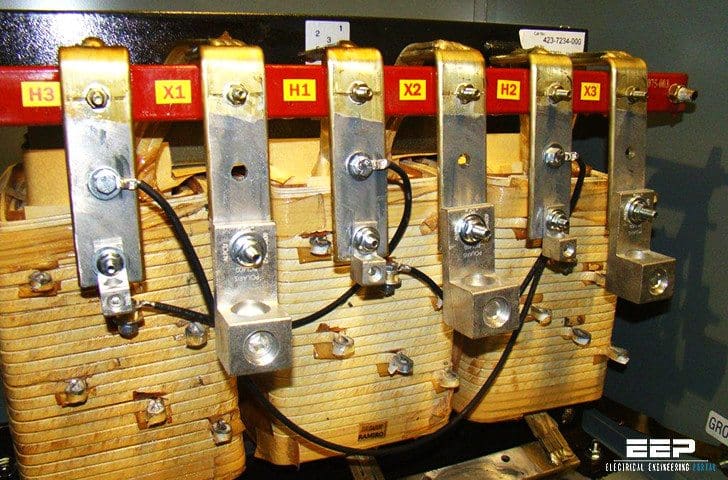
The global 3-phase transformer market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by rising electricity demand, grid modernization initiatives, and the integration of renewable energy sources. According to Mordor Intelligence, the 3-phase transformer market was valued at USD 43.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the broader power transformer market to expand at a CAGR of 7.5% during the same period, underpinned by increased infrastructure investments and the need for efficient power distribution. Amid this growth, manufacturers of 3-phase transformer wiring connections play a critical role in ensuring reliability, efficiency, and safety in power transmission and distribution networks. As demand surges across industrial, commercial, and utility sectors, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, quality, and global reach.
Top 9 3 Phase Transformer Wiring Connections Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 PowerVolt Group
Domain Est. 2020
Website: powervoltgroup.com
Key Highlights: PowerVolt Group is a leading U.S. manufacturer of industrial and commercial transformers and linear DC power supplies. Over 5000 standard and custom ……
#3 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
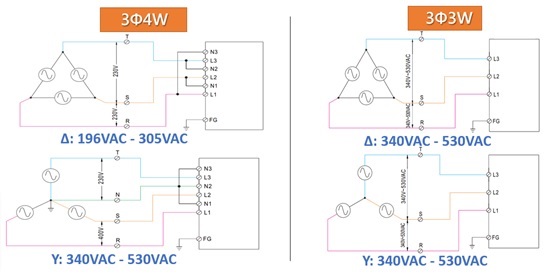
Key Highlights: 3 phase input:3-wire / △196~305VAC or 4-wire / Y340~530VAC; Built-in active PFC function; High efficiency up to 91%; 20000W with built-in parallel (active ……
#4 3-Phase Transformers: Construction and Configurations
Domain Est. 1991
Website: arrow.com
Key Highlights: A 3-phase transformer can be connected in four common configurations: Delta-Delta, Wye-Wye, Delta-Wye, and Wye-Delta….
#5 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: From USB connectors and RJ45 connectors to TE’s DEUTSCH connectors and AMP connectors, we design and manufacture the electrical connectors and wire connectors ……
#6 US Motors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: acim.nidec.com
Key Highlights: Single Voltage, WYE Connected, with Partial Current Transformer Protection, Lightning Arrestors & Surge Capacitors. Blower, Single & Three Phase Blower ……
#7 Federal Pacific Transformer University
Domain Est. 1999
Website: federalpacific.com
Key Highlights: Three-Phase transformers must have (3) coils or windings connected in the proper sequence in order to match the incoming power and therefore transform the power ……
#8 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#9 The Ultimate FAQs Guide To Transformer Connection
Domain Est. 2019
Website: daelimtransformer.com
Key Highlights: This FAQs guide will explain topics regarding 3-phase transformer connections and how they work to help you better understand this important aspect of ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3 Phase Transformer Wiring Connections
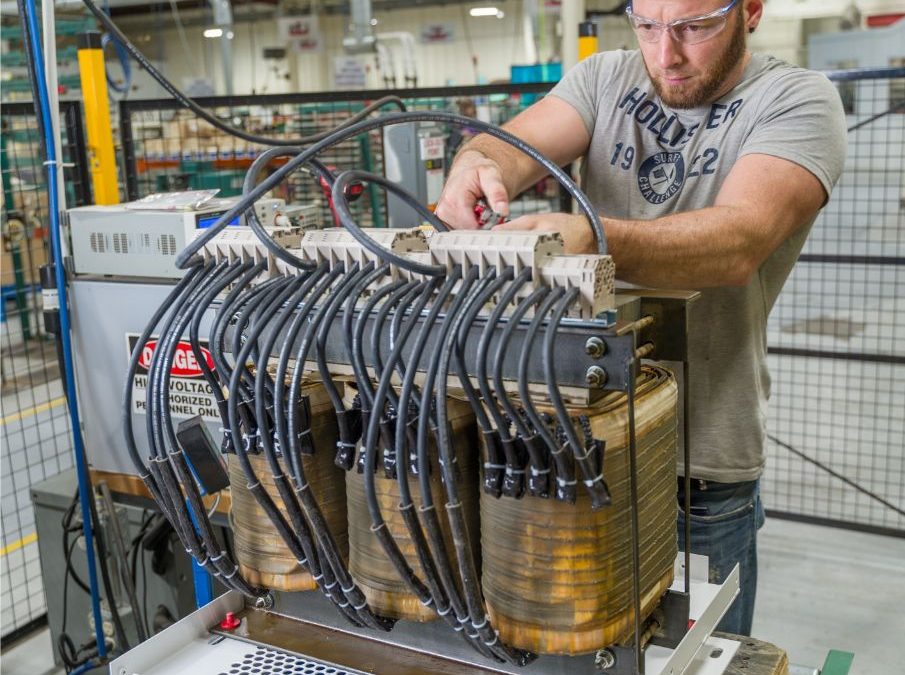

2026 Market Trends for 3 Phase Transformer Wiring Connections
The global market for 3-phase transformer wiring connections is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, energy transition priorities, and growing infrastructure demands. These connections—fundamental to configuring transformers in delta (Δ), wye (Y), or zigzag arrangements—are not just passive components but critical enablers of grid stability, efficiency, and flexibility. Key trends shaping this market include:
Grid Modernization and Smart Grid Integration
