The global transformer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising electricity demand, grid modernization initiatives, and the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global transformer market was valued at USD 10.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 14.7 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.0% during the forecast period. A key segment within this market is the 240 volt to 24 volt transformer, widely used in industrial automation, HVAC systems, and low-voltage power supplies due to its efficiency in stepping down voltage for safe, reliable operation of control circuits and electronic equipment. With increasing adoption in commercial buildings, manufacturing plants, and smart infrastructure, demand for high-quality, energy-efficient 240V to 24V transformers continues to rise. This growing need has positioned several manufacturers as leaders in performance, innovation, and reliability. Based on market presence, product scalability, and technical specifications, the following six companies stand out as top manufacturers in the 240V to 24V transformer space.
Top 6 240 Volt To 24 Volt Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PowerVolt Group
Domain Est. 2020
Website: powervoltgroup.com
Key Highlights: PowerVolt Group is a leading U.S. manufacturer of industrial and commercial transformers and linear DC power supplies. Over 5000 standard and custom ……
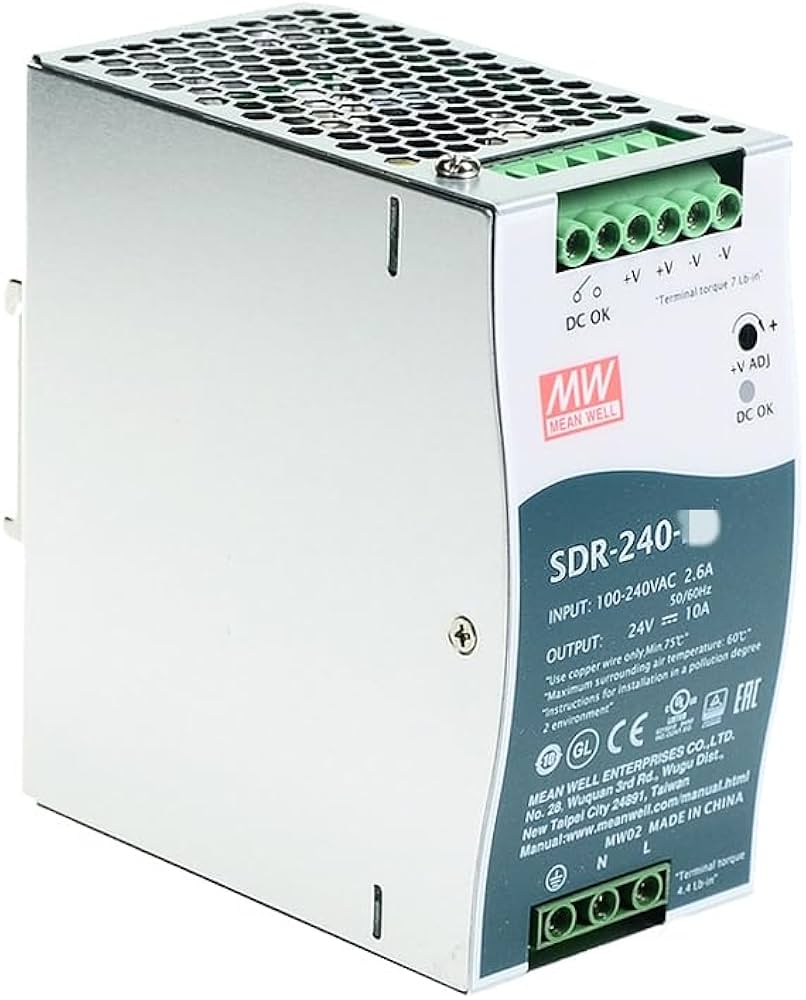
