The global 3-phase air conditioner market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions in commercial and industrial sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global air conditioning market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.5% from 2023 to 2028, with 3-phase systems gaining significant traction due to their superior performance in large-scale applications such as data centers, manufacturing facilities, and high-rise buildings. Key factors fueling this expansion include increasing urbanization, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and the growing adoption of smart HVAC technologies. As industries prioritize operational efficiency and thermal comfort, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-capacity, low-energy-consuming 3-phase units. Based on market presence, product innovation, energy efficiency ratings, and global reach, the following list highlights the top 10 3-phase air conditioner manufacturers shaping the future of commercial and industrial cooling.
Top 10 3 Phase Air Conditioner Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Goodman: Air Conditioning and Heating Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: goodmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Goodman Manufacturing offers a range of affordable air conditioning, packaged units, heat pumps and gas furnaces for residential heating and cooling needs….
#2 Friedrich Air Conditioning: Room Air Conditioning Expert
Domain Est. 1998
Website: friedrich.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1883, Friedrich Air Conditioning Co. is a leading US manufacturer of premium room A/C and other home environment products….
#3 Carrier air conditioning systems redefine comfort
Domain Est. 1995
Website: carrier.com
Key Highlights: Carrier air conditioning systems are designed to provide your home with consistently cool, comfortable air. Single-stage systems offer basic on-or-off ……
#4 YORK
Domain Est. 1995
Website: york.com
Key Highlights: From cooling systems and heating systems to HVAC components that control humidity, YORK provides indoor air quality solutions for the way you live today….
#5 VRV (Multi
Domain Est. 1996
Website: daikin.com
Key Highlights: The Daikin VRV system is a multi-split type air conditioner for commercial buildings that uses variable refrigerant flow control developed by Daikin….
#6 HVAC
Domain Est. 1996
Website: heil-hvac.com
Key Highlights: Find the right heating and cooling solution for your home, backed by trusted local experts. Explore home comfort systems designed for performance, efficiency, ……
#7 Split System Air Conditioners
Domain Est. 2000
Website: colemanac.com
Key Highlights: With impressive efficiency, rugged dependability and best-in-class warranties, Coleman® air conditioning units provide comfort that stands the test of time….
#8 Innovative Commercial Air Conditioner Split System
Domain Est. 2012
Website: daikincomfort.com
Key Highlights: Daikin air conditioners feature high-efficiency compressors and coils, delivering top-tier reliability, durability, and energy efficiency for commercial ……
#9 3 Phase Air Conditioners
Domain Est. 2015
Website: m.lennoxpros.com
Key Highlights: Find commercial Lennox 3 Phase air conditioners on LennoxPros.com. Shop commercial Lennox AC units to get the best for your customers. 170 results….
#10 Heating & Air Conditioning
Domain Est. 2019
Website: runtruhvac.com
Key Highlights: RunTru delivers quality HVAC systems at an affordable price, designed with your needs and budget in mind….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3 Phase Air Conditioner

2026 Market Trends for 3 Phase Air Conditioners
The global market for 3 phase air conditioners is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, energy efficiency regulations, and evolving commercial and industrial cooling demands. As economies recover and urbanize, the need for reliable, high-capacity cooling systems continues to rise—particularly in sectors such as data centers, healthcare, manufacturing, and commercial real estate. This analysis outlines the key market trends shaping the 3 phase air conditioner industry through 2026.
Rising Demand in Commercial and Industrial Sectors
One of the most prominent trends is the growing adoption of 3 phase air conditioning systems in commercial and industrial applications. Unlike single-phase units, 3 phase systems offer higher efficiency, better performance under continuous load, and reduced electrical stress on motors—making them ideal for large buildings, factories, and infrastructure projects. With increasing construction of smart offices, hospitals, and data centers—especially in Asia-Pacific and North America—demand for robust HVAC solutions is accelerating.
Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Pressure
Global initiatives to reduce carbon emissions are pushing governments to enforce stricter energy efficiency standards. By 2026, regulations such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and the U.S. Department of Energy’s updated HVAC efficiency standards will require higher Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios (SEER) and Integrated Energy Efficiency Ratios (IEER). 3 phase air conditioners, particularly those equipped with inverter-driven compressors and variable refrigerant flow (VRF) technology, are well-positioned to meet these standards, driving their adoption over traditional single-phase systems.
