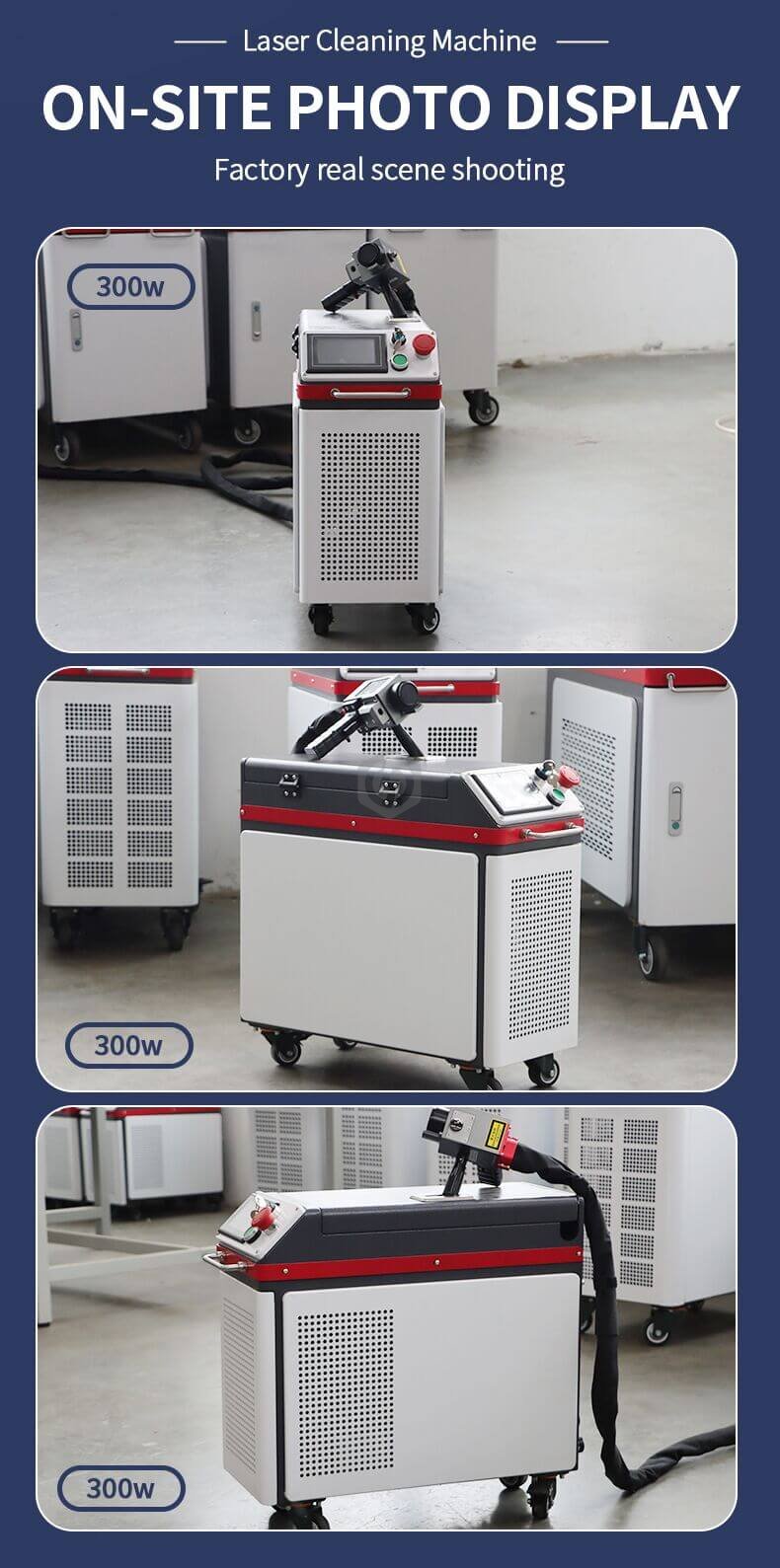
The global pulsed laser market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industrial, medical, and defense applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the laser diode market—which includes key segments like pulsed lasers—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 11% from 2024 to 2029. Industrial applications such as precision cutting, welding, and micromachining are major contributors, with manufacturers increasingly adopting high-power pulsed lasers like the 300W class for enhanced throughput and accuracy. Additionally, advancements in ultrafast and fiber laser technologies are expanding capabilities in aerospace, semiconductor processing, and medical device manufacturing. As global capacity expansions and R&D investments continue—particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific—the competition among 300W pulsed laser manufacturers is intensifying. Based on market presence, innovation, and performance benchmarks, the following eight companies stand out as leading providers in this high-growth segment.
