The global market for electrical connectors, including 240V AC plug types, is experiencing steady growth driven by rising demand in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global electrical plugs and sockets market was valued at USD 22.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 28.7 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by infrastructure development, increased electrification in emerging economies, and stringent safety regulations. As reliance on high-voltage power systems grows—especially in regions utilizing 240V standards such as Europe, Australia, and parts of Asia—the need for reliable, standardized plug solutions has never been more critical. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, compliance, and global reach to dominate the 240V AC plug segment.
Top 9 240V Ac Plug Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 Plugs, Connectors & Receptacles
Domain Est. 1995
Website: leviton.com
Key Highlights: Leviton has the broadest offering of heavy duty, watertight, NEMA and IEC plugs and connectors for commercial and industrial grade applications….
#3 Power Cord Manufacturer • Custom & Standard
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conwire.com
Key Highlights: Diverse Product Selection: We offer standard power cords in many lengths, plug types, and cord sizes to meet US and international requirements. Global Reach ……
#4 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL offers a comprehensive power solution with our versatile series of power supplies. You can use this product overview tool to find product ……
#5 Pass & Seymour Electrical Devices
Domain Est. 2004
Website: legrand.us
Key Highlights: Find innovation for commercial, residential and industrial electrical wiring. Explore Pass & Seymour switches, receptacles, GFCI outlets, USB chargers and ……
#6 Power Cords and Adapters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: We offer AC power cords, extension cords, splitters and adapters for computers, servers and PDUs. Our cords have innovative features like coiled cords and ……
#7 NEMA Straight Blade Plug & Receptacle (Outlet) Configurations …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: elliottelectric.com
Key Highlights: The following tables show the straight blade plugs and receptacles for NEMA 5, NEMA 6, NEMA 7, NEMA 10, NEMA 14, NEMA 15, NEMA 18, and NEMA TT devices….
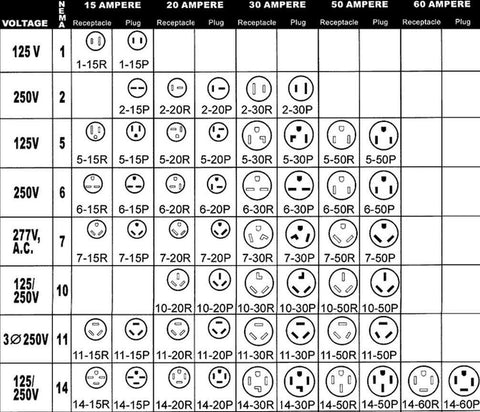
#8 NEMA Plug Charts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americord.com
Key Highlights: These charts describe the layout of the connector plugs and sockets, voltage, and current limits, for their aim is to offer a uniform means of connecting ……
#9 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
Key Highlights: The Type C electrical plug (or Europlug) is a two-wire plug that has two round pins. It fits into any socket that accepts 4.0 – 4.8 mm round contacts on 19 mm ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 240V Ac Plug Types
H2: 2026 Market Trends for 240V AC Plug Types
The global market for 240V AC plug types is undergoing significant transformation as it approaches 2026, driven by evolving safety standards, regional electrification efforts, and the expansion of high-power consumer and industrial applications. While 240V systems are primarily used in regions such as Europe, the UK, Australia, and parts of Asia and Africa, the demand for compatible plug types is being shaped by several interrelated trends.
