The global market for multi-functional industrial tools—including 3-in-1 devices combining rust removal, cutting, and welding capabilities—has seen robust growth due to increasing demand for cost-effective, space-saving solutions in manufacturing, construction, and metal fabrication. According to Grand View Research, the global welding equipment market was valued at USD 28.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030, driven by automation trends and rising infrastructure investments. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts the industrial cutting equipment market to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% during the same period, with integrated systems gaining traction due to their operational efficiency and reduced downtime. This surge in demand has elevated the prominence of manufacturers offering versatile, high-performance 3-in-1 solutions that consolidate multiple functions into a single, portable unit. The following list highlights the top six manufacturers leading innovation and market adoption in this space, selected based on product range, technological advancement, global reach, and customer reviews.
Top 6 3-In-1/Rust Removal/Cutting/Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 HITBOX 2000W/3000W Laser Welder 4 in 1 Cut/Rust Removal …
Website: hitboxweld.com
Key Highlights: HITBOX 2000W/3000W Laser Welder 4 in 1 Cut/Rust Removal/Clean 220V Protection Water Cooling Technology Laser Welding Machine. Regular price $5,288.00….
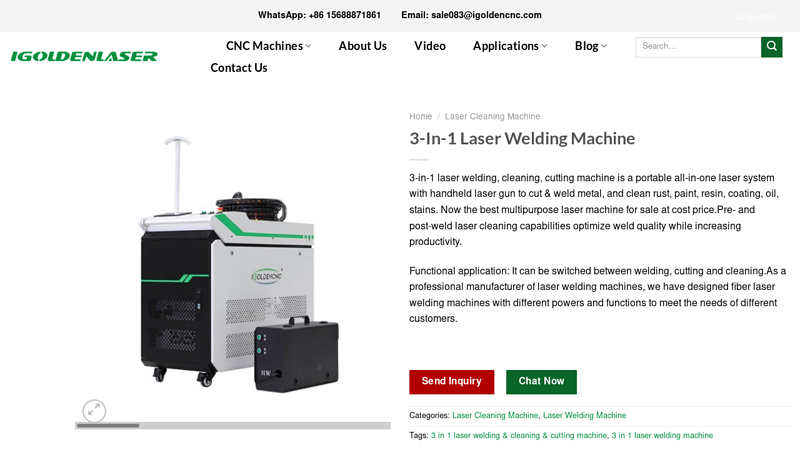
#2 3 In 1 Laser Welding Cutting Cleaning Machine
Website: igoldenlaser.com
Key Highlights: 3-in-1 Handheld Laser Welding Cleaning and Cutting Machine can not only cut and weld metal but also clean rust, paint, resin, coating, oil, and stains. This ……
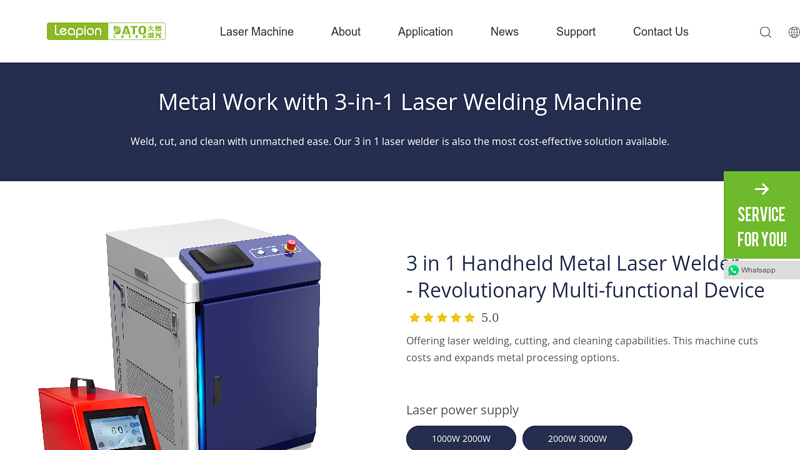
#3 Metal Work with 3
Website: leapion.com
Key Highlights: Our 3 in 1 laser welding machine provides welding, cutting, and rust removal all in one. This versatile tool processes metal with utmost precision, speed, and ……
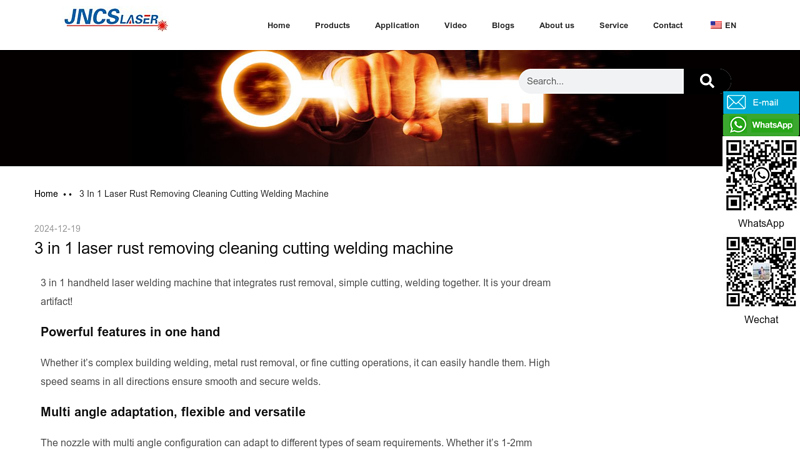
#4 3 in 1 laser rust removing cleaning cutting welding machine
Website: jncslaser.com
Key Highlights: 3 in 1 handheld laser welding machine that integrates rust removal, simple cutting, welding together. It is your dream artifact!…
#5 3 In 1 Laser Welding Cutting Cleaning Machine 1000W 1500W …
Website: ray-laser.com
Key Highlights: 3 In 1 Laser Welding Cutting Cleaning Machine 1000W 1500W 2000W 3000W Laser Welder Rust Removal ; Max. Output Power: 1500W ; Use: Matel Welding ; Warranty: 1 Year….
#6 Laser welders
Website: weldingweb.com
Key Highlights: I’m seeing more and more laser welders being advertised and the prices are coming down. Does anyone here already have a laser welder and what’s your opinion?…
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3-In-1/Rust Removal/Cutting/Welding

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 3-in-1 Rust Removal, Cutting, and Welding Equipment
The global market for multi-functional industrial tools, particularly 3-in-1 devices combining rust removal, cutting, and welding capabilities, is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in portable power systems, automation, and industrial digitization, these integrated tools are increasingly adopted across manufacturing, construction, automotive repair, and infrastructure maintenance sectors. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the 2026 landscape for 3-in-1 rust removal, cutting, and welding equipment.
-
Rising Demand for Multi-Functionality and Portability
Manufacturers and field technicians are increasingly prioritizing tools that consolidate multiple functions into a single, compact unit. The 3-in-1 design reduces equipment costs, saves workspace, and enhances job site mobility. By 2026, demand will be especially strong in developing markets and remote operations where transporting multiple heavy tools is impractical. Portable inverter-based models with lightweight designs and battery compatibility will dominate new product launches. -