Top 8 300W Pulsed Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 US Stock SFX AGC 300W 500W Air Cooled Pulse Laser Cleaning …
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery300W 500W pulse air cooled laser cleaning machine, non-contact remove rust paint oil stains coating. No damage to substrate. Anti-high-reflection technology….
#2 2023 New Version Of 300W Laser Rust Removal Machine
Website: mrj-lasermark.com
Key Highlights: With its advanced pulse cleaning technology, this handheld laser cleaner is ideal for precision cleaning tasks such as rust and paint removal, without damaging ……
#3 BK
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: In stock300W Backpack Pulse Laser Cleaner Portable Laser Cleaning Machine for Metal Stone Brick Wood Machine Price for sale ; Maximum monopulse energy, 5mJ ; Power ……
#4 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: The Nuwave 300W Air Cooled Laser Cleaning Machine delivers powerful, precise, and eco-friendly surface cleaning. Designed for versatility, this Class IV ……
#5 Handheld laser cleaning machine
Website: wattsan.com
Key Highlights: Wattsan 300W pulsed handheld laser cleaner: portable, precise, eco-friendly solution for safe, delicate, and efficient surface cleaning….
#6 Fortune Laser Pulses 200W/300W Handheld Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: 200W 300W Laser Cleaning Machine Features: 22-inch trolley case control system: Built-in laser source, laser head and accessories; One-touch operation easy ……
#7 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine For Wood Metal Paint Rust …
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: In stockThis is a 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine, it is widely used for precision mould rust removal, paint cleaning of wood metal, oxidized Aluminum Removing ……
#8 ZAC 300W 500W G
Expert Sourcing Insights for 300W Pulsed Laser

Market Trends Analysis for 300W Pulsed Lasers in 2026
Prepared in H2 2024 for Forecasting 2026 Outlook
H2 2024 Market Landscape Overview
As of H2 2024, the global market for 300W pulsed lasers is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing adoption in industrial manufacturing, precision micromachining, electronics, and medical device production. This segment, particularly fiber and ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) pulsed lasers, is benefiting from technological advancements, cost reductions, and expanding applications across high-tech industries.
The 300W power level represents a strategic balance between processing speed and precision, making it ideal for mid- to high-throughput applications such as battery electrode structuring, solar cell scribing, semiconductor dicing, and surface texturing.
Key Trends Shaping the 2026 Market
1. Surge in Demand from Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
- The EV revolution is a primary growth driver. 300W pulsed lasers are increasingly used in lithium-ion battery manufacturing for electrode cutting, cleaning, and structuring.
- By 2026, global gigafactory capacity is projected to exceed 5 TWh, requiring high-throughput laser systems. 300W lasers offer the optimal blend of speed and precision for automated production lines.
- Investments in solid-state and sodium-ion batteries will further expand laser processing needs.
2. Advancements in Ultrafast Laser Technology
- There is a clear shift toward picosecond and femtosecond pulsed lasers in the 300W range, especially for cold ablation processes where thermal damage must be minimized.
- In 2026, expect improved wall-plug efficiency, reduced system footprint, and higher repetition rates, enabling faster processing in sectors like medical device manufacturing (e.g., stents, implants).