#2 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL offers a comprehensive power solution with our versatile series of power supplies. You can use this product overview tool to find product ……
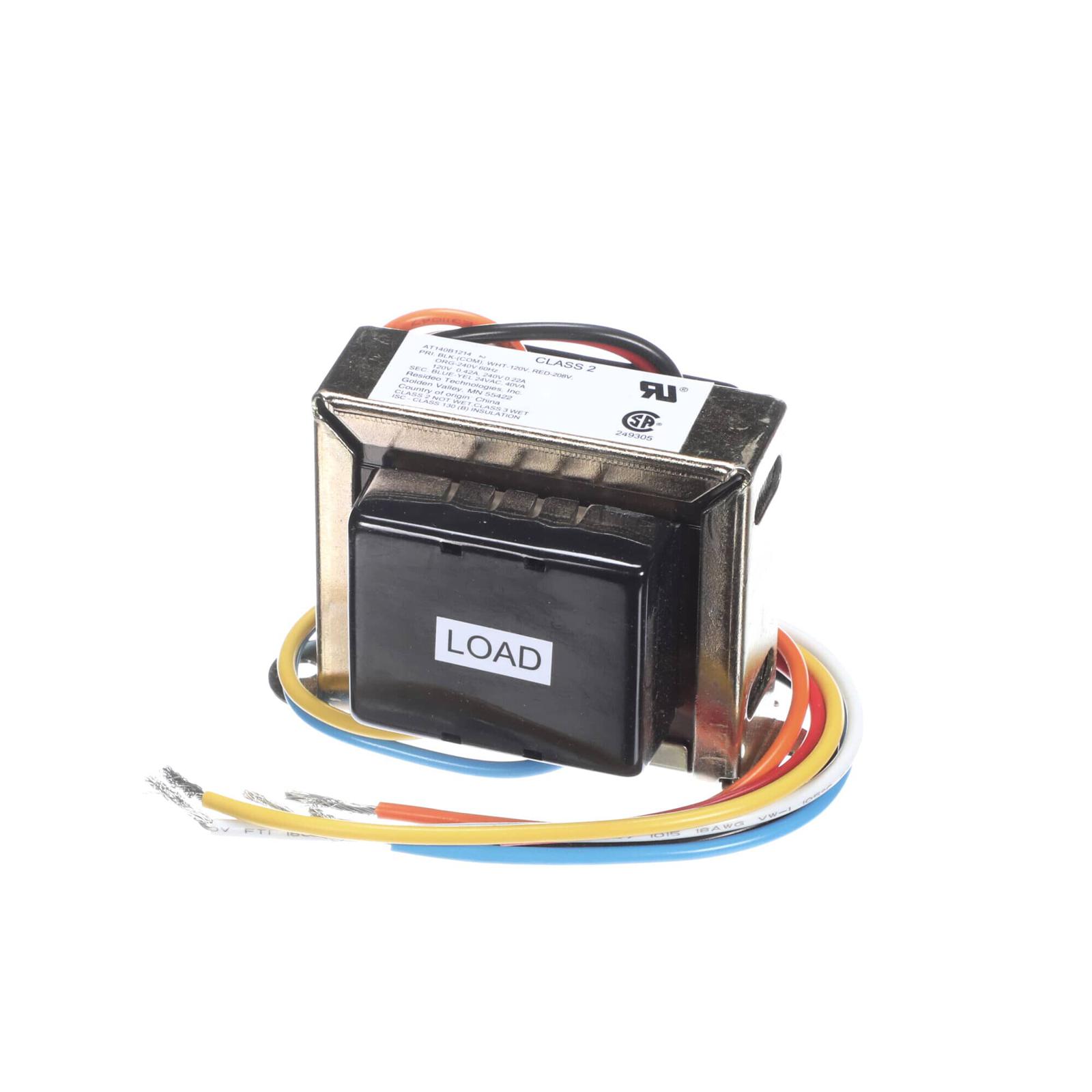
#3 Stoelting 743667 Transformer, 120/208/240 to 24 Volt, 40VA
Domain Est. 2013
Website: partstown.com.mx
Key Highlights: In stockFind OEM Stoelting 743667 Transformer, 120/208/240 to 24 Volt, 40VA replacement part at Parts Town with fast same day shipping on all in-stock orders until ……
#4 Transformers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB’s type QL K-Factor transformers are designed to withstand the additional heating that accompanies the presence of harmonics in electrical systems….
#5 Power Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
#6 24 Volt Transformer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: fire-parts.com
Key Highlights: In stock $8 deliveryBrand: Fire-Parts.com ; Current Stock. Available : 17 ; Available : 17 ; Description. 24 Volt Transformer Primary Voltage: 120/208/240. Secondary Voltage: 24…
Expert Sourcing Insights for 240 Volt To 24 Volt Transformer

2026 Market Trends for 240 Volt to 24 Volt Transformers
The market for 240V to 24V transformers, essential components for stepping down mains voltage for safe, low-voltage applications, is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by technological advancements, energy efficiency mandates, and shifting application demands, key trends will shape the landscape.
