The global electrical plug and socket market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising construction activities, increasing demand for reliable power connectivity, and the expansion of industrial and residential infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, the global electrical connectors market—of which 230 V plugs are a critical component—was valued at USD 86.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further supported by increasing urbanization, stringent safety standards, and the proliferation of electrical appliances across Europe, Asia Pacific, and North America—regions where 230 V systems are standard. As demand for high-quality, compliant, and durable electrical components rises, the need for reliable 230 V plug manufacturers becomes paramount. From legacy European brands to innovative global suppliers, the following eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders in quality, innovation, and market reach.
Top 8 230 V Plug Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial ……
#3 32A 230V Industrial Mains Plugs & Sockets
Domain Est. 1994
Website: newark.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 60-day returnsBuy 32A 230V Industrial Mains Plugs & Sockets. Newark Electronics offers fast quotes, same day dispatch, fast delivery, wide inventory, ……
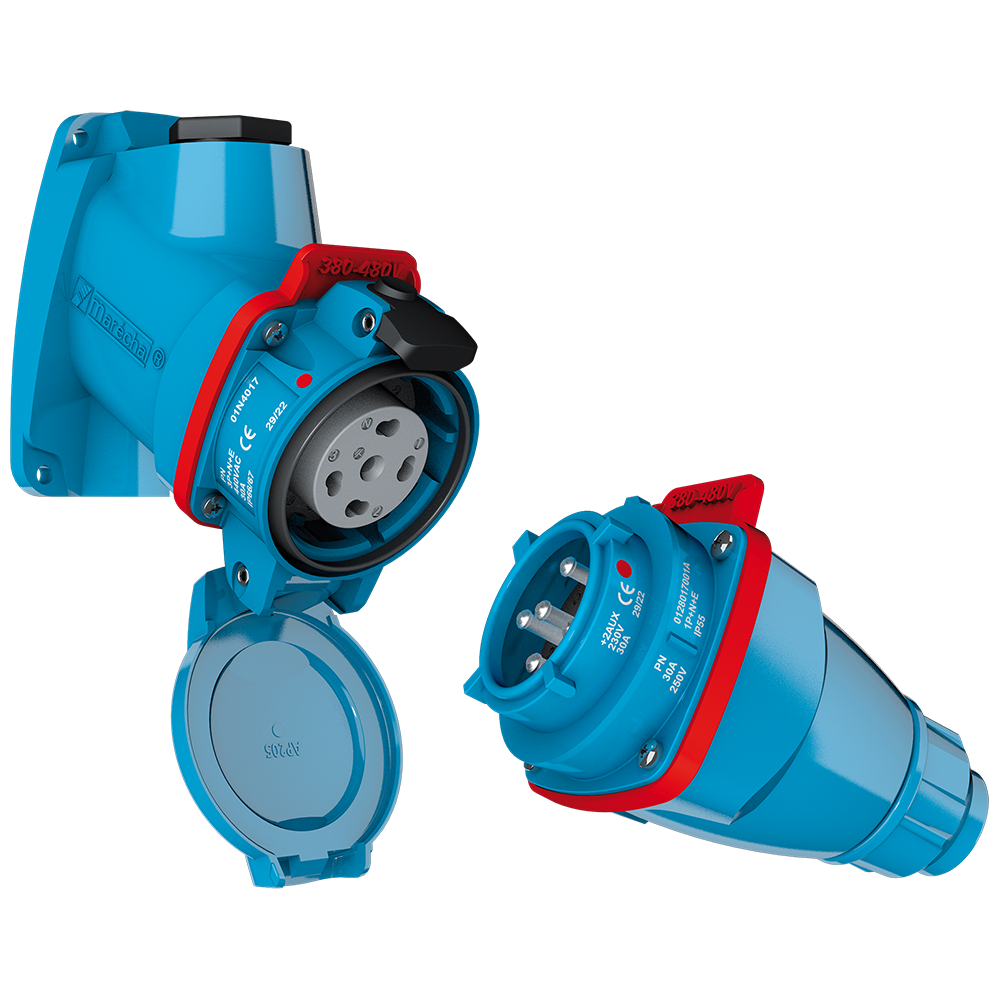
#4 MARECHAL ELECTRIC
Domain Est. 2003
Website: marechal.com
Key Highlights: World specialist in single-pole and multi-contact electrical outlets. High-performance sockets for industrial and ATEX environments….
