The global 2205 duplex stainless steel market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in oil & gas, chemical processing, and desalination industries due to the material’s exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and cost-efficiency over traditional austenitic grades. According to Grand View Research, the global duplex stainless steel market size was valued at USD 10.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, with 2205 (S32205/S31803) accounting for the largest segment due to its balanced microstructure and widespread applicability in aggressive environments. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period (2023–2028), highlighting increased infrastructure investments and offshore energy projects as key growth drivers. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in producing high-quality 2205 duplex stainless steel, setting industry benchmarks for consistency, innovation, and technical expertise. Here are the top nine global manufacturers shaping the future of this critical alloy.
Top 9 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Duplex Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rolledalloys.com
Key Highlights: Duplex stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy characterized by its dual-phase microstructure, offering a unique combination of high strength and ……
#2 Duplex 2205 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: voestalpine.com
Key Highlights: Duplex 2205 Stainless Steel – UNS S31803. High chloride stress corrosion resistance at high strength, superior to 304/316 grades in corrosion performance, ……
#3 Duplex 2205 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pennstainless.com
Key Highlights: Duplex 2205 is a two-phase, ferritic, austenitic 22% chromium, 3% molybdenum, 5 to 6% nickel alloyed stainless steel. It is the most widely used duplex ……
#4 Applications of Duplex Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: titanmf.com
Key Highlights: TITAN regularly designs, engineers and fabricates multiple types of applications of Duplex Stainless Steel and custom process equipment….
#5 2205 stainless steel plates
Domain Est. 2001
Website: usa.myjacquet.com
Key Highlights: 2205 duplex stainless steel is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex alloy composed of approximately equal parts austenite and ferrite. It offers superior strength and ……
#6 Duplex 2205 & 2507 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 2003
Website: beststainless.com
Key Highlights: Our Duplex 2205 Stainless Steel is a nitrogen-enhanced duplex used in applications requiring high strength and excellent corrosion resistance….
#7 Duplex Stainless Steels 2205
Domain Est. 2008
Website: americanspecialmetals.com
Key Highlights: Duplex Stainless Steels is designated as UNS S31803, UNS S32205. It is listed in NACE MR-01-75 for oil and gas service….
#8 ASTM A240 Type 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Sheet
Domain Est. 2010
Website: sabrealloys.com
Key Highlights: ASTM A240 type duplex 2205 sheet gives you superior performance in harsh conditions because it withstands high levels of stress and corrosion….
#9 Duplex stainless steel
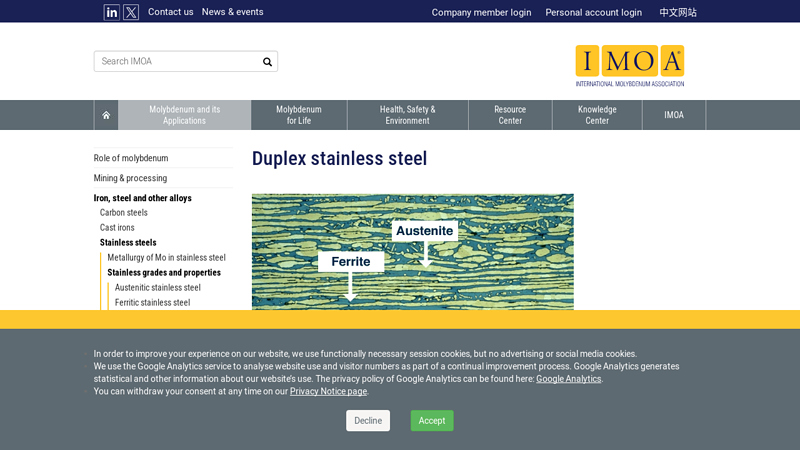
Website: imoa.info
Key Highlights: The 2205 grade has a yield strength that is more than twice that of Type 316 and a pitting and crevice corrosion resistance that is similar to Type 904L ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel

H2: Projected Market Trends for 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel in 2026
By 2026, the global market for 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel is expected to experience sustained growth driven by increasing demand across key industrial sectors, technological advancements in material processing, and a shift toward corrosion-resistant, high-performance alloys in aggressive environments.