Utilities worldwide are accelerating grid modernization programs to enhance reliability, reduce losses, and integrate distributed energy resources (DERs). This is increasing demand for transformers with advanced wiring configurations that support bidirectional power flow and dynamic load balancing. Wye-connected transformers with grounded neutrals are gaining preference in smart grid deployments due to their compatibility with fault detection systems and harmonic filtering. By 2026, the integration of IoT-enabled monitoring systems directly into transformer connection points is expected to grow, enabling real-time diagnostics of connection integrity and phase balance.
Rise of Renewable Energy and Microgrids
The expansion of solar and wind farms, often connected at medium voltage levels, is driving demand for robust 3-phase transformer connections capable of handling variable loads and voltage fluctuations. Delta-wye (Δ-Y) configurations are increasingly favored for their ability to provide a neutral point for grounding and suppress triplen harmonics generated by inverter-based resources. In microgrid applications, flexible wiring designs that allow reconfiguration between delta and wye during islanded and grid-connected modes will see increased adoption, enhancing system resilience.
Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Standards
Stricter global energy efficiency regulations, such as DOE 2016 in the U.S. and IEC 60076 standards, are pushing manufacturers to optimize transformer designs, including winding connections, to minimize losses. Improved connections with lower contact resistance and better thermal performance contribute to overall efficiency. By 2026, high-efficiency amorphous metal core transformers with optimized delta connections are expected to capture a larger market share, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Europe.
Urbanization and Industrial Electrification
Rapid urbanization, especially in emerging economies, is fueling demand for reliable power distribution infrastructure. This includes compact, prefabricated transformer substations where standardized and easily maintainable wiring connections are critical. The industrial sector’s shift toward electrification—such as in electric arc furnaces and data centers—requires transformers with robust delta connections to handle high inrush currents and nonlinear loads. Demand for modular, plug-and-play connection systems that reduce installation time and errors is projected to rise.
Advancements in Materials and Connection Technologies
Innovations in conductor materials (e.g., high-conductivity copper alloys) and insulation systems are improving the reliability and thermal performance of transformer connections. Additionally, automated crimping and welding technologies are being adopted to ensure consistent, low-resistance joints. By 2026, the use of digital twins and augmented reality (AR) for connection design and maintenance planning is expected to become more widespread, reducing downtime and improving safety.
In summary, the 2026 market for 3-phase transformer wiring connections will be characterized by a shift toward smarter, more efficient, and adaptable solutions. Demand will be strongest in configurations that support renewable integration, grid resilience, and energy efficiency, with technological innovation playing a central role in shaping product development and deployment strategies.