Growing Demand in Smart Buildings and Automation
The proliferation of smart home and building automation systems is a primary growth driver. 24V AC/DC power is the standard for powering HVAC controls, security systems (access control, cameras), lighting controls (dimmers, sensors), and building management systems (BMS). As global construction, particularly in smart infrastructure, continues to rise, the demand for reliable, efficient 240V to 24V transformers within these integrated systems will surge. The trend towards centralized control and IoT connectivity necessitates robust and often redundant low-voltage power supplies, boosting the market for these transformers.
Stringent Energy Efficiency Regulations
Regulatory pressure is a major force. Governments worldwide, particularly in Europe (EU Ecodesign Directive) and North America (DoE regulations), are implementing increasingly strict efficiency standards for external power supplies and voltage conversion equipment. By 2026, transformers will need to meet higher efficiency tiers (e.g., moving beyond Level VI to potentially proposed Level VII standards), significantly reducing no-load power consumption and improving active efficiency. This will accelerate the shift away from traditional, less efficient laminated core (toroidal or EI) transformers towards more efficient electronic solutions like switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) and advanced hybrid designs, even where pure AC output is required. Compliance will be non-negotiable for market access.
Dominance of Switch-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
While traditional magnetic transformers will retain a niche for specific applications requiring pure sine wave output or high surge tolerance, SMPS technology will dominate the market by 2026. SMPS units offer superior efficiency (often >85-90%), significantly smaller size and weight, better thermal management, and easier integration of features like over-voltage/over-current protection and regulated DC output. Their ability to meet stringent efficiency standards and provide the stable 24V DC power required by modern electronics makes them the preferred choice for most new installations in lighting, security, and automation.
Focus on Miniaturization, Integration, and Reliability
Driven by space constraints in modern electrical panels and devices, there will be a strong push for smaller, more compact transformer designs. SMPS inherently supports this, but further miniaturization through advanced component integration and thermal design will be key. Reliability and longevity will remain paramount, especially for critical applications like security and fire alarms. Manufacturers will focus on improving component quality (e.g., long-life electrolytic capacitors), thermal management (better heat sinking, conformal coating), and robust protection circuits to ensure transformer lifespans exceed 10-15 years, reducing maintenance costs.
Rise of Hybrid and Smart Transformers
Innovations will bridge the gap between traditional and electronic solutions. “Hybrid” transformers combining a small magnetic stage with efficient electronics might emerge for specific noise-sensitive or high-surge applications. More significantly, “smart” transformers with integrated monitoring (voltage, current, temperature, fault detection) and communication capabilities (e.g., simple dry contacts or even IoT connectivity) will gain traction. These allow for predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and integration into larger building management systems, adding value beyond basic power conversion.
Supply Chain Resilience and Material Innovation
Geopolitical factors and past disruptions will push manufacturers towards more resilient and geographically diversified supply chains. There will be increased focus on sourcing critical components (like semiconductors and magnetics) from stable regions. Material innovation, particularly in magnetics (e.g., advanced amorphous or nanocrystalline cores for niche high-efficiency magnetic transformers) and high-temperature/long-life capacitors for SMPS, will continue to improve performance and reliability.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 240V to 24V transformer market will be characterized by a decisive shift towards high-efficiency SMPS technologies driven by regulation and application needs. Growth will be fueled by the expansion of smart buildings and automation. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver compact, reliable, ultra-efficient, and increasingly intelligent power conversion solutions that meet global regulatory standards while ensuring long-term performance and supply chain stability. The focus will be firmly on value-added, integrated power supply systems rather than basic voltage conversion.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 240 Volt to 24 Volt Transformer (Quality and IP Rating)
Sourcing a 240V to 24V transformer may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to safety hazards, premature failure, or system downtime. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Ignoring Build Quality and Materials
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting transformers based solely on price without evaluating internal construction. Low-quality units often use inferior core materials (like low-grade silicon steel) and copper wire with insufficient gauge or poor insulation. This results in higher energy losses, excessive heat generation, and reduced lifespan. Always verify material specifications and opt for units with UL, CE, or IEC certifications indicating compliance with safety and performance standards.