-
Standardization and Harmonization Efforts
By 2026, there is growing momentum toward greater harmonization of plug types across regions, particularly within the European Union and ASEAN markets. The IEC 60906-1 standard—which supports 240V systems and offers a safer, more universal design—is seeing increased adoption, especially in new construction and public infrastructure. Countries like South Africa have already transitioned to IEC 60906-1, and others are evaluating its implementation to reduce reliance on legacy plug types such as Type C, G, D, M, and I. -
Rise in Electrification and High-Power Appliances
The deployment of 240V circuits is expanding due to the proliferation of high-power appliances such as electric vehicle (EV) chargers, heat pumps, induction cooktops, and industrial machinery. This is increasing demand for robust plug types capable of handling sustained 240V loads. Type G (UK), Type F (Schuko), and Type I (Australia) are experiencing higher usage in residential and commercial installations, with manufacturers enhancing durability and safety features such as shuttered sockets and improved grounding. -
Growth in Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
One of the most significant drivers of 240V plug demand is the global expansion of Level 2 EV charging, which typically operates at 240V. While dedicated connectors like Type 2 (Mennekes) in Europe and SAE J1772 in North America dominate, these systems often rely on 240V infrastructure and may use adapted 240V plug standards for portable charging units. By 2026, the integration of smart, high-efficiency 240V charging solutions is expected to drive innovation in plug design, including enhanced thermal management and digital communication capabilities. -
Regional Shifts and Regulatory Influence
Regulatory changes are influencing plug adoption. For example, the EU’s push for a common charging solution (via the Radio Equipment Directive) has primarily focused on USB-C for small devices but reinforces broader goals of interoperability. Although not directly targeting 240V AC plugs, this regulatory environment encourages standardization that could indirectly benefit adoption of universal 240V connectors. Meanwhile, countries in Southeast Asia and Africa are modernizing grids and may opt for future-proof plug designs during infrastructure upgrades. -
Sustainability and Smart Technologies
By 2026, sustainability concerns are pushing manufacturers to develop plugs and sockets with longer lifespans, recyclable materials, and energy-monitoring features. Smart outlets compatible with 240V systems—capable of remote control, load balancing, and integration with home energy management systems—are gaining traction, particularly in smart home and commercial applications. These innovations are most prevalent in Type F and Type G ecosystems. -
Safety and Compliance Enhancements
Safety remains a paramount concern, especially in emerging markets. There is a rising emphasis on compliance with IEC standards, child-safe designs, and protection against overload and overheating. Plug manufacturers are investing in certifications and quality control to meet stricter regional regulations, reducing the prevalence of non-compliant or counterfeit products.
Conclusion
As of 2026, the 240V AC plug market is characterized by a tension between regional diversity and the global push for standardization. While legacy plug types remain dominant, forward-looking trends—driven by electrification, EV adoption, and smart technology—are accelerating the development of safer, more efficient, and interoperable solutions. The IEC 60906-1 standard may emerge as a key contender for broader adoption, especially in new infrastructure projects, setting the stage for a more unified 240V plug ecosystem in the coming decade.
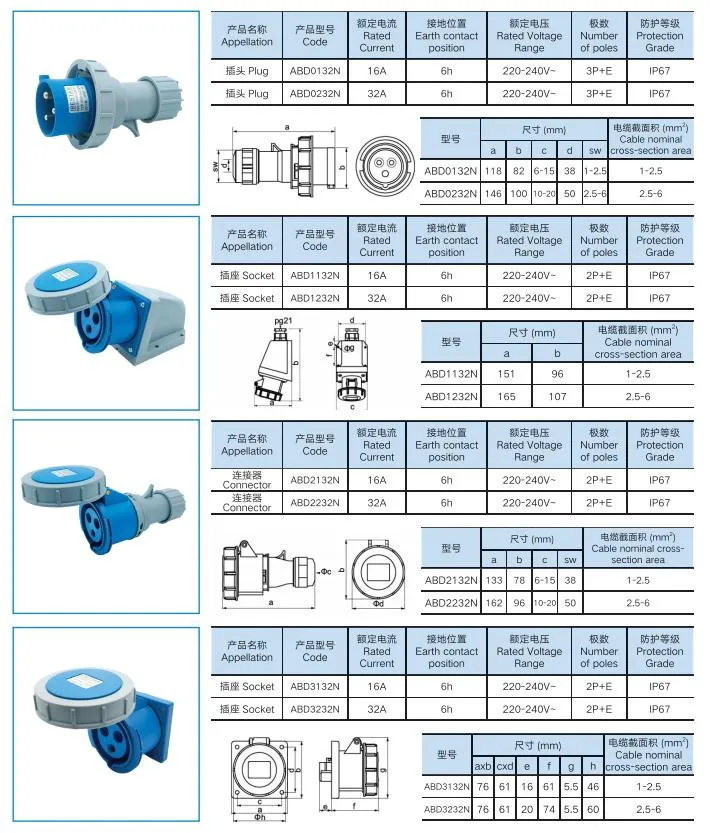
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 240V AC Plug Types (Quality and IP Rating)
When sourcing 240V AC plug types—especially for industrial, commercial, or outdoor applications—focusing solely on voltage compatibility and physical fit can lead to significant issues. Two critical factors often overlooked are build quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating. Below are common pitfalls related to these aspects:
Poor Build Quality Leading to Safety Hazards
One of the most frequent pitfalls is selecting plugs based on cost rather than construction quality. Low-quality 240V plugs may use substandard materials such as brittle thermoplastics or undersized conductors. These can overheat under load, increasing the risk of melting, arcing, or electrical fires. Additionally, poorly manufactured contacts may loosen over time, causing intermittent connections and voltage drops, which compromise both equipment performance and user safety.