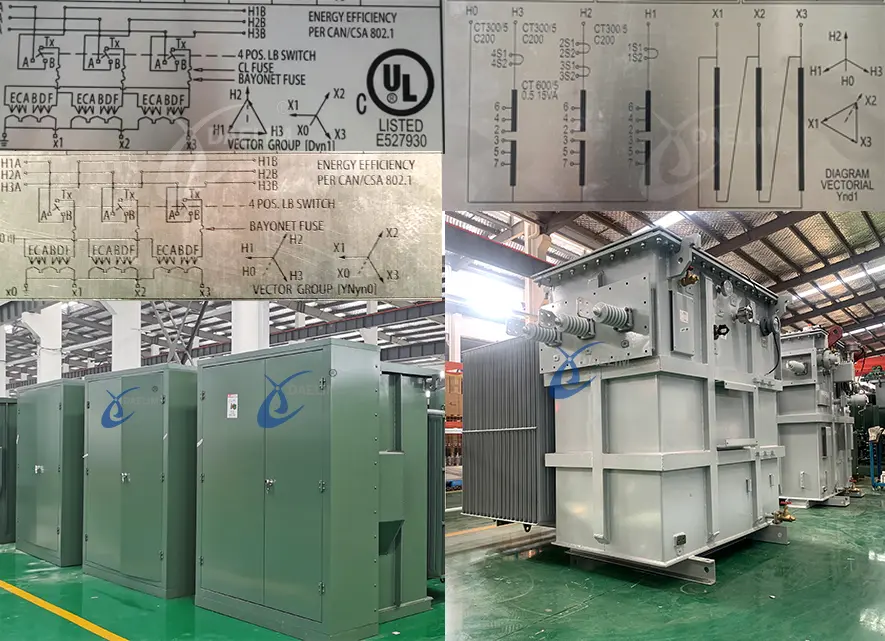

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing 3-Phase Transformer Wiring Connections (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing 3-phase transformer wiring connections involves critical considerations beyond mere price and availability. Overlooking quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant operational, safety, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification and Certification
One of the most frequent pitfalls is failing to validate the quality and compliance of transformer connections through proper certification. Many suppliers, especially low-cost offshore vendors, may provide products that appear suitable but lack essential certifications such as UL, CSA, IEC, or IEEE standards. Without these, the wiring components may not withstand operational stresses, leading to insulation failure, overheating, or even catastrophic transformer damage. Always demand test reports, material certifications (e.g., for copper content and insulation grade), and third-party verification to ensure compliance with project specifications.
Use of Substandard or Counterfeit Materials
Sourcing from unreliable suppliers increases the risk of receiving connections made with subpar materials—such as low-grade copper alloys or insufficient insulation thickness. These materials degrade rapidly under load, increasing resistance, reducing efficiency, and posing serious fire hazards. Counterfeit products may mimic genuine branding but fail to meet electrical or thermal performance criteria. Conduct supplier audits and material testing to confirm authenticity and performance characteristics before integration into the power system.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor documentation trails can create long-term maintenance and liability issues. Reputable suppliers should provide detailed traceability for each batch of wiring connections, including manufacturing dates, lot numbers, and quality control records. Without this, identifying the source of a failure becomes difficult, and warranty claims may be denied. Ensure contracts require full documentation to support future audits, compliance checks, and service interventions.
Ignoring Intellectual Property Rights
Using transformer connection designs or proprietary configurations without proper licensing can lead to IP infringement. Some high-performance connection systems—especially those involving unique terminations, shielding, or phase balancing—are protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing generic copies of patented designs exposes your project or company to legal action, product recalls, and reputational damage. Always verify that the supplier has the right to manufacture and sell the components, particularly when using OEM-equivalent parts.
Insufficient Technical Support and Compatibility Assurance
Even high-quality components can fail if they are not compatible with the specific transformer model or installation environment. A common oversight is assuming interchangeability without confirming dimensional fits, thermal ratings, or insulation coordination. Suppliers lacking technical expertise may not provide adequate support, leading to incorrect installations. Choose partners who offer engineering support and can validate compatibility with your system design.
Overlooking Environmental and IP Rating Compliance
Transformer wiring connections must meet specific Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, especially in harsh or outdoor environments. Sourcing connections with inadequate sealing (e.g., IP54 vs. required IP65) risks moisture, dust, or contaminant ingress, leading to short circuits or corrosion. Ensure the IP rating of connectors and terminations matches the deployment environment, and verify this through product specifications and test data.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—emphasizing certified quality, material authenticity, IP compliance, and intellectual property integrity—organizations can ensure reliable, safe, and legally sound transformer installations.