#5 Plugs and sockets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: catalogue.bals.com
Key Highlights: A large selection of Bals connectors. We manufacture plugs and sockets in different variants and thus cover all your needs for different connection solutions ……
#6 230V Cord and Plug
Domain Est. 1997
#7 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
Key Highlights: Select a location, electric potential or frequency to discover what plug type(s), voltage and frequency are used there….
#8 The best connection
Website: abl.de
Key Highlights: Our Connectivity product range includes connecting devices according to the SCHUKO, French/Belgian and other international electrical standards….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 230 V Plug

H2: Market Trends for 230 V Plugs in 2026
As the global energy and technology landscape evolves, the market for 230 V plugs—commonly used across Europe, much of Asia, Africa, and parts of South America—is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026. Driven by regulatory changes, sustainability initiatives, digitalization, and the rise of smart infrastructure, several key trends are shaping the demand, design, and functionality of 230 V plug systems.
-
Standardization and Harmonization Efforts
By 2026, increased regional and cross-border harmonization of plug standards is expected, particularly within the European Union and ASEAN regions. The EU’s continued push for a universal charging solution (as seen with USB-C for small electronics) may influence broader electrical interface policies. While full plug standardization remains unlikely due to legacy infrastructure, efforts to streamline compatibility and safety certifications will grow, especially for cross-border appliances and electric vehicle (EV) charging. -
Integration with Smart Home Ecosystems
Smart 230 V outlets and plugs are gaining momentum, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% from 2023 to 2026. By 2026, a growing share of 230 V plugs will include IoT capabilities such as energy monitoring, remote control via smartphone apps, voice assistant integration (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant), and AI-driven energy optimization. These smart plugs support energy efficiency goals and are increasingly adopted in residential and commercial buildings. -
Energy Efficiency and Green Regulations
Stricter energy efficiency regulations, such as the EU Ecodesign Directive and Energy Labelling Regulation, are pushing manufacturers to produce low-standby-power and high-efficiency plug systems. By 2026, 230 V plugs used in consumer electronics and appliances are expected to incorporate automatic shut-off features, leakage current reduction, and materials with lower environmental impact. This aligns with net-zero targets and circular economy principles. -
Rise of Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure
The expansion of EV adoption across 230 V markets is a major driver. Most European homes use 230 V single-phase power, making Type F (Schuko) and Type E plugs common for Level 1 and Level 2 EV charging. By 2026, demand for durable, high-current-rated 230 V plug solutions—especially in semi-public and residential charging stations—is expected to surge. Enhanced safety features, overload protection, and smart grid communication (V2G readiness) will become standard. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers toward recyclable, halogen-free, and bio-based materials for plug housings and components. By 2026, leading brands are expected to offer 230 V plugs with extended lifespans, modular designs for easy repair, and take-back programs. Compliance with directives like RoHS and REACH will be mandatory, influencing global supply chains. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
Countries in Africa, Southeast Asia, and South America with 230 V infrastructure are experiencing rising electrification and appliance ownership. This drives volume growth in 230 V plug demand, particularly for affordable, safe, and durable designs. Local manufacturing and regional adaptations (e.g., weather-resistant outdoor plugs) will become more common. -
Cybersecurity and Plug Safety
With the rise of smart plugs, cybersecurity is becoming a critical concern. By 2026, regulatory bodies and industry consortia are expected to enforce stronger cybersecurity standards for connected 230 V plugs to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Concurrently, physical safety features—childproof shutters, arc-fault detection, and temperature monitoring—will become more widespread.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 230 V plug market will be characterized by smarter, safer, and more sustainable solutions shaped by digital integration, regulatory pressure, and evolving consumer needs. While legacy plug types will persist, innovation will focus on intelligence, energy efficiency, and interoperability—positioning the humble plug as a key node in the future energy ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 230 V Plugs (Quality and IP Rating)
Sourcing 230 V plugs, especially for industrial, commercial, or safety-critical applications, requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking key factors can lead to safety hazards, product failures, or non-compliance. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Materials and Construction
One of the most frequent issues is selecting plugs made from substandard materials. Low-cost alternatives may use brittle plastics, undersized conductors, or inadequate insulation. These can lead to overheating, arcing, or mechanical failure under normal use. Always verify that the plug meets relevant standards (e.g., IEC 60309, VDE, BS 1363) and use reputable suppliers with verifiable certifications.