Misunderstanding or Misrepresenting IP Ratings
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings define the level of protection against solids and liquids. A common mistake is assuming that all industrial-looking plugs offer adequate environmental protection. For example, selecting an IP44-rated plug for outdoor or wet environments may be insufficient—IP66 or higher is typically required. Worse, some suppliers may falsely advertise IP ratings without third-party certification. Always verify IP ratings through recognized testing standards (e.g., IEC 60529) and request certification documents.
Inadequate Strain Relief and Durability
Low-quality plugs often lack robust strain relief mechanisms, leading to premature cable damage and conductor exposure. In high-movement or industrial settings, this can result in short circuits or electric shock hazards. Ensuring the plug includes a secure, molded strain relief compatible with the cable diameter is essential for long-term reliability.
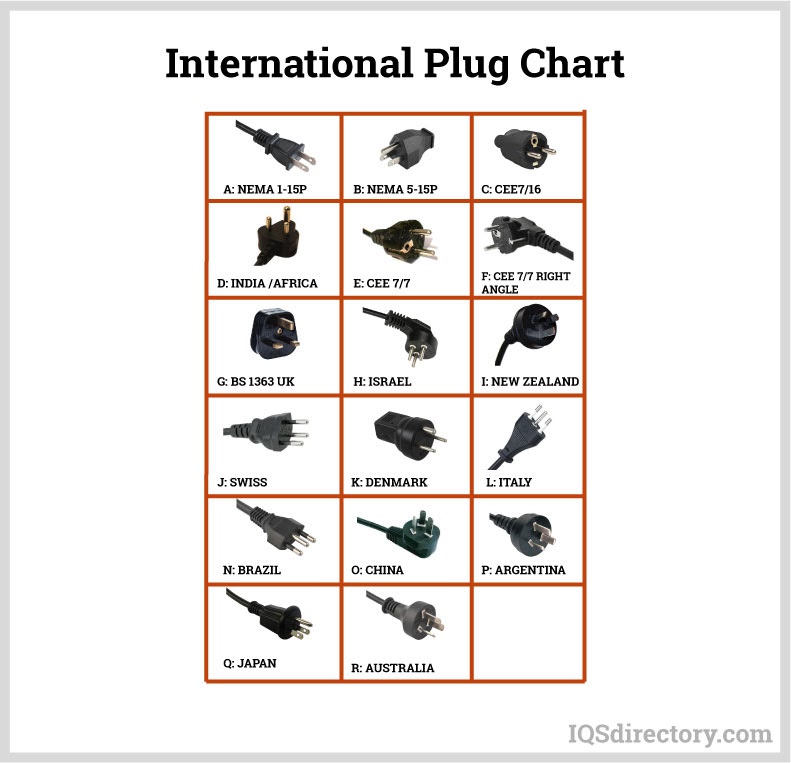
Lack of Compliance with Regional Standards
Different regions use specific 240V plug types (e.g., Type G in the UK, Type I in Australia, Type F in Europe). Sourcing non-compliant or counterfeit plugs can result in poor socket fit, overheating, and failure to meet local electrical codes. Always confirm that the plug meets regional safety certifications (e.g., BS 1363, AS/NZS 3112, CE, or UL).