2. Overlooking Temperature Rise and Insulation Class
Transformers generate heat during operation, and inadequate thermal design can lead to overheating. A common pitfall is choosing a transformer with a high temperature rise (e.g., 80°C or more) without considering the ambient environment. Ensure the unit has an appropriate insulation class (e.g., Class F or H) and a temperature rise rating suitable for your application to prevent insulation breakdown and fire risks.
3. Misjudging Load Requirements and Overloading
Selecting a transformer based only on nominal voltage without accounting for actual load (in VA or watts) can cause chronic overloading. Overloading leads to overheating, voltage drops, and shortened transformer life. Always size the transformer to handle at least 20–25% above the maximum expected load to accommodate inrush currents and future expansion.
4. Neglecting IP Rating for the Environment
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is critical for ensuring suitability in specific environments. A common error is using an indoor-rated transformer (e.g., IP20) in damp or dusty areas. For outdoor, industrial, or washdown environments, choose units with appropriate IP ratings—such as IP65 for dust-tight and water-jet resistance, or IP67 for temporary submersion. Failure to match the IP rating to the environment risks moisture ingress, corrosion, and electrical failure.
5. Assuming All Transformers Are Isolated or Safety Compliant
Not all 240V to 24V transformers provide reinforced isolation or meet safety extra-low voltage (SELV) requirements. In medical, industrial control, or outdoor lighting applications, using a non-isolated or non-compliant transformer can violate electrical codes and endanger personnel. Confirm the transformer meets relevant safety standards (e.g., EN 61558-2-6 for control transformers) and provides proper galvanic isolation.
6. Overlooking Mounting and Ventilation Needs
Poor installation practices—such as enclosing the transformer in a sealed cabinet without ventilation or mounting it near heat sources—can drastically reduce performance and lifespan. Even high-IP-rated transformers require adequate airflow if they are not specifically designed for sealed environments. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for clearance and mounting orientation.
7. Failing to Verify Regulatory and Regional Compliance
Using a transformer not certified for your region’s electrical standards (e.g., UL for North America, CE for Europe) can result in failed inspections, voided warranties, or insurance issues. Always confirm the unit carries the necessary certifications for your location and application.
By addressing these common pitfalls related to quality and IP rating, you ensure a safer, more reliable, and longer-lasting power solution for your 24V system.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 240 Volt to 24 Volt Transformer
Product Overview
A 240V to 24V transformer is an electrical device designed to step down mains voltage (typically 240V AC) to a safer, lower voltage (24V AC) for use in control circuits, industrial equipment, lighting systems (e.g., low-voltage halogen or LED), and HVAC applications. These transformers are essential for ensuring safe and efficient power distribution in commercial, industrial, and residential settings.
Regulatory Compliance
Electrical Safety Standards
- IEC 61558-1 & IEC 61558-2-6: International standards covering safety requirements for power transformers, including insulation, temperature limits, and construction. Transformers must comply with these for global market access.
- UL 5085 (USA): Standard for safety of power transformers, including requirements for dielectric strength, temperature rise, and mechanical durability. Required for sale in North America.
- BS EN 61558-1 (UK/Europe): Harmonized European standard aligning with IEC 61558. Mandatory for CE marking.
- AS/NZS 61558.1 (Australia/New Zealand): Required for compliance in Australia and New Zealand under the Electrical Equipment Safety System (EESS).
CE Marking (Europe)
- Required for all transformers placed on the EU market.
- Indicates conformity with the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU).
- Must be accompanied by a Declaration of Conformity and technical documentation.
RoHS Compliance
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS 2 – Directive 2011/65/EU) applies.
- Ensures the transformer contains no lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, PBB, or PBDE above permitted levels.
- Applies to all electrical and electronic equipment sold in the EU.
REACH Regulation
- Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (EC 1907/2006).
- Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in components.
- Applies to all materials used in transformer construction.
UKCA Marking (United Kingdom)
- Required for products placed on the market in Great Britain (England, Scotland, Wales).