Technological Advancements and Smart Integration
The integration of IoT and smart building management systems (BMS) is transforming 3 phase air conditioners into intelligent climate control units. By 2026, a growing number of systems will feature remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven optimization. These capabilities not only enhance energy savings but also reduce downtime and operational costs—key priorities for facility managers in large-scale operations.
Growth in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are experiencing rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in cooling infrastructure due to rising temperatures and expanding urban populations. 3 phase air conditioners are becoming the preferred choice for new commercial buildings and industrial facilities due to their reliability and scalability.
Shift Toward Sustainable Refrigerants
Environmental concerns are prompting a shift away from high-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants such as R-410A. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to increasingly adopt eco-friendly alternatives like R-32 and natural refrigerants (e.g., CO₂ and propane) in 3 phase systems. This transition is supported by international agreements such as the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, which mandates the phasedown of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Trends
The 3 phase AC market is also being reshaped by supply chain dynamics. Post-pandemic disruptions have led companies to localize production and diversify suppliers. Additionally, rising raw material costs—particularly for copper and aluminum—are pushing manufacturers to innovate in heat exchanger design and system miniaturization to maintain margins without compromising performance.
Competitive Landscape
Major HVAC players such as Daikin, Carrier, Mitsubishi Electric, and LG are intensifying R&D efforts to capture market share. Competitive differentiation is increasingly based on energy efficiency, smart features, and lifecycle cost savings. By 2026, partnerships between HVAC manufacturers and building automation firms are expected to become more common, offering integrated cooling solutions tailored to specific industries.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 3 phase air conditioner market will be defined by a convergence of regulatory, technological, and economic forces. Energy efficiency, digitalization, and sustainability will be central to product development and customer adoption. As demand grows across both developed and emerging markets, companies that innovate in smart controls, low-GWP refrigerants, and scalable system design will lead the next phase of industry growth.
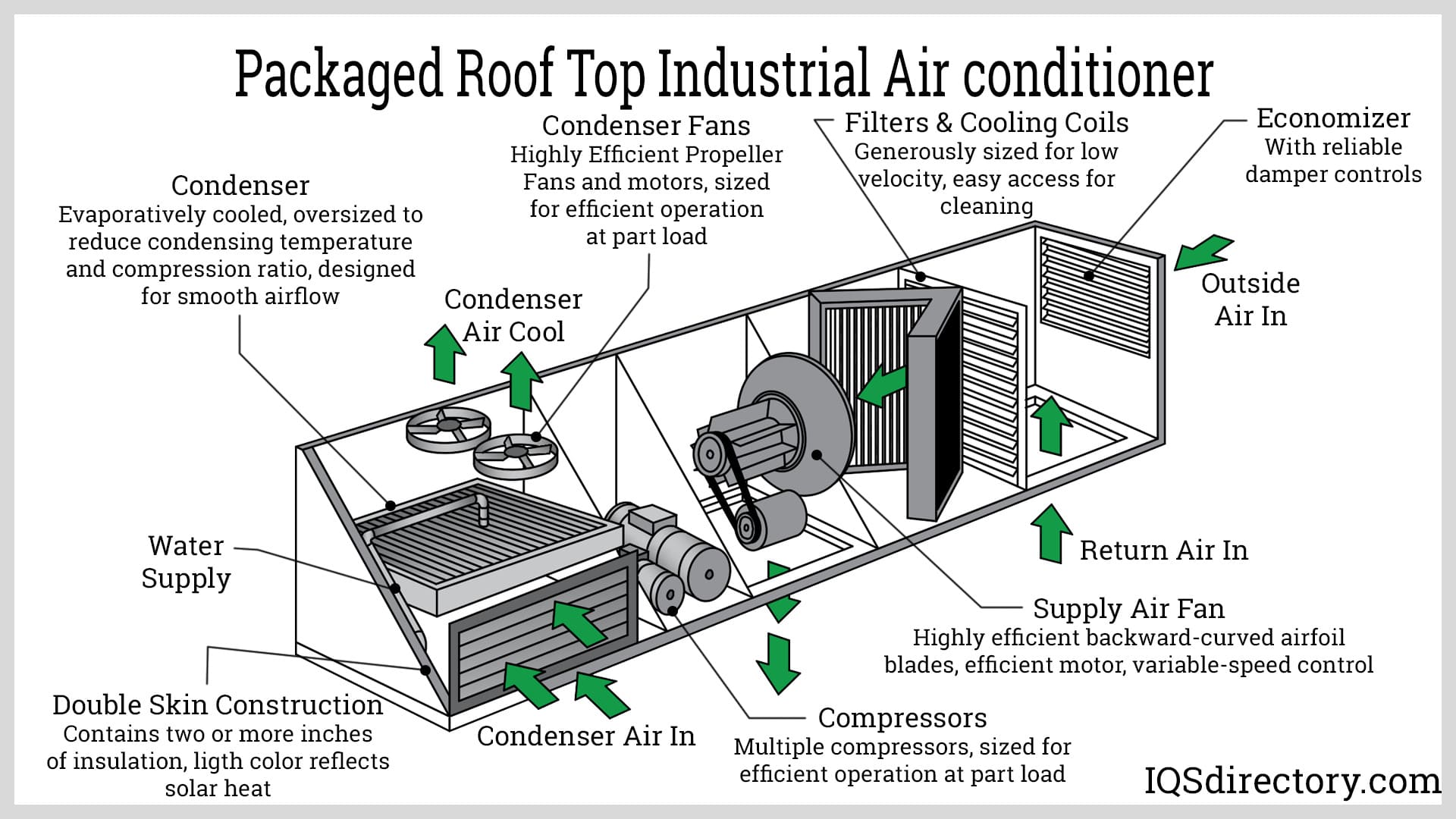
Common Pitfalls Sourcing a 3-Phase Air Conditioner (Quality & IP Rating)
Sourcing a 3-phase air conditioner requires careful attention to technical specifications and manufacturer claims, particularly regarding quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, premature failure, safety hazards, and costly replacements. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
