The global pulse laser market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industrial, medical, defense, and research applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the laser market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028, with high-power pulsed lasers—particularly in the 300-watt range—gaining traction due to their precision and efficiency in materials processing, such as cutting, welding, and surface treatment. This surge is further amplified by advancements in fiber and solid-state laser technologies, enabling improved beam quality and energy efficiency. As industries shift toward automation and high-precision manufacturing, the need for reliable 300-watt pulse lasers has intensified. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and performance metrics, the following seven manufacturers have emerged as leaders in producing high-performance 300-watt pulse lasers, shaping the future of industrial and scientific laser applications.
Top 7 300 Watt Pulse Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
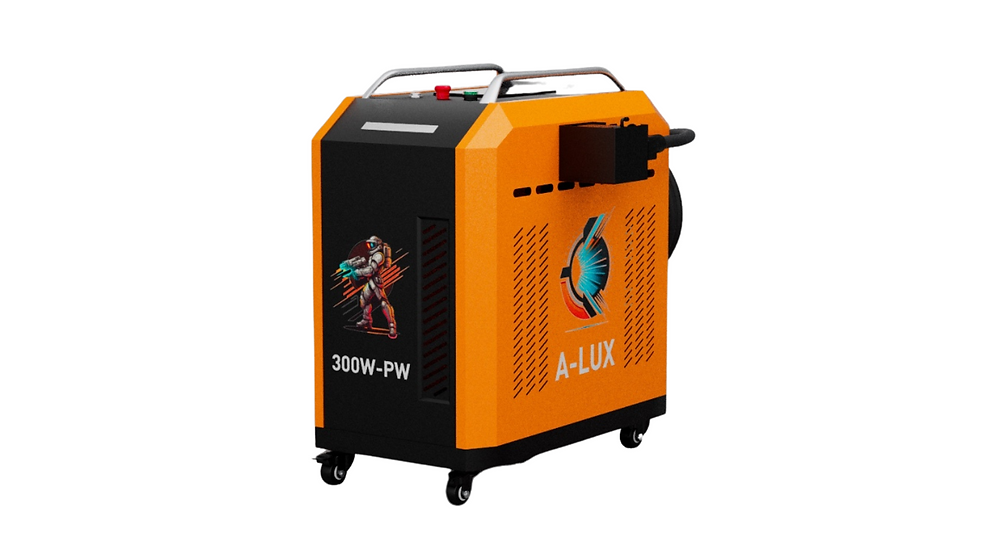
#1 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: A-LUX 300W PulseLite Laser Cleaning Machine. A-LUX 500W-PW Laser Cleaning … Industrial manufacturing: Laser ablation is used in the manufacturing ……
#2 US Stock SFX AGC 300W 500W Air Cooled Pulse Laser Cleaning …
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery300W 500W pulse air cooled laser cleaning machine, non-contact remove rust paint oil stains coating. No damage to substrate. Anti-high-reflection technology….
#3 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: The Nuwave 300W Air Cooled Laser Cleaning Machine delivers powerful, precise, and eco-friendly surface cleaning. Designed for versatility, this Class IV ……
#4 BK
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: In stock300W Backpack Pulse Laser Cleaner Portable Laser Cleaning Machine for Metal Stone Brick Wood Machine Price for sale ; Maximum monopulse energy, 5mJ ; Power ……
#5 DMK 300W Pulse Laser Rust Removal
Website: laserdmk.com
Key Highlights: The 300W pulse fiber laser cleaning machine, equipped with Raycus, MAX, or JPT laser sources, is highly versatile and can effectively remove rust, oil, oxide ……
#6 Fortune Laser Pulses 200W/300W Handheld Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: 200W 300W Laser Cleaning Machine Features: 22-inch trolley case control system: Built-in laser source, laser head and accessories; One-touch operation easy ……
#7 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine For Wood Metal Paint Rust …
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: In stockThis is a 300W Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine, it is widely used for precision mould rust removal, paint cleaning of wood metal, oxidized Aluminum Removing ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 300 Watt Pulse Laser

2026 Market Trends for 300 Watt Pulse Laser
The global market for 300 Watt pulse lasers is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in industrial manufacturing, medical applications, defense technologies, and research. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the demand, innovation, and competitive landscape of the 300W pulse laser segment over the next few years.