Advancements in Plasma and Laser Technology
Innovations in plasma arc and fiber laser systems are enabling more efficient cutting and rust-removal capabilities within integrated welding platforms. By 2026, expect to see 3-in-1 units incorporating intelligent plasma cutting with built-in oxide layer detection and automated rust stripping modes. These systems will use real-time sensors and AI-driven process optimization to deliver precision and reduce operator error. -
Integration with IoT and Smart Diagnostics
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming traditional welding and cutting equipment into smart, connected tools. By 2026, leading 3-in-1 systems will feature embedded sensors, cloud connectivity, and predictive maintenance alerts. Users will access performance analytics via mobile apps, enabling remote monitoring of consumable usage, duty cycles, and maintenance needs—improving uptime and reducing operational costs. -
Growth in Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Solutions
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers toward energy-efficient, low-emission tools. In 2026, 3-in-1 equipment will increasingly feature regenerative power systems, energy recovery during idle modes, and compatibility with renewable energy sources (e.g., solar-charged batteries). Additionally, advancements in dry ice blasting or electrochemical rust removal—integrated into multi-tool platforms—will reduce reliance on chemical treatments and abrasive methods. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Infrastructure development in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America is fueling demand for affordable, versatile metalworking tools. Chinese and Indian manufacturers are leading in cost-effective 3-in-1 solutions tailored to small workshops and DIY users. By 2026, localized production and modular designs will enable easier servicing and reduced import dependency, further accelerating market penetration. -
Focus on Safety and Operator Training
As 3-in-1 tools become more powerful and complex, safety features will be a key differentiator. Anticipated trends include automatic arc detection, anti-static coatings, and augmented reality (AR)-assisted training modules. OEMs will partner with vocational training institutes to standardize the use of multi-function equipment, ensuring safe and efficient operation across skill levels. -
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The market will see increased competition between established players (e.g., Miller Electric, Lincoln Electric) and agile startups offering modular, software-upgradable tools. Strategic mergers and partnerships focused on integrating AI, robotics, and automation are expected by 2026, particularly in the development of semi-autonomous welding and surface treatment units.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 3-in-1 rust removal, cutting, and welding equipment market will be defined by smarter, greener, and more user-centric innovations. The convergence of multi-functionality, digital integration, and sustainable engineering will drive adoption across both industrial and consumer segments. Companies that invest in intelligent features, energy efficiency, and global scalability will lead the next wave of industrial tool evolution.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing 3-in-1 Rust Removal, Cutting, and Welding Equipment (Quality & IP Risks)
Sourcing multi-functional tools like 3-in-1 machines that combine rust removal, cutting, and welding capabilities can offer cost and space savings. However, buyers often encounter significant pitfalls related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) that can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, and legal exposure. Being aware of these risks is critical for informed procurement decisions.