-
Growing Demand in Oil & Gas and Chemical Processing
The oil and gas industry remains a primary consumer of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel due to its excellent resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking, high strength, and durability in offshore and subsea applications. With continued investments in deepwater drilling and LNG infrastructure—particularly in regions like the Middle East, North America, and Southeast Asia—demand for 2205 is projected to rise. Additionally, the chemical processing industry is increasingly adopting 2205 for piping, heat exchangers, and reactors, where resistance to acids and chlorides is critical. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy and Desalination Projects
The global push toward renewable energy and water security is fueling demand for 2205 in desalination plants and offshore wind farms. Its superior performance in saline environments makes it ideal for seawater handling systems and structural components exposed to marine conditions. Countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and North Africa, investing heavily in large-scale desalination, are expected to be major contributors to market growth. -
Infrastructure and Construction Applications
Urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging markets are leading to increased use of 2205 in architectural cladding, bridges, and wastewater treatment facilities. Its combination of mechanical strength and corrosion resistance reduces lifecycle costs, making it attractive for long-term infrastructure projects, especially in coastal and high-humidity regions. -
Supply Chain and Production Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain dominant in both production and consumption. Chinese manufacturers are investing in advanced refining techniques such as AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) to improve nitrogen content control, enhancing the consistency and performance of 2205 grades. However, volatility in raw material prices—especially nickel and molybdenum—may impact production costs, prompting research into optimized alloying and recycling methods. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Drivers
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are encouraging industries to adopt longer-lasting, recyclable materials. 2205’s high recyclability and extended service life align with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) objectives, further boosting adoption. Regulatory standards such as ISO 15156 for materials in H2S environments will continue to support its specification in upstream oil and gas operations. -
Technological Advancements and Market Competition
Ongoing R&D is focused on improving weldability and formability of 2205, reducing fabrication challenges. Competing materials, such as super duplex and lean duplex stainless steels, may pressure pricing and market share, but 2205 is expected to maintain its position as the most balanced and cost-effective solution for mid-range corrosive environments.
In summary, the 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel market in 2026 will be shaped by robust demand in energy, water, and infrastructure sectors, supported by material performance advantages and evolving sustainability mandates. Market expansion is projected at a CAGR of approximately 5–6% from 2023 to 2026, with Asia-Pacific and the Middle East leading regional growth.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (Quality & IP)
Sourcing 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel requires diligence to avoid significant quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Key pitfalls include:
- Substandard Material Composition & Microstructure: Suppliers may provide material with incorrect alloying element ratios (e.g., insufficient Cr, Mo, N; excessive C) or improper heat treatment, leading to inadequate ferrite/austenite balance. This compromises corrosion resistance (pitting, stress corrosion cracking) and mechanical strength.
- Insufficient/Inaccurate Certification: Accepting Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) without verifying traceability (heat/lot numbers), full chemical analysis, mechanical properties (yield, tensile, impact), and corrosion test results (e.g., ASTM G48 ferric chloride) risks receiving non-compliant material.
- Counterfeit or Diverted Material: Unscrupulous suppliers may re-label lower-grade stainless steel (e.g., 316L) or sell material diverted from other projects as 2205, often with forged documentation.
- Inadequate Quality Control & Traceability: Poor record-keeping, lack of third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, BV), and insufficient process control during manufacturing (melting, forging, heat treatment) increase the risk of undetected defects.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement: Using proprietary 2205 variants (e.g., SAF 2205™, ZERON® 100) without proper licensing from the original developer (e.g., Outokumpu, Rolled Alloys) can lead to legal disputes, supply chain disruptions, and reputational damage. Generic “2205” may not meet the performance of licensed grades.
- Poor Welding & Fabrication Practices: Sourcing material without ensuring the supplier/fabricator has expertise in duplex steel welding (proper shielding, interpass temperature control, post-weld heat treatment) risks creating harmful secondary phases (e.g., sigma phase, chi phase) that embrittle the material.
Mitigation: Source from reputable, certified suppliers (ISO 9001, PED, NORSOK), demand full traceability and validated MTCs, conduct independent material testing (PMI, metallography), verify IP rights for branded grades, and ensure fabrication partners are qualified for duplex stainless steel.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel
2205 Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S32205/S31803) offers excellent strength and corrosion resistance, but its handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance require specific protocols. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, efficient, and compliant logistics.
H2.1 Material Handling & Storage
- Contamination Prevention:
- Segregation: Store 2205 separately from carbon steel, low-alloy steel, and dissimilar metals. Use dedicated racks, pallets, or clearly marked areas. Never place 2205 directly on carbon steel surfaces (e.g., truck beds, warehouse floors) without protective barriers (plastic sheeting, wood).
- Tools: Use dedicated, clean tools (cutting, grinding, lifting) for 2205 only. Clean any tools used on carbon steel thoroughly before contacting 2205. Prevent iron particle embedment (ferritic contamination) which can initiate corrosion.
- Cleaning: Keep surfaces clean and dry. Remove dirt, debris, chlorides (salts, seawater splashes), and moisture promptly. Avoid contact with carbon steel shavings or grinding dust.
- Lifting & Rigging:
- Use lifting slings, hooks, and clamps made of stainless steel or non-metallic materials (e.g., synthetic web slings) to prevent surface damage and contamination. Steel cables/wire ropes can cause galling and embed iron.
- Ensure lifting points are designed for the material’s weight and avoid point loads that could damage edges or surfaces.
- Storage Environment:
- Dry & Covered: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area whenever possible. Protect from rain, snow, and high humidity.
- Elevated: Keep material off the ground on clean, dry, non-metallic supports (wood skids, plastic pallets).
- Protection: Cover with breathable, non-chlorinated plastic sheeting if outdoor storage is unavoidable. Ensure ventilation to prevent condensation buildup underneath the cover. Do not use PVC sheeting (chloride risk).