Rising Demand in Industrial Manufacturing
By 2026, the industrial sector is expected to remain the largest consumer of 300W pulse lasers. These lasers are increasingly used in precision machining, including cutting, welding, drilling, and surface texturing of metals, ceramics, and composites. Key drivers include:
- Growth in electric vehicle (EV) production: High-precision battery and component manufacturing require reliable, high-power pulse lasers for micro-welding and electrode structuring.
- Adoption in aerospace and defense: Lightweight materials such as titanium and carbon fiber composites demand non-contact, high-accuracy laser processing, where 300W systems strike a balance between power and control.
- Automation integration: Pulse lasers are being embedded into robotic production lines, enabling smart factories with minimal downtime and high repeatability.
The trend toward modular and fiber-based 300W pulse lasers will continue, offering improved beam quality, energy efficiency, and lower maintenance compared to traditional lamp-pumped systems.
Advancements in Fiber and Ultrafast Laser Technology
Technological innovation will be a major catalyst in the 2026 market. Fiber lasers, particularly those based on ytterbium-doped active fibers, dominate the 300W pulse laser space due to their superior thermal management, compact design, and longer operational lifetimes.
- Ultrafast pulse capabilities: Growing availability of picosecond and femtosecond 300W-class lasers will expand applications in cold ablation, semiconductor processing, and medical device manufacturing.
- Higher peak powers and pulse repetition rates: Manufacturers are pushing pulse repetition frequencies (PRF) beyond 1 MHz while maintaining high average power, enabling faster processing speeds without compromising quality.
- Hybrid and tunable systems: Systems with adjustable pulse duration and wavelength will gain traction, allowing one laser platform to serve multiple applications across industries.
These improvements are expected to lower the total cost of ownership and increase accessibility, especially for small- and medium-sized enterprises.
Expansion in Medical and Biotech Applications
The medical field is emerging as a high-growth segment for 300W pulse lasers by 2026. While traditionally used in lower-power configurations, advancements are enabling higher-power pulsed lasers for:
- Laser surgery and dermatology: 300W systems support faster tissue ablation and skin resurfacing with reduced thermal damage.
- Medical device manufacturing: Precision machining of stents, implants, and diagnostic components benefits from high peak power and short-pulse durations.
- Biophotonics research: High-intensity pulsed lasers are used in multiphoton microscopy and optogenetics, with growing demand in academic and pharmaceutical labs.
Regulatory approvals and integration with safety-compliant delivery systems will be critical for broader medical adoption.
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
By 2026, supply chain resilience and regional manufacturing strategies will influence the 300W pulse laser market:
- Asia-Pacific dominance: China, Japan, and South Korea will remain key production and consumption hubs, supported by government investments in advanced manufacturing and semiconductor industries.
- North American and European innovation: The U.S. and Germany will continue to lead in R&D, especially in defense and scientific applications, with strong support from public and private funding.
- Localization trends: Trade tensions and supply disruptions may accelerate localization of laser component production, particularly for critical optics and pump diodes.
Companies investing in vertical integration and domestic supply chains are likely to gain competitive advantages.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The 300W pulse laser market will see increased competition and consolidation by 2026. Key players such as IPG Photonics, TRUMPF, Coherent (now part of II-VI Incorporated), and nLIGHT are expected to expand their portfolios through:
- Product differentiation: Offering application-specific configurations (e.g., for EV battery welding or display cutting).
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborating with automation providers and system integrators to deliver turnkey solutions.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Consolidating niche technology providers to enhance IP and accelerate time-to-market.