Misunderstanding or Misrepresenting IP Ratings
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating indicates a plug’s resistance to dust and water. A common mistake is assuming that any outdoor-rated plug is sufficient, without checking the exact IP code. For example, IP44 offers basic splash resistance, but IP67 is required for temporary submersion. Using an IP44 plug in a high-moisture environment can result in short circuits or electric shock. Always match the IP rating to the environmental conditions.
Inadequate Strain Relief and Cable Grip
Low-quality plugs often lack effective strain relief mechanisms. Without proper cable anchoring, repeated movement or tension on the cord can damage internal connections, leading to loose wires, overheating, or disconnection. Ensure the plug design includes robust strain relief that secures the cable sheath and prevents stress on solder joints or terminals.
Non-Compliance with Regional Standards
Electrical regulations vary by country (e.g., Schuko in Germany, BS 1363 in the UK, CEI 23-50 in Italy). Sourcing a plug that meets one standard does not guarantee compliance elsewhere. Using non-compliant plugs can void insurance, fail inspections, or pose legal liability. Always confirm regional certification requirements before procurement.
Overlooking Temperature and Current Ratings
Some plugs are rated only for intermittent or low-duty use. Exceeding the specified current (e.g., 16 A vs 32 A) or operating in high-temperature environments without a suitable rating can degrade insulation and contacts over time. Verify both the current-carrying capacity and temperature class (e.g., up to 120°C) match the application demands.
Fake or Counterfeit Certifications
Be cautious of suppliers claiming certifications (such as VDE, UL, CE) without providing verifiable documentation. Counterfeit markings are common in low-cost markets. Request test reports or certification files from accredited bodies to confirm authenticity.
Poor Sealing and Gasket Degradation
Even with a high IP rating, poor-quality seals or rubber gaskets can degrade quickly due to UV exposure, ozone, or temperature cycling. This leads to compromised protection over time. Choose plugs with durable, weather-resistant elastomers (e.g., silicone or EPDM) and inspect gasket integrity upon delivery.
By addressing these pitfalls during the sourcing process, you can ensure reliable, safe, and compliant 230 V plug installations. Always prioritize certified, high-quality components from trusted manufacturers over cost savings that risk performance and safety.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 230 V Plug
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for products equipped with or intended for use with a 230 V plug, ensuring safe, legal, and efficient distribution and operation.
H3: Voltage & Electrical Safety Compliance
- Regional Voltage Standards: Confirm the nominal voltage (230 V) aligns with the target market’s standard (e.g., EU, UK, Australia, most of Asia/Africa). Tolerance is typically ±10% (207–253 V).
- Plug Type Certification: The physical plug must match the destination country’s standard (e.g., Type C/E/F in EU, Type G in UK, Type I in Australia). Ensure the plug is certified to local safety standards.
- Product Certification: The entire product must carry relevant safety marks:
- EU/EEA: CE Marking (covering Low Voltage Directive – LVD, EMC Directive, RoHS).
- UK: UKCA Marking (or CE until 2025 for most goods).
- Australia/NZ: RCM Mark (AS/NZS 3112, AS/NZS 60335).
- Other Markets: Identify required marks (e.g., CCC for China, KC for Korea).
- Safety Standards: Product must comply with IEC/EN 60335-1 (Household Appliances Safety) or relevant product-specific standards (e.g., IEC 60950-1 for IT equipment, IEC 60065 for AV equipment).
- Electrical Safety Testing: Conduct mandatory testing for insulation resistance, dielectric strength (hi-pot), leakage current, and grounding continuity (if applicable).