One of the most significant pitfalls is focusing solely on price while neglecting the actual build quality. Low-cost units may use inferior materials—such as thin-gauge steel, substandard compressors, or low-efficiency fans—that compromise longevity and performance. Poor welding, inadequate insulation, and flimsy electrical connections increase the risk of mechanical failure and safety hazards. Always verify the reputation of the manufacturer, review third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, CE), and inspect sample units for robust construction.
Misinterpreting or Trusting Inflated IP Ratings
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings define the level of protection against dust and moisture. A common mistake is assuming a higher IP rating (e.g., IP55 or IP65) guarantees suitability for harsh environments without verifying testing standards. Some suppliers may exaggerate or self-assign IP ratings without independent certification. Always request test reports from accredited laboratories (e.g., IEC 60529 compliance) and confirm whether the rating applies to the entire unit—including electrical compartments and service panels—under real operating conditions.
Ignoring Environmental Compatibility
Even with a high IP rating, the unit must be suitable for the specific environment. For example, coastal installations require corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., galvanized or stainless steel, anti-corrosion coatings) regardless of IP rating. Similarly, units in dusty industrial settings need effective air filtration and sealed electrical components. Failing to match the unit’s design to environmental stressors can negate the benefits of a high IP rating and lead to rapid degradation.
Skipping Verification of Electrical and Safety Standards
3-phase units operate at high voltages and must comply with regional electrical codes (e.g., NEC, IEC, AS/NZS). A major pitfall is sourcing units without proper safety certifications (e.g., UL, CSA, TÜV). Non-compliant units may lack adequate grounding, overcurrent protection, or phase-loss protection, posing serious fire and electrocution risks. Always confirm compliance with local regulations and ensure the unit includes necessary safety features for 3-phase operation.
Relying on Inadequate Warranty and After-Sales Support
Low-quality or uncertified manufacturers often offer limited or unenforceable warranties. A lack of accessible technical support, spare parts, or service networks can leave you stranded if the unit fails. Prioritize suppliers with comprehensive warranties, clear service agreements, and a proven track record of customer support, especially for industrial or mission-critical cooling applications.
By diligently assessing quality, validating IP ratings through documentation, and ensuring environmental and regulatory compatibility, you can avoid costly mistakes and select a reliable, durable 3-phase air conditioning solution.
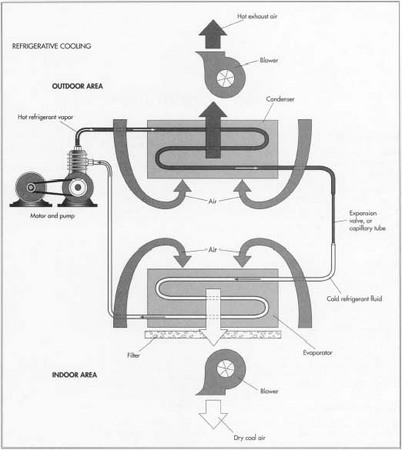
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3 Phase Air Conditioner
Overview
This guide provides key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, import/export, installation, and operation of 3 Phase Air Conditioners. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, safe handling, and efficient supply chain management.