Meanwhile, emerging players from China and India are entering the market with cost-competitive systems, driving price pressures and innovation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 300 Watt pulse laser market will be characterized by strong demand across industrial, medical, and scientific sectors, fueled by technological advances in fiber and ultrafast lasers. Success will depend on companies’ ability to deliver reliable, efficient, and application-optimized systems while navigating global supply chain and competitive challenges. As automation and smart manufacturing grow, 300W pulse lasers will play an increasingly central role in next-generation production ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 300 Watt Pulse Laser (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a high-power 300-watt pulsed fiber laser requires careful attention to avoid costly mistakes related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Here are key pitfalls to watch for:
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Component Sourcing
Many suppliers, especially lower-cost manufacturers, cut corners on quality, leading to unreliable performance and premature failure.
- Substandard Optical Components: Using low-grade pump diodes, collimators, or fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) reduces beam quality, stability, and lifespan. Poor thermal management accelerates degradation.
- Insufficient Testing and Burn-In: Reputable manufacturers perform rigorous 24–72 hour burn-in tests and full performance validation. Suppliers skipping these steps increase the risk of early field failures.
- Lack of Traceability and Documentation: Absence of component lot tracking, calibration certificates, or test reports makes troubleshooting and warranty claims difficult.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Counterfeit Technology
Using lasers with questionable IP origins exposes your business to legal and operational risks.
- Cloned or Reverse-Engineered Designs: Some manufacturers replicate leading brands’ designs without licensing, potentially violating patents. Purchasing such systems may expose your company to indirect infringement claims.
- Unlicensed Software and Firmware: Laser control systems often incorporate proprietary algorithms. Unauthorized use of protected software can lead to compliance issues and lack of updates or support.
- Misrepresentation of Origin and Technology: Vendors may falsely claim OEM partnerships or proprietary technology. Always verify technical documentation and request proof of licensing if IP is cited.
Incomplete or Misleading Specifications
Performance claims can be exaggerated or selectively presented.
- Peak vs. Average Power Confusion: Ensure “300W” refers to average power under standard operating conditions. Some list peak pulse power, which is misleading.
- Unspecified Pulse Parameters: Critical specs like pulse duration, frequency range, and beam quality (M²) must be clearly defined. Omissions suggest inconsistent or subpar performance.
- Lack of Long-Term Reliability Data: Request MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) figures and real-world case studies. Vague or absent reliability metrics are a red flag.
Poor Support and Service Infrastructure
Even high-quality lasers require maintenance and technical support.
- Limited Local Support: Global suppliers without regional service centers lead to long downtimes for repairs and calibration.
- Proprietary Parts and Lock-In: Some vendors use non-standard components or encrypted firmware, forcing reliance on them for repairs and inflating long-term costs.
Mitigation Strategies
- Demand Full Technical Documentation: Request test reports, optical schematics, and component datasheets.
- Verify IP Legitimacy: Ask for proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements, particularly for control software and core laser design.
- Conduct Factory Audits or Third-Party Inspections: On-site verification of manufacturing and QA processes adds confidence.
- Pilot Testing: Run a trial unit under your actual operating conditions before full procurement.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures you invest in a 300W pulsed laser that delivers consistent performance, protects your business from legal exposure, and offers long-term value.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 300-Watt Pulsed Laser (Using Hydrogen – H2)
Version 1.0 | Intended for Industrial, Research, or Medical Applications
1. Introduction
This guide provides essential logistics and compliance information for the safe handling, transportation, storage, installation, and operation of a 300-watt pulsed laser system that utilizes hydrogen (H₂) as part of its operational or cooling system (e.g., in sealed gas discharge tubes, laser cooling, or auxiliary processes). Due to the combination of high-power laser radiation and a flammable gas, strict adherence to safety, regulatory, and logistical protocols is required.