Poor Build Quality and Performance Inconsistencies
Many low-cost 3-in-1 units on the market, particularly from unverified suppliers, suffer from substandard materials and inconsistent manufacturing. Components such as power supplies, cooling systems, and torch assemblies may fail prematurely under industrial use. This results in frequent downtime, higher maintenance costs, and unreliable performance across the different functions—especially when switching between welding and cutting modes. Users often find that the equipment performs adequately in one mode (e.g., rust removal) but underperforms or becomes unsafe in others (e.g., high-amp welding).
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Industry Standards
A major quality concern is non-compliance with international safety certifications such as CE, UL, or ISO standards. Some suppliers falsify certifications or use logos without proper validation. Equipment lacking genuine compliance may pose serious risks, including electrical hazards, fire, or exposure to harmful fumes during rust removal or welding. In regulated industries, using non-compliant tools can lead to fines, project delays, or voided insurance policies.
Inadequate or Misleading IP Disclosure
Many 3-in-1 devices incorporate patented technologies—such as pulsed arc cleaning, inverter-based power control, or multi-process switching logic—without proper licensing. Sourcing from manufacturers that infringe on existing IP exposes buyers to legal risk. If a supplier is later found to be using protected technology without authorization, customers could face cease-and-desist orders, product seizures, or liability for contributory infringement, especially in markets with strong IP enforcement like the EU or the U.S.
Counterfeit or Clone Products
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” models that closely mimic branded tools but lack original engineering and quality control. These clones often copy industrial design and user interfaces, blurring IP boundaries. While they may appear cost-effective initially, they typically lack technical support, firmware updates, and spare parts availability. Moreover, purchasing counterfeit equipment can damage a company’s reputation and undermine commitments to ethical sourcing.
Hidden Costs from Poor After-Sales Support
Low initial pricing often masks long-term costs tied to poor technical support and unavailable spare parts. When quality issues arise, buyers may find that suppliers are unresponsive or that replacement components are either unavailable or disproportionately expensive. This is especially problematic for mission-critical operations where equipment uptime is essential.
Recommendations to Mitigate Risks
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and certification verification.
– Request proof of IP ownership or licensing for critical technologies.
– Prioritize vendors with a track record of compliance and after-sales service.
– Test equipment under real-world conditions before large-scale procurement.
– Consult legal counsel when sourcing from high-risk regions with lax IP enforcement.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure they procure reliable, compliant, and legally sound 3-in-1 welding solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3-in-1 Rust Removal, Cutting, and Welding Equipment
Overview of 3-in-1 Equipment
3-in-1 machines combining rust removal, cutting, and welding functionalities offer versatility for industrial, construction, and maintenance applications. These multi-process tools streamline operations but require careful logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards due to their complex nature and inherent hazards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA – U.S.)
- General Duty Clause: Employers must provide a workplace free from recognized hazards.
- Welding, Cutting, and Brazing (29 CFR 1910.252): Mandates fire prevention, ventilation, protective equipment, and safe handling of compressed gases.
- Electrical Safety (29 CFR 1910.303): Requires proper grounding, insulation, and guarding of electrical components.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) (29 CFR 1910.132): Employers must assess hazards and provide appropriate PPE, including helmets, gloves, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection.
International Standards (ISO/EN)
- ISO 14122 (Safety of Machinery – Permanent Means of Access): Applies to equipment access and guarding.
- EN 60204-1 (Safety of Machinery – Electrical Equipment of Machines): Governs electrical safety for industrial machinery in the EU.
- ISO 15534 (Safety of Machinery – Ergonomic Design Principles): Addresses user interface and operational safety.