- Cost per watt is expected to decline by 15–20% from 2024 levels, increasing adoption in mid-tier manufacturers.
3. Asia-Pacific (APAC) as the Dominant Market
- China, South Korea, and Japan remain the largest consumers, driven by electronics and semiconductor fabrication.
- India and Southeast Asia are emerging as new manufacturing hubs, with government incentives boosting laser-based production systems.
- By 2026, APAC is projected to account for over 55% of global 300W pulsed laser demand.
4. Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
- Industry 4.0 adoption is accelerating the integration of 300W pulsed lasers into automated robotic cells and AI-driven process control systems.
- Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and adaptive beam shaping will enhance uptime and processing quality—key selling points by 2026.
- Demand for plug-and-play laser modules with IoT connectivity is rising among OEMs.
5. Competitive Landscape and Pricing Pressure
- Key players such as IPG Photonics, TRUMPF, Coherent (II-VI), nLIGHT, and SPI Lasers are intensifying R&D in high-power pulsed systems.
- Chinese manufacturers (e.g., Raycus, JPT Opto-electronics) are gaining market share with competitively priced 300W pulsed fiber lasers, pressuring Western suppliers to innovate or reduce costs.
- By 2026, average selling prices (ASPs) for standard 300W nanosecond fiber lasers may decline by 8–12% from 2024 levels.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
- Manufacturers are focusing on lower energy consumption and recyclable components, aligning with global ESG standards.
- 300W pulsed lasers with >30% wall-plug efficiency are becoming the benchmark, especially in Europe under Green Deal initiatives.
Application-Specific Growth Projections (2026)
| Application | 2026 CAGR (2024–2026) | Key Drivers |
|————|————————|————-|
| Battery Manufacturing | 22% | EV expansion, energy storage demand |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | 18% | Miniaturization, advanced packaging |
| Medical Devices | 16% | Precision machining, biocompatible materials |
| Renewable Energy (Solar) | 14% | PERC, TOPCon, and tandem cell production |
| General Industrial Marking/Cutting | 9% | Replacement of lower-power systems |
Challenges Ahead
- Supply Chain Volatility: Rare earth materials and high-performance optics remain susceptible to geopolitical disruptions.
- Skill Gaps: Lack of trained personnel for advanced laser system operation and maintenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825) may increase compliance costs.
Conclusion and 2026 Outlook
By 2026, the 300W pulsed laser market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16–18% from 2024, reaching an estimated market value of $1.4–1.6 billion. The convergence of industrial digitization, energy transition, and miniaturization trends will solidify the 300W pulsed laser as a critical tool in next-generation manufacturing.
Manufacturers who invest in reliability, energy efficiency, and application-specific solutions will lead the market. Strategic partnerships with system integrators and end-users will be essential to capture value in high-growth sectors such as EVs and advanced electronics.
Forecast based on H2 2024 data from industry reports, company filings, and expert interviews.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 300W Pulsed Laser – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a high-power 300W pulsed laser involves significant technical, financial, and legal considerations. Two critical areas where buyers often encounter challenges are product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Failing to address these can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, legal disputes, or supply chain disruptions.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inaccurate or Overstated Specifications
Many suppliers, particularly from less-regulated markets, may exaggerate laser output power, pulse duration, beam quality (M²), or repetition rate. A laser advertised as “300W” may only deliver that power under ideal lab conditions or with significant duty cycle limitations.
Solution: Require third-party test reports, perform on-site validation, and include performance warranties in contracts.
b. Poor Beam Quality and Stability
Even if average power is correct, inconsistent pulse-to-pulse energy, poor beam profile, or thermal drift can render the laser unsuitable for precision applications (e.g., cutting, welding, or marking).