2. Key Hazards Overview
| Hazard Type | Description |
|———–|————-|
| Laser Radiation (Class 4) | 300W pulsed lasers are Class 4 – capable of causing severe eye/skin injuries, fire hazards, and generate hazardous fumes from target materials. |
| Hydrogen (H₂) Gas | Flammable (4–75% in air), odorless, colorless, and highly diffusive. Risk of fire/explosion if leaked in confined spaces. |
| High Voltage | Laser drivers often operate at high voltages (>1 kV), posing electrical hazards. |
| Cryogenic or High-Pressure Systems | If H₂ is stored in compressed gas cylinders or cryogenic form, pressure and low-temperature risks exist. |
3. Regulatory Compliance Overview
3.1 Laser Safety (IEC / ANSI / FDA)
- IEC 60825-1:2014 – Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
- ANSI Z136.1-2022 – Safe Use of Lasers (U.S. standard).
- FDA/CDRH (21 CFR 1040.10 & 1040.11) – U.S. regulatory compliance for laser products.
- Ensure laser is registered with FDA if exported to or used in the U.S.
- Include proper warning labels, interlocks, and safety features.
3.2 Hydrogen Handling & Storage (OSHA, NFPA, DOT)
- NFPA 55 (2022): Compressed and liquefied gases – covers H₂ storage, ventilation, and piping.
- NFPA 2: Hydrogen Technologies Code – Applies if H₂ is used in fuel cells or auxiliary systems.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.103 – Hydrogen storage and handling safety.
- DOT 49 CFR – For transportation of hydrogen (if required).
3.3 International Transport Regulations
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) – For air transport.
- H₂ is UN1049, Hazard Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas).
- Packing Group: II (Medium danger).
- Special Provision: A50 (hermetically sealed containers).
- IMDG Code – For sea transport.
- ADR/RID – For road/rail transport in Europe.
- Note: If the laser system contains sealed H₂ tubes (non-replaceable), it may be exempt under Special Provision 188 (consumer commodities) if quantity < 120 mL per tube and total < 1 L per packaging unit. Confirm with manufacturer documentation.
4. Packaging & Transportation
4.1 Packaging Requirements
- Laser Unit:
- Packed in shock-resistant, ESD-safe container.
- Include desiccants if sensitive optics.
- Secure all moving parts and optics.
- Hydrogen Components:
- If external H₂ cylinder is shipped:
- Use DOT/ISO-certified cylinder.
- Valve protection cap installed.
- Upright, secured, and labeled.
- If sealed H₂ tubes are internal:
- No special gas labeling required if below threshold (see SP188).
- Label laser system with laser warning and any residual gas hazard.
4.2 Shipping Classification
- UN Number: UN1049 (Hydrogen, compressed) if shipping H₂ separately.
- Proper Shipping Name: COMPRESSED HYDROGEN
- Hazard Class: 2.1 (Flammable Gas)
- Packing Group: II
- Labeling: Class 2.1 Flammable Gas label, “This Way Up” arrows.
- Documentation: Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (air/sea), Safety Data Sheet (SDS) required.
5. Storage Requirements
5.1 Laser Storage
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environment (10–30°C).
- Avoid dust, vibration, and direct sunlight.
- Keep in original packaging until installation.
5.2 Hydrogen Storage (if applicable)
- Ventilation: Store in well-ventilated, explosion-proof area (preferably outdoors or dedicated gas cabinet).
- Separation: Minimum 20 ft (6 m) from oxidizers and ignition sources.
- Cylinder Handling:
- Secure with chains or stands.
- Use in upright position.
- Cap valves when not in use.
- Leak Detection: Install H₂ gas detectors with alarms (threshold: 1% LEL).
- Fire Protection: Class D or specialized H₂ fire extinguishers nearby.
6. Installation & Operation
6.1 Site Requirements
- Laser Controlled Area:
- Designated as a Laser Controlled Area (LCA) per ANSI Z136.