- Duration: Minimize storage time, especially in harsh environments. Inspect stored material periodically for signs of corrosion or contamination.
H2.2 Transportation
- Vehicle Preparation:
- Cleanliness: Thoroughly clean the transport vehicle (truck, container, railcar) before loading. Remove all debris, dirt, oils, and especially carbon steel shavings/dust.
- Protection: Line the vehicle bed with clean, dry, non-metallic material (e.g., plywood, plastic sheeting). Avoid direct contact with carbon steel surfaces.
- Loading & Securing:
- Follow H2.1.1 lifting and handling procedures during loading.
- Secure loads firmly to prevent movement, shifting, or impact during transit. Use appropriate straps, chains (with protective sleeves), or blocking.
- Prevent contact between 2205 loads and carbon steel loads on the same vehicle unless effectively isolated.
- Protection During Transit:
- Cover loads with clean, non-chlorinated, breathable tarps or use enclosed containers to protect from weather, road spray, and debris.
- Avoid routes through areas with high salt spray (e.g., near oceans in winter) if possible, or ensure robust protection.
- Minimize transit time where feasible.
- Documentation: Ensure shipping documents clearly identify the material as “2205 Duplex Stainless Steel” and include any special handling instructions.
H2.3 Regulatory Compliance & Documentation
- Material Certification (MTC/COA):
- Essential: Always require and verify the Mill Test Certificate (MTC) or Certificate of Analysis (COA) from the supplier/manufacturer.
- Key Data: The MTC must confirm compliance with the relevant standard (e.g., ASTM A240, ASTM A182, ASTM A790, EN 10088-1) and specify:
- Heat/lot number traceability.
- Chemical composition (verified against standard limits for Cr, Ni, Mo, N, etc.).
- Mechanical properties (Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, Elongation, Hardness – typically Rockwell B or C).
- Impact test results (if required by specification, e.g., Charpy V-notch at low temperatures).
- Corrosion test results (e.g., Ferroxyl test for surface iron, ASTM A923 intergranular corrosion test – often required for critical applications).
- Non-Destructive Examination (NDE) results (e.g., UT, PT, MT – as per order requirements).
- Hazard Communication (GHS/SDS):
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Obtain the current SDS from the supplier. While 2205 is generally considered low hazard in solid form, the SDS details hazards during processing (e.g., fumes from welding/grinding, potential for eye/skin irritation from dust, fire hazard if finely divided).
- Labeling: Ensure containers or bundles are labeled with the material grade (2205, S32205) and any relevant hazard warnings (primarily for processing, not handling solid product).
- Customs & Import/Export (International Shipments):
- Classification: Verify correct HS (Harmonized System) code for 2205 (e.g., 7219.32.xx for flat-rolled, 7222.20.xx for bars, 7304.41.xx for seamless tubes). Accuracy is crucial for duties and regulations.
- Origin: Provide proof of origin (e.g., Certificate of Origin) if required for trade agreements or quotas.
- Export Controls: Check if the material or its intended end-use falls under any export control regulations (e.g., dual-use items, ITAR – though less common for standard 2205, specific high-purity or nuclear grades might be restricted). Consult relevant authorities (e.g., BIS in the US).
- Industry-Specific Standards:
- Pressure Vessels/Piping (ASME): If used in ASME Code vessels or piping, material must comply with ASME Section II specifications (e.g., SA-240, SA-182, SA-790) and require full documentation traceability (MTRs) as part of the vessel/piping file.
- NACE MR0175/ISO 15156: For sour (H2S-containing) oil & gas environments, verify the material meets the requirements of this standard, particularly regarding hardness limits (typically max 32 HRC for 2205 in this service) and potentially requiring specific heat treatment and testing. The MTC must explicitly state NACE compliance if required.
- Nuclear (N-stamp): Nuclear applications require the most stringent traceability and documentation (e.g., NQA-1 compliance), often including full heat trace and specific NDE requirements.
Key Takeaway: Meticulous attention to preventing contamination (especially iron), maintaining dry storage, using proper handling tools, and ensuring comprehensive, verifiable documentation (especially the MTC) are the cornerstones of successful logistics and compliance for 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Always confirm specific requirements with your supplier and end-user specifications.
Conclusion for Sourcing 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel:
Sourcing 2205 duplex stainless steel proves to be a strategic decision for applications requiring a superior balance of corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength, and cost-efficiency. Its dual-phase microstructure offers enhanced performance in aggressive environments—particularly in chloride-rich, marine, and chemical processing applications—reducing the risk of stress corrosion cracking compared to standard austenitic grades like 316L.
When sourcing, it is critical to partner with reputable, certified suppliers who adhere to international standards (such as ASTM A240, A789, and ISO 14344) and provide full material traceability (mill test certificates, PMI reports). Evaluating factors such as lead times, quality control processes, fabrication support, and competitive pricing further ensures a reliable and efficient supply chain.
In summary, sourcing 2205 duplex stainless steel from qualified suppliers not only meets technical and regulatory requirements but also contributes to long-term operational reliability and reduced lifecycle costs in demanding industrial environments.