Regulatory Compliance
Electrical Standards
3 Phase Air Conditioners must comply with regional electrical safety standards such as:
– IEC 60335-2-40 (International standard for HVAC safety)
– UL 484 (U.S. standard for room air conditioners)
– EN 60335-2-40 (European Union safety requirements)
Ensure equipment bears relevant certification marks (CE, UL, CCC, etc.) depending on the destination market.
Energy Efficiency Regulations
Comply with local energy performance standards:
– U.S.: DOE (Department of Energy) minimum efficiency requirements
– EU: Ecodesign Directive (ErP) and Energy Labeling Regulation
– Asia: MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standards) in countries like Australia, India, and China
Verify SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings meet local thresholds.
Environmental Compliance
- Refrigerant Regulations: Adhere to F-Gas regulations (EU), AIM Act (U.S.), or Kigali Amendment (global) for refrigerants like R-410A, R-32, or R-454B. Ensure proper handling, recovery, and reporting.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm absence of restricted hazardous substances.
- WEEE Directive (EU): Plan for end-of-life take-back and recycling.
Packaging & Handling
Packaging Requirements
- Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging suitable for heavy units.
- Include corner protectors and internal bracing to prevent compressor and coil damage.
- Clearly label with:
- “Fragile”
- “This Side Up”
- Weight and center of gravity indicators
- Pallet load capacity (if applicable)
Handling Instructions
- Use mechanical lifting equipment (forklifts, cranes) for outdoor units; never carry manually.
- Maintain upright orientation during transport and storage to prevent oil migration.
- Avoid tilting beyond 30 degrees unless specified by manufacturer.
Transportation & Shipping
Domestic & International Shipping
- Classify under correct HS Code (e.g., 8415.81 for air conditioners).
- Complete accurate commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
- For international shipments, ensure compliance with destination country’s import regulations (e.g., SABER in Saudi Arabia, SONCAP in Nigeria).
Mode-Specific Considerations
- Sea Freight: Secure units on pallets using straps or shrink wrap; avoid container condensation with desiccants.
- Air Freight: Confirm weight and dimensional restrictions; prioritize faster transit to reduce exposure to temperature extremes.
- Overland Transport: Use covered trucks; secure load to prevent shifting.
Installation & Site Compliance
Electrical Requirements
- Verify local voltage (e.g., 380V, 400V, 480V), frequency (50Hz or 60Hz), and phase balance.
- Use qualified electricians to connect to a dedicated 3-phase circuit with proper grounding and disconnect switch.
- Comply with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in U.S., IEC 60364 internationally).
Mechanical & Safety Standards
- Follow manufacturer’s clearance guidelines for airflow and service access.
- Ensure structural support for rooftop or wall-mounted units.
- Install condensate drain lines with proper slope and trap to prevent overflow.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Required Documentation
- Technical specifications and installation manuals
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
- Energy efficiency test reports
- Refrigerant charge label and handling certification
- Warranty and service information
Recordkeeping
- Maintain logs of refrigerant handling (including recovery and recycling).
- Store compliance certificates for audit purposes (minimum 5–7 years depending on jurisdiction).
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance with electrical, environmental, and safety regulations are essential for the successful deployment of 3 Phase Air Conditioners. Always consult local authorities and manufacturers to ensure adherence to the latest requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 3-Phase Air Conditioner
Sourcing a 3-phase air conditioner is a strategic decision that offers significant advantages for commercial, industrial, or large-scale residential applications. These units provide superior efficiency, reliable performance under heavy loads, and smoother motor operation due to the balanced power delivery of a 3-phase power supply. When sourcing such equipment, it is essential to consider factors including cooling capacity, energy efficiency (SEER/EER ratings), compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure, brand reliability, maintenance requirements, and total cost of ownership.
Furthermore, engaging with reputable suppliers or manufacturers, ensuring proper installation by qualified technicians, and adhering to local electrical codes and standards are crucial for optimal performance and safety. While the initial investment may be higher compared to single-phase units, the long-term benefits—such as reduced energy consumption, extended equipment lifespan, and enhanced operational stability—justify the cost, particularly in high-demand environments.
In conclusion, sourcing a 3-phase air conditioner is a prudent choice for facilities requiring robust and efficient cooling solutions. A thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier credibility, and lifecycle costs ensures a reliable and cost-effective cooling system that meets current and future needs.