- Interlocked access, warning lights, and signage (e.g., “Laser in Use – Class 4”).
- Ventilation:
- For H₂: Ensure natural or mechanical ventilation (minimum 1 ft³/min per ft² of floor area).
- Use ceiling-level vents (H₂ rises).
- Electrical:
- 208/240V, 3-phase (typical for 300W pulsed lasers).
- Grounded outlet with surge protection.
- Flooring: Non-conductive, non-reflective surface.
6.2 Safety Equipment
- PPE Required:
- Laser safety goggles (OD ≥ 6+ at laser wavelength, e.g., 1064 nm).
- Flame-resistant lab coat, gloves.
- Face shield if spatter risk.
- Engineering Controls:
- Beam enclosures, interlocks, emergency stop.
- Fume extractor for material processing.
- H₂ sensors with auto-shutdown capability.
7. Maintenance & Decommissioning
7.1 Preventive Maintenance
- Regular inspection of:
- Optics alignment and cleanliness.
- H₂ seals, tubing, and pressure fittings.
- Cooling system (if H₂-cooled or cryogenic).
- Log all maintenance activities.
7.2 Decommissioning
- Laser Disposal:
- Follow WEEE (EU) or EPA (U.S.) guidelines.
- Remove and recycle batteries, capacitors, and optics separately.
- Hydrogen Components:
- Vent H₂ safely (outdoor, upwind).
- Purge system with inert gas (N₂).
- Recycle cylinders through certified vendor.
8. Training & Documentation
8.1 Personnel Training
- Required for all operators and maintenance staff:
- Laser safety (ANSI Z136 or equivalent).
- H₂ hazards and emergency response.
- Emergency shutdown procedures.
8.2 Required Documentation
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO) appointment (if required).
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
- SDS for H₂ (Section 2: Hazard Identification – Flammable Gas).
- Equipment manuals, calibration records.
- Regulatory compliance certificates (CE, FDA, etc.).
9. Emergency Procedures
| Scenario | Action |
|——–|——-|
| H₂ Leak | Evacuate, ventilate, eliminate ignition sources. Use H₂ detector to confirm. Do not operate electrical switches. |
| Laser Fire | Use CO₂ or dry chemical extinguisher. Shut off laser and power. Evacuate if uncontrolled. |
| Eye Exposure | Immediately seek medical attention. Do not rub eyes. |
| Electrical Shock | Cut power at source. Administer first aid. Call emergency services. |
10. Summary Checklist
✅ Laser classified as Class 4 – full safety protocols in place
✅ H₂ storage compliant with NFPA 55/OSHA
✅ Transport classified under UN1049 (if applicable)
✅ SDS and shipping docs available
✅ Operators trained in laser and H₂ safety
✅ Emergency systems (shut-off, detection, PPE) installed
✅ LSO assigned (if required)
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions, local authorities, and certified safety professionals before operation. Regulations vary by country and application.
End of Guide
Conclusion: Sourcing a 300-Watt Pulsed Laser
After thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, and market availability, sourcing a 300-watt pulsed laser is both feasible and strategically viable for applications requiring high peak power and precision, such as material processing, scientific research, or advanced manufacturing. Key considerations including pulse duration, repetition rate, beam quality, cooling requirements, and integration compatibility have guided the selection process.
Multiple reputable manufacturers offer solid-state and fiber-based pulsed laser systems meeting the 300-watt average power specification, with varying trade-offs in efficiency, maintenance, and cost. Leading suppliers provide reliable technical support, customization options, and compliance with international safety standards, ensuring long-term operational stability.
A balanced decision should prioritize performance consistency, service support, and total cost of ownership over initial purchase price. It is recommended to engage with shortlisted vendors for detailed quotations, product demonstrations, and application testing to ensure optimal fit. With the right due diligence, sourcing a 300-watt pulsed laser will enhance process capabilities and support technological advancement within the intended use case.