The global step-up transformer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by expanding power generation capacities, rising investments in renewable energy integration, and the modernization of aging transmission infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, the global power transformer market size was valued at USD 52.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2024 to 2030. A key contributor to this expansion is the increased demand for step-up transformers—particularly those in the 240 to 480 kV range—used extensively in wind farms, solar power plants, and high-capacity thermal stations to efficiently transmit electricity over long distances. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trend, forecasting a steady CAGR of over 6.5% for the power transformer market through the decade, with Asia-Pacific leading adoption due to ongoing grid upgrades and strong government support for sustainable energy. As demand intensifies, manufacturers specializing in reliable, high-efficiency 240 to 480 kV step-up transformers are playing a pivotal role in enabling grid stability and energy transition. The following list highlights the top eight manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market presence in this critical segment.
Top 8 240 To 480 Step Up Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China 240 To 480 Step Up Transformer Factories
Domain Est. 2024
Website: subian-electric.com
Key Highlights: Looking for a reliable 240 to 480 step up transformer factory? Jiangsu Subian Power Equipment Co., Ltd. offers high-quality transformers for your power ……
#2 3
Domain Est. 1997
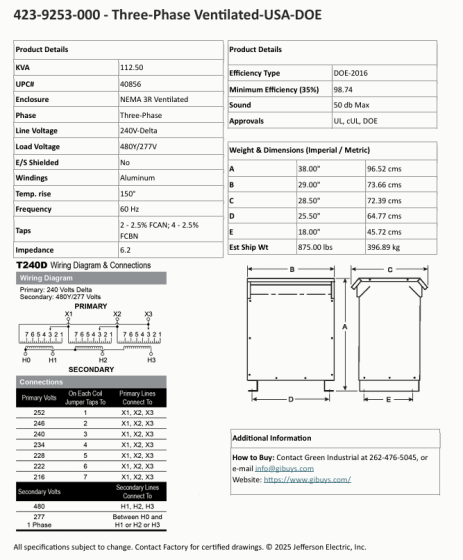
#3 Factory New 112.5 KVA Step Up Dry Transformer 240 Delta 480Y …
Domain Est. 2006
Website: gibuys.com
Key Highlights: In stock 30-day returnsThis is a step up transformer / specially made to take a lower 240 voltage, 3 Phase-3 Wire & step up to 480Y/277 Volts, 3 Phase-4 Wire….
#4 Dry type transformer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: 240 x 480 V (362). 270 V (1). 277 V (39). 380 V (87). 380 V, 400 V, 415 V, 440 V … STEP-UP, ELECTROSTATIC SHIELD (1). VENTILATED (2). WYE-WYE CONFIGURATION ……
#5 MGM assortment now includes step
Domain Est. 2001
Website: mgmtransformers.com
Key Highlights: MGM assortment now includes step-up transformers and other popular voltage configurations · 208D – 480Y/277 GD · 240D – 480Y/277 CD · 480D – 480Y/277 AD · 208D – ……
#6 25 kVA 240/480 Volt to 120/240 Volt Single phase Epoxy …
Domain Est. 2008
Website: canadatransformers.com
Key Highlights: Epoxy Encapsulated Transformer 25 kVA • Single Phase • Primary: 240/480 Volt • Secondary: 120/240 Volt Conductor: Copper. • Frequency 60 Hz….
#7 240v single phase to 480v 3 phase step up transformer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: shinenergy.net
Key Highlights: Shinenergy specializes in manufacturing transformers. If you’re looking for a 240v single phase to 480v 3 phase step up transformer….
#8 Single and 3 Phase Step Up and Down Transformers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: northamericaphaseconverters.com
Key Highlights: NAPCco offers a variety of single and 3 phase step up and down transformers. Compare our quality selection including 240V to 480V options ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 240 To 480 Step Up Transformer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 240 to 480V Step-Up Transformers
The global market for 240 to 480V step-up transformers is projected to experience steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing electrification, industrial modernization, and the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. These transformers, commonly used to boost voltage levels for efficient power transmission in industrial, commercial, and utility applications, are becoming more critical amid rising energy demands and grid modernization efforts.