- Replaces CE marking post-Brexit (though CE is still accepted in some cases until 2025).
- Must meet UK statutory requirements equivalent to CE directives.
Logistics Considerations
Packaging
- Use shock-absorbent, anti-static packaging to protect against physical and electrical damage.
- Include moisture-resistant wrapping, especially for sea freight.
- Clearly label with handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”).
- Include safety data sheets (SDS) and compliance documentation in shipping packages.
Labeling Requirements
- Manufacturer name, model number, input/output voltage (240V → 24V), frequency (e.g., 50/60 Hz), power rating (VA or kVA), and serial number.
- Compliance marks: CE, UKCA, UL, or other regional certifications.
- Warning labels (e.g., “For Indoor Use Only,” “Earth Connection Required,” “Do Not Operate Open”).
Transportation
- Air Freight (IATA): Classify as non-hazardous electrical equipment. No special restrictions if no batteries are included.
- Sea Freight (IMDG Code): Standard cargo; ensure proper containerization to prevent moisture ingress.
- Ground Transport (ADR): Not classified as dangerous goods unless containing oil or hazardous materials (typically dry-type transformers are exempt).
Import & Customs
- HS Code: Typically 8504.23 (Reactors and transformers, other than for telecommunication, of power handling capacity ≤1 kVA) or 8504.31 (>1 kVA). Confirm country-specific classifications.
- Import Duties & Taxes: Vary by country. Check local tariff schedules (e.g., US Harmonized Tariff Schedule, EU TARIC).
- Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, certificate of origin, and Declaration of Conformity.
- Customs Compliance: Ensure all certification (CE, UL, etc.) is verifiable and matches declared product specifications.
Storage
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 0°C to 40°C).
- Avoid exposure to dust, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres.
- Keep in original packaging until installation.
Installation & Operational Compliance
Environmental Conditions
- Operate only in well-ventilated, indoor environments unless specifically rated for outdoor or hazardous locations.
- Avoid locations with high humidity, flammable gases, or excessive vibration.
Grounding & Wiring
- Must be properly earthed/grounded per local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the US, IEC 60364 internationally).
- Use correct cable sizes and overcurrent protection (fuse or circuit breaker) as specified by manufacturer.
Maintenance & Inspection
- Periodic inspection for insulation damage, overheating, or corrosion.
- Follow manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and safety guidelines.
Disposal & End-of-Life
WEEE Directive (EU)
- Transformers fall under Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) category.
- Must be collected and recycled through approved schemes.
- Label with the “crossed-out wheeled bin” symbol.
Recycling
- Components (copper windings, steel core, plastic housing) are recyclable.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers.
Summary Checklist
| Requirement | Action Required |
|——————————|————————————————–|
| Safety Certification | Confirm UL, CE, UKCA, or regional certification |
| RoHS/REACH Compliance | Verify material declarations |
| Packaging & Labeling | Use protective packaging with correct labels |
| HS Code & Customs Docs | Include accurate classification and paperwork |
| Transport Mode | Follow IATA/IMDG/ADR as applicable |
| Storage Conditions | Dry, indoor, temperature-controlled |
| End-of-Life Handling | Comply with WEEE or local e-waste laws |
Always consult local authorities and regulatory bodies to ensure full compliance with national and regional requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 240V to 24V Transformer:
After evaluating the technical requirements, safety standards, and supplier options, sourcing a reliable 240V to 24V transformer is essential for safely stepping down mains voltage for low-voltage applications such as control circuits, HVAC systems, lighting, or industrial equipment. Key considerations—including power rating (VA or wattage), efficiency, thermal protection, compliance with regional electrical standards (e.g., UL, CE, IEC), and environmental conditions—must be addressed to ensure safe and reliable operation.
It is recommended to select a transformer from a reputable manufacturer that offers certifications, proven durability, and technical support. Additionally, opting for models with built-in protections such as overcurrent and thermal overload safeguards can enhance system reliability and safety. Whether choosing a toroidal, laminated, or electronic transformer, proper sizing and installation in accordance with local electrical codes are crucial.
In conclusion, a well-sourced 240V to 24V transformer not only ensures efficient voltage conversion but also contributes to the longevity and safety of the connected equipment, making it a critical component in both residential and industrial electrical systems.