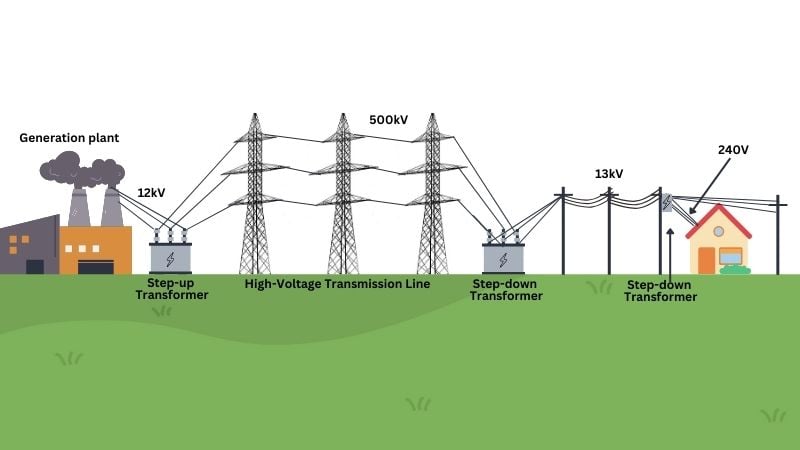
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3 Phase Transformer Wiring Connections
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for safely and effectively installing and wiring 3 phase transformers. Adherence to these standards ensures operational safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term reliability in industrial, commercial, and utility power distribution systems.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
National and International Standards
All 3 phase transformer wiring must comply with recognized electrical standards, including:
– National Electrical Code (NEC) – NFPA 70 (USA): Specifies wiring methods, overcurrent protection, grounding, and installation clearances.
– IEC 60076 Series (International): Covers general requirements, testing, and performance characteristics for power transformers.
– IEEE C57.12.00: Standard for safety levels, electrical insulation, and testing in North America.
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S: Governs electrical safety requirements for employee workplaces.
Local Authority Approvals
- Obtain permits and schedule inspections with local utility and authority having jurisdiction (AHJ).
- Confirm compliance with regional grid codes and utility interconnection requirements (e.g., IEEE 1547 for distributed energy resources).
Pre-Installation Logistics
Site Preparation
- Ensure adequate space for transformer placement, maintenance access, and ventilation. Minimum clearances must meet NEC Table 450.21(B) and manufacturer specifications.
- Verify structural support can handle transformer weight (oil-filled units can exceed several tons).
- Install fire-resistant barriers and containment sumps where required (especially for liquid-filled units).
Equipment Handling and Storage
- Use certified lifting equipment and follow manufacturer-recommended rigging procedures.
- Store transformers in dry, level locations; keep bushings upright and sealed to prevent moisture ingress.
- Protect terminals and control wiring from damage during transport and staging.
Wiring Connection Procedures
Primary and Secondary Voltage Configuration
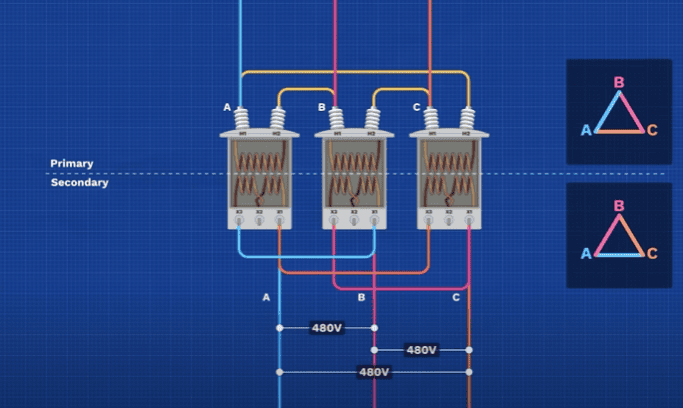
- Confirm transformer nameplate rating matches system voltage (e.g., 13.8kV Delta / 480V Wye).
- Verify proper phasing and rotation before energizing (use phase rotation meter).