H3: Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- EMC Directives: Comply with EMC regulations to prevent interference with other devices and ensure immunity to common disturbances.
- Testing Requirements: Perform conducted and radiated emissions testing, and immunity testing (ESD, surge, fast transients, RF fields).
- Standards: Adhere to harmonized standards like EN 55032 (emissions) and EN 55035 (immunity) for multimedia equipment, or relevant product-specific standards.
H3: Environmental & Chemical Compliance
- RoHS (EU/China/UK/etc.): Restrict hazardous substances (Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, etc.) in electrical equipment. Requires material declarations and testing.
- REACH (EU): Register, evaluate, and restrict chemicals. Ensure no use of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) above thresholds.
- WEEE (EU/UK/etc.): Register as a producer in target countries and provide take-back/financing for end-of-life product recycling. Mark product with “crossed-out wheeled bin” symbol.
- Battery Directives (if applicable): Comply with collection and labeling requirements for batteries.
H3: Packaging & Labeling
- Voltage & Frequency: Clearly label input voltage (e.g., “230 V ~ 50 Hz”) and power consumption (W or VA) on the product and packaging.
- Safety Symbols: Use standardized symbols (e.g., warning for high voltage, earth connection symbol).
- Manufacturer/Importer Info: Display the name, trademark, and address of the manufacturer or authorized representative.
- Compliance Marks: Prominently display required certification marks (CE, UKCA, RCM, etc.).
- Language: Labels and user manuals must be in the official language(s) of the destination country.
- User Manual: Include safety instructions, operating instructions, maintenance, and disposal information compliant with local regulations.
H3: Logistics & Supply Chain
- Plug Variants: Manage inventory for different plug types if selling in multiple regions. Clearly label packaging to prevent wrong plug shipment.
- Packaging Integrity: Ensure packaging protects against moisture, physical damage, and static discharge during transit. Use anti-static bags if sensitive electronics.
- Shipping Documentation: Include accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and safety data sheets (if required). Declare voltage and plug type clearly.
- Transport Regulations:
- Lithium Batteries: If included, comply with IATA DGR (air) or IMDG Code (sea) for lithium battery transport (marking, packaging, documentation).
- General: Follow standard hazardous materials regulations if applicable (e.g., for certain chemicals in displays).
- Warehousing: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments. Avoid stacking that damages plugs or cables.
H3: Import/Export Regulations
- Customs Classification: Use correct HS (Harmonized System) codes for accurate duty/tax calculation.
- Product-Specific Regulations: Research any import bans, restrictions, or special permits (e.g., for radio equipment, medical devices).
- Local Representative: In the EU, appoint an Authorized Representative; in the UK, a UK Responsible Person if the manufacturer is outside the territory.
- Technical Documentation: Maintain comprehensive technical files (risk assessment, design specs, test reports, certificates) available for market surveillance authorities.
H3: Post-Market Surveillance & Recalls
- Incident Reporting: Establish a system to monitor and report safety incidents or non-compliances to relevant authorities (e.g., RAPEX in EU).
- Traceability: Implement batch/lot numbering for effective recalls if needed.
- Recall Plan: Have a clear procedure for communicating and executing product recalls.
Key Takeaway: Compliance is not a one-time task. Regularly monitor regulatory changes in target markets and conduct internal audits to maintain ongoing conformity. Always consult with local regulatory experts or notified bodies for specific product and market requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing a 230V plug requires careful consideration of regional electrical standards, safety certifications, and compatibility with both the device and the local power infrastructure. It is essential to identify the correct plug type (such as Type C, D, E, F, G, etc.) based on the target country’s regulations and ensure the plug is rated for the appropriate voltage and current (typically 230V, 50Hz in most regions). Sourcing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers that comply with international standards (e.g., CE, BS, IEC) ensures reliability and safety. Additionally, considering factors such as durability, cable length, and ease of installation can enhance user satisfaction and product performance. Proper vetting of suppliers, including assessing quality control and lead times, will ultimately contribute to a successful and cost-effective sourcing strategy for 230V plugs.