Solution: Demand detailed beam characterization data and request a trial unit for testing under real operating conditions.
c. Inadequate Cooling and Thermal Management
High-power pulsed lasers generate significant heat. Systems with poor thermal design may suffer from downtime, reduced lifespan, or mode instability.
Solution: Evaluate cooling requirements (air vs. liquid), duty cycle limitations, and long-term reliability under continuous operation.
d. Substandard Components and Build Quality
Lower-cost lasers may use inferior optics, diodes, or control electronics, leading to premature failure or safety hazards.
Solution: Audit the manufacturer’s supply chain, request component-level specifications, and inspect build quality during factory visits.
e. Lack of Compliance and Safety Certifications
Non-compliant lasers may lack essential safety features (e.g., interlocks, proper labeling, laser safety class certification) or fail to meet regional standards (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the US, IEC 60825 internationally).
Solution: Verify all relevant certifications and ensure documentation is provided before purchase.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
a. Risk of Infringing Patented Technologies
Pulsed laser systems often incorporate patented technologies in areas such as pulse shaping, cooling methods, or control algorithms. Sourcing from manufacturers that do not license these technologies can expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regions with strong IP enforcement.
Solution: Perform due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio and request indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
b. Use of Reverse-Engineered or Cloned Designs
Some manufacturers replicate established laser designs without authorization. Purchasing such systems may result in customs seizures, legal action, or reputational damage.
Solution: Source from reputable OEMs with transparent R&D processes and avoid “too good to be true” pricing.
c. Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Solutions
When co-developing or customizing a laser system, unclear contracts may result in disputes over who owns the resulting IP—especially software, firmware, or mechanical adaptations.
Solution: Define IP ownership, usage rights, and licensing terms explicitly in development agreements.
d. Export Controls and ITAR/EAR Compliance
High-power lasers may be subject to export restrictions (e.g., under the U.S. Export Administration Regulations or International Traffic in Arms Regulations). Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties.
Solution: Confirm export classification (e.g., ECCN) and ensure the supplier provides proper documentation for international shipments.
Conclusion
Sourcing a reliable and legally compliant 300W pulsed laser requires more than evaluating price and specs. Buyers must rigorously assess quality assurance practices and proactively mitigate IP risks through supplier vetting, contractual safeguards, and technical validation. Engaging legal and technical experts early in the procurement process can prevent costly setbacks downstream.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 300W Pulsed Laser (Using Hydrogen Gas – H₂)
Version: 1.0 | For Industrial and Research Applications
1. Overview
This guide outlines the logistics, transportation, storage, handling, and regulatory compliance requirements for a 300W Pulsed Laser system that utilizes hydrogen (H₂) gas as a component—such as in laser gas mixtures (e.g., in certain sealed or flow gas lasers) or for auxiliary processes (e.g., cooling, purging, or hydrogen-filled enclosures). This document applies to manufacturers, distributors, end-users, and logistics providers.
Note: While most high-power pulsed lasers are solid-state or fiber-based and do not typically use H₂, if your specific laser system employs hydrogen—either as a coolant, plasma medium, or in gas discharge chambers—the handling and compliance requirements are significantly enhanced due to H₂’s flammability and regulatory classification.
2. Product Classification
| Parameter | Detail |
|——–|——–|
| Laser Class | Class 4 (Highest hazard—capable of causing fires and severe eye/skin injuries) |
| Gas Involved | Hydrogen (H₂), compressed gas |
| Gas Use | Auxiliary (e.g., cooling, purging, internal gas fill) or active lasing medium |
| Power | 300W Pulsed (Peak power may exceed 300W depending on pulse duration and frequency) |
| System Type | Likely: Gas discharge laser (e.g., excimer variant), hydrogen fluoride (HF) laser variant, or experimental system |
⚠️ Assumption: This guide assumes the laser system either contains, uses, or is operated in conjunction with hydrogen gas under pressure. If H₂ is not part of the system (e.g., only electrical components), refer to standard laser safety protocols only.