Connection Types
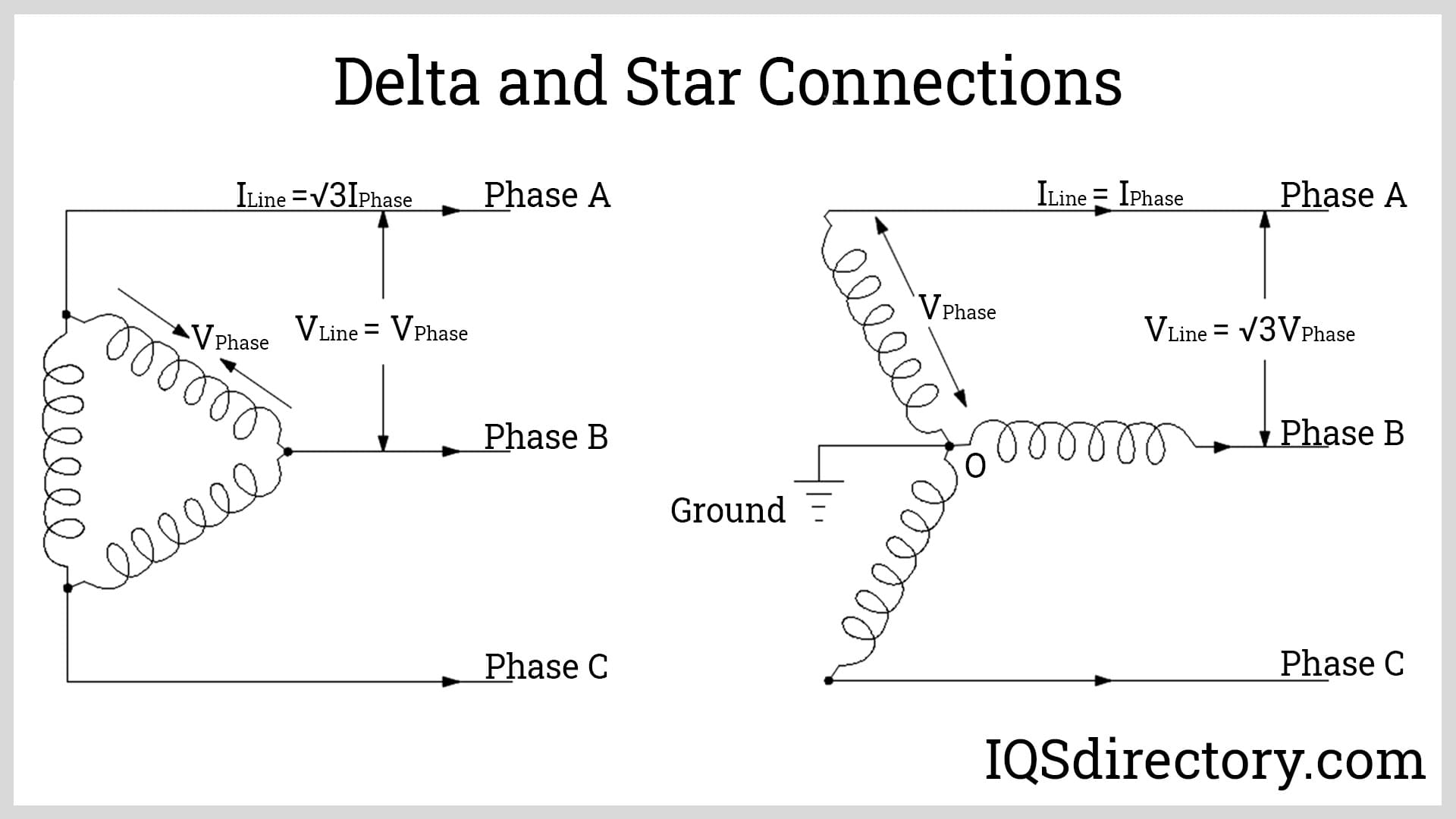
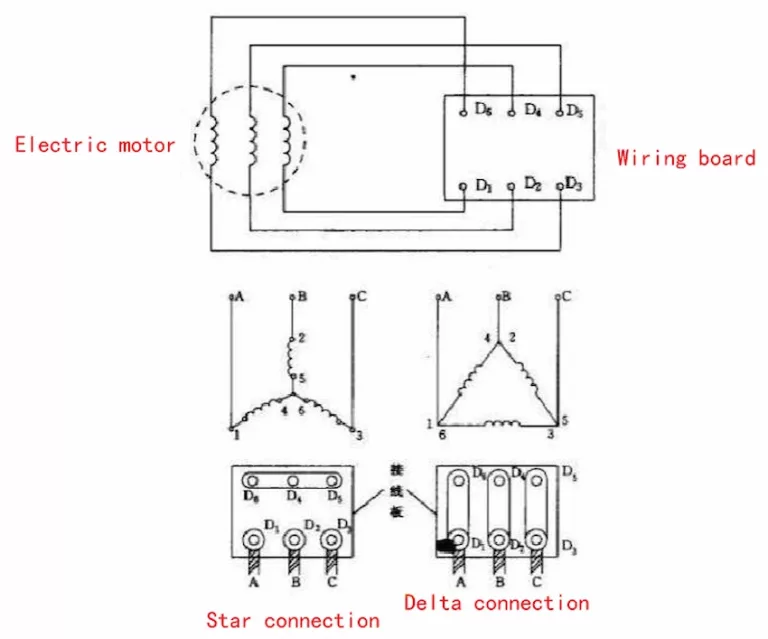
- Delta (Δ) Connection: Connect line leads end-to-end in a closed loop; no neutral point. Suitable for balanced industrial loads.