-
Rising Industrial and Commercial Demand
Industries such as manufacturing, data centers, and commercial real estate are investing heavily in reliable power systems. As equipment and machinery require stable and higher voltage inputs, the need for 240 to 480V step-up transformers increases. The global push toward automation and Industry 4.0 is accelerating infrastructure upgrades, supporting market growth. -
Renewable Energy Integration
The expansion of solar and wind power projects is a key driver. Many renewable energy systems generate power at lower voltages and require step-up transformers to interface with distribution grids. With governments and private sectors committing to net-zero targets, installations of such transformers in solar farms and distributed generation systems will rise through 2026. -
Grid Modernization and Smart Grid Development
Utilities worldwide are modernizing aging power infrastructure to improve efficiency, reduce losses, and integrate distributed energy resources. Step-up transformers play a vital role in local voltage boosting and grid stability. Investments in smart grid technologies are promoting demand for more efficient and digitally monitored transformers. -
Technological Advancements
Manufacturers are focusing on energy-efficient designs, such as low-loss amorphous core transformers and digitally controlled models. Enhanced monitoring via IoT integration allows real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance—features increasingly demanded in critical applications. -
Regional Growth Patterns
- North America and Europe: Driven by grid upgrades and clean energy mandates.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and government infrastructure projects (especially in India and Southeast Asia) are fueling demand.
-
Latin America and Africa: Growing off-grid and mini-grid deployments are increasing the need for compact, reliable step-up solutions.
-
Regulatory and Efficiency Standards
Stricter energy efficiency regulations (e.g., DOE standards in the U.S. and EU Ecodesign directives) are pushing manufacturers to produce compliant, high-efficiency transformers. This is shaping product innovation and influencing procurement decisions. -
Supply Chain and Material Costs
Fluctuations in copper and steel prices remain a challenge. However, advancements in alternative materials and modular designs are helping mitigate cost pressures. Localization of manufacturing is also emerging as a strategy to reduce lead times and logistical risks.
In summary, the 240 to 480V step-up transformer market is poised for sustained growth through 2026, supported by industrialization, renewable energy adoption, and smart infrastructure development. Companies that prioritize efficiency, digital integration, and regional customization will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 240V to 480V Step-Up Transformer (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a 240V to 480V step-up transformer involves several critical considerations, particularly around quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these factors can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, or legal complications. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Components and Construction
One of the biggest risks when sourcing step-up transformers is compromising on build quality. Many low-cost suppliers use substandard materials—such as inferior-grade copper windings, low-efficiency core laminations, or inadequate insulation—leading to overheating, energy loss, and premature failure. Always verify that the transformer meets international standards (e.g., IEEE, IEC, or UL) and request test reports or certifications.
Lack of Proper Certification and Compliance
Transformers used in industrial or commercial applications must comply with regional electrical safety codes. Sourcing units without proper certifications (e.g., CE, UL, CSA) can result in failed inspections, equipment downtime, or non-compliance penalties. Ensure the supplier provides documentation proving compliance with local and international regulations.
Inadequate Thermal and Load Management Design
A poorly designed transformer may not handle continuous load or thermal stress efficiently. Some manufacturers exaggerate power ratings or omit derating information, leading to overheating under real-world conditions. Confirm the transformer’s temperature rise rating (e.g., 80°C, 115°C) and ensure it’s suitable for your operating environment and duty cycle.
Counterfeit or Clone Products
In global markets, especially online, there’s a risk of receiving counterfeit or cloned transformers that mimic reputable brands. These clones often lack the original engineering integrity and may infringe on intellectual property rights. Always source from authorized distributors or directly from established manufacturers with verifiable credentials.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Using or distributing transformers that replicate patented designs, trademarks, or proprietary technology can expose you to legal liability. This is particularly relevant when sourcing OEM/ODM units from overseas suppliers. Conduct due diligence to ensure the product does not violate existing patents or registered designs, and consider including IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts.
Incomplete or Missing Technical Documentation
Reliable transformers should come with comprehensive documentation, including schematics, test reports, nameplate data, and installation manuals. Lack of proper documentation not only hampers integration and maintenance but can also signal that the product is non-compliant or illicitly produced.