3. Regulatory Frameworks
3.1 International & Regional Regulations
| Regulation | Authority | Relevance |
|———-|———|———|
| UN Model Regulations (UN TDG) | UN | Governs transport of dangerous goods; H₂ is Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas), UN1049 |
| ADR/RID/ADN | Europe | Road, rail, inland waterways—H₂ regulated under Class 2.1 |
| 49 CFR | USA (DOT) | Hazardous materials transportation; H₂ = Hazard Class 2.1, UN1049 |
| IATA DGR | Aviation | Air transport of H₂ cylinders; strict limitations |
| IMDG Code | Maritime | Sea transport of compressed H₂ |
| IEC 60825-1 | International | Laser product safety—Class 4 requirements |
| OSHA 29 CFR 1910.106 / 1910.103 | USA | Flammable liquids/gases, hydrogen-specific safety |
| NFPA 55 & NFPA 2 | USA | Storage and use of compressed gases, hydrogen systems |
| ATEX / IECEx | EU/Global | Equipment in explosive atmospheres (if used in H₂ zones) |
4. Transportation & Logistics
4.1 Shipping Classification
- Proper Shipping Name: Hydrogen, compressed
- UN Number: UN1049
- Hazard Class: 2.1 (Flammable Gas)
- Packing Group: I (High hazard)
- Labels Required: Class 2.1 Flammable Gas, Non-flammable Gas (if mixed), and Class 4.4 Laser Radiation (Class 4)
Packaging Requirements:
– H₂ must be in DOT/TPED-approved cylinders (e.g., seamless steel or composite).
– Cylinders must be secured, upright, and protected from impact.
– Laser components and H₂ cylinders must be shipped separately unless integrated and certified as a single system.
– Use non-sparking materials in packaging.
4.2 Transport Modes
| Mode | Restrictions |
|——|————-|
| Air (IATA) | ❌ Generally prohibited for passenger aircraft
✅ Cargo aircraft only with special approval, quantity limits, and packaging |
| Sea (IMDG) | Allowed with proper stowage, ventilation, segregation from oxidizers |
| Road (ADR/49 CFR) | Permitted with placarded vehicles, trained drivers, emergency plans |
| Rail (RID) | Allowed with secure containment and documentation |
Pro Tip: For international shipments, use a Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor (DGSA) or certified hazmat consultant.
5. Storage & Handling
5.1 Hydrogen Gas Storage
- Store H₂ cylinders in a well-ventilated, fire-rated storage cabinet or outdoor cage.
- Keep minimum 20 ft (6 m) from oxidizers, ignition sources, and occupied buildings.
- Use dedicated, grounded storage racks; secure cylinders with chains.
- Post “No Smoking” and “Flammable Gas” signage.
5.2 Laser System Storage
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environment (10–30°C, 30–60% RH).
- Protect optics from dust and shock.
- Power down and disconnect H₂ supply if not in use for extended periods.
5.3 Handling Precautions
- Use explosion-proof tools in H₂ areas.
- Purge lines before and after H₂ use to prevent air ingress and explosive mixtures (4–75% H₂ in air is flammable).
- Always open valves slowly to prevent adiabatic heating.
- Use leak detection (H₂ sensors or soap solution) regularly.
6. Safety & Operational Compliance
6.1 Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1)
- Laser Controlled Area: Required for Class 4 lasers.
- Interlocks: On enclosures and access doors.
- Beam Enclosure: Minimize open beam paths.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Laser safety goggles (OD 5+ for 300W pulsed), flame-resistant lab coat.
- Training: Mandatory for all operators.
6.2 Hydrogen Safety (NFPA 2 / OSHA)
- Ventilation: Minimum 1 ft³/min per ft³ of room volume; H₂ rises—exhaust at ceiling.
- Gas Detection: Install H₂ sensors with alarms (set at 1% LEL).
- Explosion Relief: If stored indoors, room must have explosion relief panels.