- Wye (Y) Connection: Connect one end of each winding to a common neutral point; allows single-phase loads and grounding.
- Select configuration based on load requirements and system grounding strategy.
Grounding and Bonding
- Bond transformer tank and neutral point (if applicable) to the facility grounding electrode system per NEC Article 250.
- Use appropriately sized grounding conductors (minimum 6 AWG copper for small units; larger for high-fault-current systems).
- Implement impedance grounding or solid grounding as per system design and safety studies.
Conductor Sizing and Termination
- Size conductors based on full load current, temperature rating, and voltage drop limits (NEC Article 310).
- Use listed lugs and torque connections to manufacturer specifications (typically 25–50 ft-lbs, depending on size).
- Label all conductors clearly (phase, function, circuit ID) per NEC 110.22.
Testing and Commissioning
Pre-Energization Checks
- Perform insulation resistance (Megger) tests on windings and grounding systems.
- Verify continuity and correct phasing of all connections.
- Inspect for loose hardware, debris, and proper sealing of enclosures.
Energization and Load Testing
- Energize transformer gradually using a step-up procedure, monitoring for abnormal noise, vibration, or temperature rise.
- Conduct load tests under full rated conditions to validate performance.
- Document test results for compliance and future reference.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Required Documentation
- As-built wiring diagrams and single-line drawings.
- Test reports (insulation resistance, turns ratio, polarity, and load tests).
- Certificate of compliance with NEC, IEEE, or IEC standards.
- Maintenance and warranty information provided by manufacturer.
Asset Management
- Register transformer in facility asset management system with unique ID and location.
- Schedule routine inspections and oil testing (for liquid-filled units) per IEEE C57.106.
Safety and Training
Personnel Requirements
- Only qualified electricians or licensed engineers should perform wiring and testing.
- Enforce lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during installation per OSHA 1910.147.
- Provide arc flash hazard analysis and appropriate PPE (e.g., Category 3 or 4 arc-rated gear).
Emergency Preparedness
- Post emergency shutdown procedures and transformer fluid spill response plans.
- Ensure fire suppression systems are in place and accessible.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and strict compliance with electrical codes are critical for the safe and efficient operation of 3 phase transformer installations. Following this guide ensures adherence to industry best practices, minimizes risks, and supports long-term reliability of power distribution systems.
Conclusion on Sourcing 3-Phase Transformer Wiring Connections:
Sourcing the correct wiring connections for a 3-phase transformer is crucial for ensuring efficient, safe, and reliable operation within an electrical power system. The choice between configurations—such as Delta (Δ) and Wye (Y) on both primary and secondary sides—depends on specific application requirements, including voltage levels, load balance, grounding needs, harmonics mitigation, and system compatibility.
When sourcing 3-phase transformers, it is essential to consider the intended connection type (e.g., Delta-Delta, Delta-Wye, Wye-Delta, or Wye-Wye), as each offers distinct advantages in different scenarios. For example, Delta-Wye connections are widely preferred for distribution systems due to their ability to provide a neutral point for single-phase loads and reduce harmonic currents.
Additionally, proper specifications—such as voltage ratings, kVA capacity, impedance, and connection flexibility—must be clearly defined to match site requirements. Compliance with industry standards (e.g., IEEE, IEC), quality of materials, and manufacturer reputation further influence performance and longevity.
In conclusion, selecting and sourcing 3-phase transformer wiring connections requires a thorough understanding of electrical system needs, load characteristics, and applicable standards. A well-informed sourcing decision ensures optimal power transformation, minimizes losses, enhances safety, and supports the overall stability of the electrical network.