Overlooking Temperature and Environmental Ratings
Even with proper IP ratings, some plugs are not rated for extreme temperatures or UV exposure. Using standard indoor-rated plugs in outdoor or high-temperature environments accelerates material degradation. Ensure the plug’s temperature class and housing material (e.g., UV-resistant thermoplastic) match the intended operating conditions.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: sourcing from reputable suppliers, verifying certifications, and testing samples under real-world conditions. Investing in high-quality, correctly rated 240V AC plugs ensures safety, compliance, and long-term reliability.
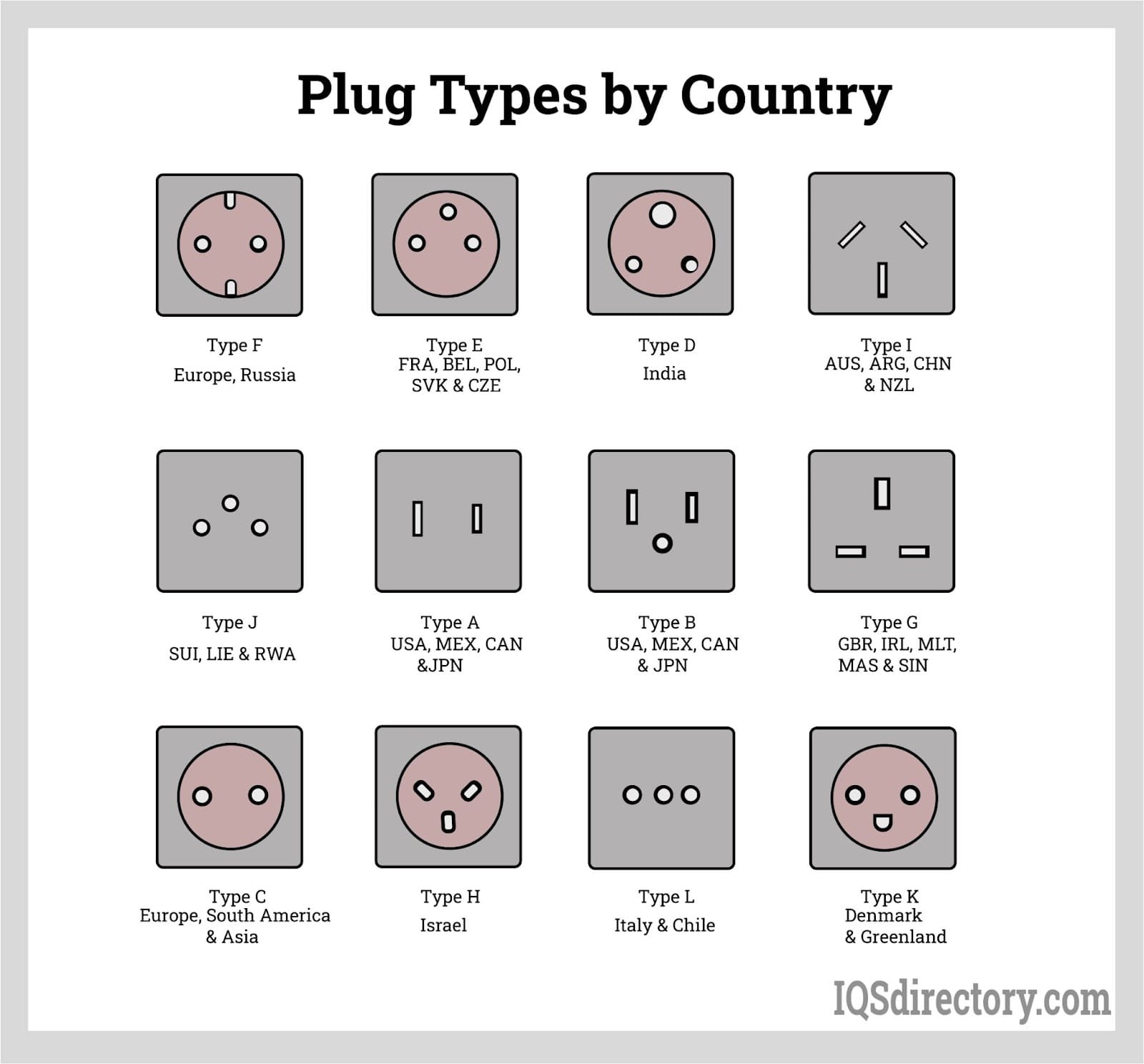
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 240V AC Plug Types
Understanding the logistics and compliance requirements for 240V AC plug types is essential for the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of electrical equipment across international markets. This guide outlines key considerations for manufacturers, distributors, and importers.