Environmental Regulations
- Hazardous Waste (EPA – RCRA): Spent abrasives (e.g., sand, grit) used in rust removal may be classified as hazardous waste if contaminated with lead or other toxins. Proper disposal documentation and manifesting are required.
- Air Quality (EPA NESHAPs): Dust and fumes from rust removal and welding may require air filtration systems or emission controls, especially in enclosed spaces.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Restrict the use of hazardous substances in electrical equipment and ensure safe chemical handling.
Transportation and Handling
Domestic and International Shipping
- UN/DOT Classification: If equipment contains compressed gas cylinders (e.g., for plasma cutting), classify under appropriate UN numbers (e.g., UN1013 for argon, UN1045 for oxygen). Use certified pressure vessels and secure packaging.
- IATA/IMDG Regulations: For air or sea freight, comply with hazardous materials shipping rules when transporting gas cylinders or equipment with residual flammable components.
- Battery-Powered Units: Lithium-ion batteries must meet UN38.3 testing standards and be shipped at ≤30% charge, with proper labeling (e.g., UN3480).
Packaging and Labeling
- Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging with internal bracing to prevent movement.
- Label with:
- “Fragile – Handle with Care”
- “This Side Up”
- Hazard labels (e.g., electrical hazard, hot surface, compressed gas if applicable)
- Compliance marks (CE, UKCA, EAC, etc., depending on destination)
Storage and Site Management
On-Site Storage
- Store in dry, well-ventilated areas away from combustible materials.
- Keep gas cylinders upright and secured with chains or stands; separate fuel and oxidizer gases.
- Protect equipment from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures to prevent electrical or mechanical failure.
Operational Safety Protocols
- Conduct job hazard analyses (JHAs) before each use.
- Implement hot work permits for cutting and welding activities.
- Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) or fume extraction systems during welding and abrasive blasting.
- Ground the workpiece and equipment to prevent electric shock.
Training and Documentation
Personnel Training
- Operators must be certified in:
- Multi-process welding techniques (SMAW, GMAW, etc.)
- Safe use of abrasive blasting tools
- Plasma or oxy-fuel cutting procedures
- Training should cover emergency shutdown, fire response, and PPE usage.
Compliance Documentation
- Maintain records of:
- Equipment inspection and maintenance logs
- Operator certifications
- Safety data sheets (SDS) for consumables (welding rods, gases, abrasives)
- Regulatory permits (e.g., hot work, emissions)
- Incident reports and near-miss logs
Maintenance and Inspection
Routine Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for servicing.
- Inspect cables, hoses, nozzles, and grounding clamps regularly for wear or damage.
- Calibrate welding parameters and gas flow rates as needed.
Compliance Audits
- Conduct periodic safety audits to ensure adherence to OSHA, ISO, and site-specific regulations.
- Validate that all modifications or repairs comply with original equipment safety standards.
Disposal and End-of-Life
Equipment Decommissioning
- Recycle metal components through certified scrap handlers.
- Dispose of electronic control units in compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions.
- Drain and recycle hydraulic fluids or coolants per environmental regulations.
Consumables and Waste
- Collect spent abrasive media in sealed containers; test for hazardous content before disposal.
- Recycle used welding wire spools and gas cylinders through authorized vendors.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for 3-in-1 rust removal, cutting, and welding equipment require integrated planning across transportation, operational safety, environmental stewardship, and regulatory alignment. By maintaining rigorous documentation, training, and adherence to local and international standards, organizations can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant use of these powerful multi-functional tools.
Conclusion:
After evaluating various options for sourcing a multi-functional solution that combines 3-in-1 capability—rust removal, cutting, and welding—the most effective approach is to prioritize versatile, high-quality tools that offer efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness over time. Integrated systems such as plasma cutters with built-in air compressors and welders, or specialized combo units designed for metal fabrication and restoration, provide significant advantages in terms of workspace optimization and operational flexibility.
Sourcing should focus on reputable manufacturers known for robust engineering and strong after-sales support. While initial investment may be higher for all-in-one or modular systems, the long-term benefits—including reduced equipment footprint, streamlined operations, and lower maintenance costs—justify the expenditure, especially for workshops with diverse metalworking needs.
Additionally, consideration should be given to power requirements, portability, and user skill level to ensure optimal performance. Whether opting for industrial-grade equipment or compact models for smaller-scale operations, proper sourcing balances functionality, reliability, and value. Ultimately, selecting the right 3-in-1 or combination tool enhances productivity and versatility in rust removal, cutting, and welding applications, making it a strategic investment for both professional and advanced DIY users.