No After-Sales Support or Warranty
Low-cost transformers often come with limited or no warranty and minimal technical support. If the unit fails, you may face long downtimes and high replacement costs. Choose suppliers that offer clear warranty terms, responsive customer service, and access to spare parts or repair services.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, insist on compliance documentation, and prioritize long-term reliability over upfront cost savings. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and ensuring IP-safe sourcing practices will safeguard both your operations and legal standing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 240V to 480V Step-Up Transformers
Product Overview and Classification
A 240V to 480V step-up transformer is an electrical device designed to increase input voltage from 240 volts to an output of 480 volts, commonly used in industrial, commercial, and construction applications to match equipment voltage requirements. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the international or domestic shipment, handling, and installation of such transformers.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit. Transformers must be securely mounted on wooden pallets using bracing or crating to minimize movement. Use moisture-resistant wrapping and desiccants to protect against humidity. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. For larger units, include lifting points and follow OEM instructions for rigging and handling to avoid core or winding damage.
Transportation and Shipping
Transport transformers via flatbed trucks or enclosed freight carriers depending on size and weight. Units over 1,000 lbs may require specialized equipment for loading/unloading. Confirm bridge weight limits and route restrictions for oversized loads. Maintain stable temperatures during transit—avoid exposure to freezing conditions or excessive heat. For air or sea freight, comply with IATA or IMDG regulations if applicable (note: most transformers do not contain hazardous materials but may contain insulating oil subject to regulation).
Import/Export Compliance
Verify tariff classifications under the Harmonized System (HS Code). Step-up transformers typically fall under 8504.23.00 (single-phase) or 8504.29.00 (three-phase) in the U.S. HTS, but local classifications may vary. Ensure compliance with export control regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Most standard transformers are classified as EAR99 and do not require a license for most destinations, but confirm based on end-use and destination country.
Electrical and Safety Standards
The transformer must comply with regional electrical safety standards:
– North America: UL 5085 (Standard for Safety of Power Transformers), CSA C22.2 No. 66
– European Union: CE marking per Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and EN 61558 series
– Other Regions: Confirm IEC 61558-1 and local certification (e.g., UKCA, CCC for China, RCM for Australia)
Provide test reports and certification documentation with shipments to facilitate customs clearance and local compliance.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Check whether the transformer contains insulating oil (e.g., mineral oil, silicone fluid). If present, determine if it is classified as a hazardous substance under local environmental laws (e.g., EPA TSCA in the U.S.). PCB-free declaration is required in many jurisdictions. For dry-type transformers, ensure compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations in the EU.
Documentation Requirements
Prepare the following for seamless logistics and customs:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed description, value, HS code)
– Packing List (weight, dimensions, quantity)
– Certificate of Conformity (to UL, CSA, CE, or other standards)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Export Declaration (e.g., AES filing for U.S. exports over $2,500)
– Manufacturer’s Test Reports (dielectric, temperature rise, efficiency)
Installation and Site Compliance
Upon delivery, verify site conditions meet electrical code requirements (e.g., NEC Article 450 in the U.S., IEC 60364 internationally). Ensure proper grounding, ventilation, and clearance per manufacturer specifications. Only qualified electricians should perform installation, following local permitting and inspection protocols. Retain all compliance documentation for audit and insurance purposes.
Warranty and Support Logistics
Coordinate with suppliers or distributors to ensure warranty coverage is transferable and service support is available locally. Maintain records of serial numbers, shipment dates, and compliance certificates for future servicing or regulatory audits.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 240V to 480V Step-Up Transformer:
Sourcing a 240V to 480V step-up transformer requires careful consideration of technical specifications, load requirements, quality standards, and compliance regulations. After evaluating available options, it is clear that selecting the right transformer involves matching the power rating (kVA), efficiency, cooling method, insulation class, and mounting configuration to the specific application—whether for industrial machinery, commercial facilities, or renewable energy systems.
Key factors in the sourcing decision include ensuring the transformer meets national and international standards (e.g., IEEE, UL, CSA), verifying manufacturer reputation and warranty terms, and assessing total cost of ownership, including installation and energy losses. Additionally, considering future scalability and availability of spare parts or service support enhances long-term reliability.
In conclusion, sourcing a reliable and efficient 240V to 480V step-up transformer is critical for safe and stable voltage conversion. By prioritizing quality, compliance, and application-specific requirements, organizations can ensure optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency in their electrical systems.