Regulatory Compliance by Region
Different countries and regions mandate specific plug types and safety standards for 240V electrical systems. Non-compliance can result in product recalls, fines, or market access denial. Key regions include:
-
Australia, New Zealand, and Pacific Islands (Plug Type I)
Comply with AS/NZS 3112 standards. Plugs must feature angled pins and be rated for 10A or 15A. Certification through the Regulatory Compliance Mark (RCM) is mandatory. -
European Union (Plug Type C, E, F – 230V nominal)
While voltage is typically 230V, systems are compatible with 240V devices. Compliance with CE marking directives (e.g., LVD 2014/35/EU and EMC 2014/30/EU) is required. Type F (Schuko) is common in Germany and much of continental Europe. -
United Kingdom (Plug Type G)
BS 1363 standard governs 240V-compatible plugs. Fused plugs (typically 3A or 13A), insulated pin shrouds, and approval by a UK-recognized certification body (e.g., BSI, Intertek) are mandatory. UKCA marking replaces CE in the UK post-Brexit. -
South Africa (Plug Type M, also uses Type D)
SABS IEC 60884-1 compliance required. Type M (16A) is standard for heavy-duty appliances. SABS approval is mandatory for market entry. -
India (Plug Type C, D, M)
IS 1293 and IS 732 standards apply. Type D (5A/15A) and Type M (15A) are common. BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) certification is legally required.
Voltage Tolerance and Equipment Design
Electrical systems labeled as 240V often operate within a tolerance range (e.g., 220–240V or 230V ±10%). Equipment must be designed to accommodate regional voltage variations. Labeling should indicate input voltage range (e.g., “220–240V AC, 50Hz”) to ensure compatibility and avoid damage.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Clearly indicate the plug type and voltage compatibility on packaging.
- Include multilingual safety warnings where applicable.
- Attach compliance marks (e.g., CE, UKCA, RCM, BIS) visibly on product and packaging.
- Provide user instructions covering correct socket usage and adapter warnings (if applicable).
Logistics and Distribution Considerations
- Plug Variants and SKUs: Maintain region-specific SKUs with correct plug types to avoid last-minute modifications.
- Adapters vs. Hardwired Plugs: Avoid shipping devices with incompatible plugs and external adapters unless compliant with local safety regulations. Hardwiring region-specific plugs is preferred.
- Warehousing and Inventory: Store plug variants separately to prevent misshipping. Use barcode systems to manage regional configurations.
- Returns and Servicing: Establish local service centers capable of handling region-specific electrical configurations.
Certification and Testing
- Partner with accredited testing laboratories (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek) for safety and EMC testing.
- Maintain technical documentation (EC Declaration of Conformity, test reports, risk assessments) for audits.
- Conduct periodic factory inspections if required by certification bodies.
Summary
Adhering to regional 240V AC plug standards ensures regulatory compliance, user safety, and market success. Early integration of compliance planning into product design and supply chain logistics minimizes delays and reduces risk. Always verify local requirements with national standards bodies or legal counsel before market entry.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate 240V AC plug type requires careful consideration of the target region’s electrical standards, safety certifications, and compatibility with local socket configurations. Common plug types for 240V environments include Type G (UK), Type I (Australia, New Zealand), Type D, M, and C (various parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe), each with unique physical and safety characteristics. It is essential to match the plug type to the destination country’s regulatory requirements and voltage specifications to ensure safe and reliable operation of electrical equipment. Additionally, factors such as availability, cost, durability, and compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, BS, AS/NZS) should guide the selection and sourcing process. When in doubt, consulting local regulations or using universally compatible, certified adapters or modular plug solutions can help mitigate risks and ensure compliance.