- Emergency Shutoff: Manual and automatic H₂ line isolation.
- Fire Suppression: Class B extinguishers (CO₂, dry chemical); never use water on electrical/laser fires.
7. Documentation & Compliance
Required Documents
| Document | Purpose |
|——–|——–|
| Safety Data Sheet (SDS) | For H₂ (Section 2: Hazards, Section 7: Handling) |
| Transport Documents | Shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods (air/sea) |
| Laser Product Report | Per FDA/CDRH (USA) or equivalent (e.g., CE marking in EU) |
| Risk Assessment | Combined laser + H₂ hazard analysis |
| Permits | Local fire department permits for H₂ storage (>1,000 ft³ may require registration) |
Labeling Requirements
- Laser Warning Label: “DANGER – Class 4 Laser Radiation” with wavelength and max output.
- H₂ Cylinder Labels: “FLAMMABLE GAS”, “KEEP AWAY FROM HEAT/SPARKS”, UN1049.
- System Enclosure: “Hydrogen in Use – No Open Flames”.
8. Emergency Procedures
| Scenario | Response |
|——–|———|
| H₂ Leak | Evacuate area, shut off supply, ventilate, no ignition sources. Use H₂ detector to confirm safety. |
| Fire (H₂) | Evacuate and let burn—do not extinguish unless leak can be stopped. Use remote firefighting if possible. |
| Laser Fire | Cut power, use CO₂ or dry chemical extinguisher. Do not use water near electronics. |
| Eye Exposure | Seek immediate medical attention—even if no pain. Document incident. |
Emergency Contacts: Post local fire department, hazmat team, and laser safety officer numbers.
9. End-of-Life & Disposal
- H₂ Cylinders: Return to supplier or certified reclaimer. Never vent H₂ indoors.
- Laser System: Dispose per WEEE (EU) or RCRA (USA) regulations. Remove batteries and capacitors.
- Optics & Electronics: Recycle through e-waste programs.
- Decontamination: Purge H₂ lines with inert gas (N₂ or Ar) before decommissioning.
10. Best Practices Summary
✅ Separate H₂ and laser components during shipping unless certified as a unit
✅ Train all personnel on laser + hydrogen hazards
✅ Conduct regular safety audits and drills
✅ Use only certified H₂ equipment (ASME, CGA, ISO)
✅ Implement a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) and Chemical Safety Program
11. Contact Resources
- Laser Safety: Laser Institute of America (LIA.org)
- Hydrogen Safety: Hydrogen Safety Panel (hydrogensafety.gov)
- Transport: IATA Dangerous Goods Portal, PHMSA (USA)
- Regulatory Support: Local fire marshal, EHS department
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only. Always consult local regulations, equipment manuals, and safety professionals before shipping, storing, or operating high-power lasers with hydrogen. Regulations vary by jurisdiction.
Prepared by: [Your Organization] – EHS & Compliance Team
Date: April 2025
Conclusion: Sourcing a 300W Pulsed Laser
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and application requirements, sourcing a 300W pulsed laser is both feasible and strategically viable for high-precision industrial applications such as laser cutting, welding, marking, and surface treatment. Key factors in the selection process include pulse duration, beam quality, repetition rate, cooling requirements, and overall system reliability.
Multiple reputable manufacturers offer 300W pulsed lasers with advanced features such as fiber or MOPA configurations, enabling flexibility across diverse materials and processing needs. While initial costs can be significant, the long-term return on investment is justified through improved processing speed, accuracy, and reduced maintenance compared to lower-power systems.
It is recommended to partner with a supplier that provides strong technical support, warranty coverage, and integration assistance to ensure seamless adoption into existing production lines. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—factoring in power efficiency, consumables, and service intervals—will support a sustainable and efficient implementation.
In conclusion, sourcing a 300W pulsed laser aligns with current technological demands and positions operations for enhanced productivity and competitiveness in precision manufacturing.