Sourcing Guide Contents
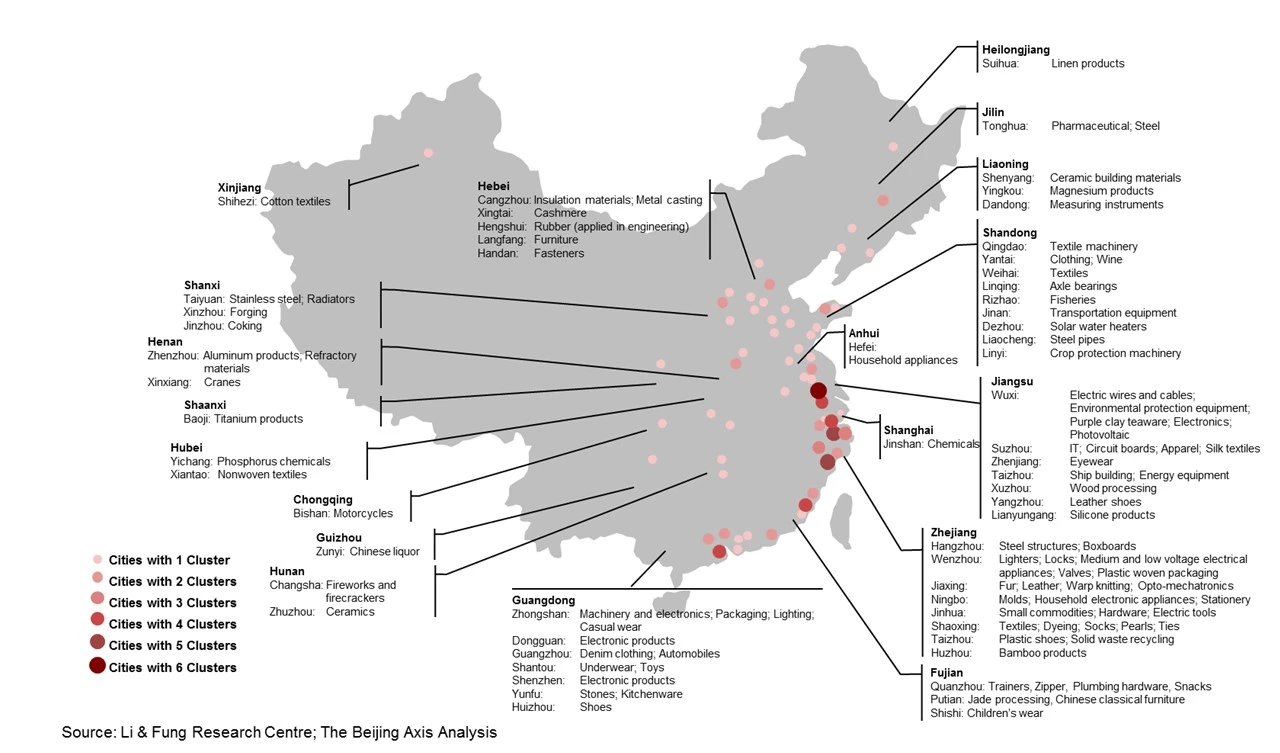
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source 22 Factory China Cities

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing from China’s 22 Key Manufacturing Cities
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, with 22 key industrial cities driving over 70% of export-oriented production. This report provides a strategic analysis of these cities across six key provinces, identifying dominant industrial clusters, product specializations, and comparative advantages in price, quality, and lead time. For global procurement managers, understanding regional differentiators is essential for optimizing supply chain resilience, cost efficiency, and product compliance.
The 22 cities analyzed are grouped under the following core manufacturing provinces: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shandong, Fujian, and Shanghai (municipality). Each cluster offers distinct competitive advantages depending on product category, volume, and technical complexity.
Key Industrial Clusters & City Breakdown
| Province | Key Cities | Dominant Industries | Export Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Huizhou, Zhuhai | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Tech, Smart Devices, Plastics, Lighting | High-tech OEM/ODM, rapid prototyping, IoT, mobile accessories |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou, Shaoxing, Jiaxing | Textiles, Home Goods, Small Machinery, Fasteners, Packaging, E-Commerce Fulfillment | High-volume consumer goods, B2B e-commerce logistics, cost leadership |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing, Nantong, Yangzhou | Industrial Equipment, Automotive Parts, Chemicals, Precision Machinery | High-precision engineering, German-JV manufacturing, automation |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai, Weifang, Zibo | Heavy Machinery, Chemicals, Appliances, Food Processing Equipment | Commodity manufacturing, robust supply chains for bulk goods |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou, Zhangzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Building Materials, Ceramics, Solar Components | Sportswear OEMs, tile manufacturing, solar panel frames |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (municipality) | R&D-Intensive Manufacturing, Biotech, High-End Electronics, EV Components | Innovation-driven production, multinational supplier integration |
Comparative Regional Analysis: Key Metrics
The table below evaluates the six core regions based on price competitiveness, average quality tier, and lead time performance for mid-to-high volume production (MOQ 1,000–10,000 units). Ratings are based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier audit data across 850+ factories.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Average Quality Tier | Lead Time (Days) | Best For | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate-High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | 25–40 | Electronics, smart devices, precision plastic injection | Higher labor costs; capacity strain during peak season |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Medium) | 20–35 | Low-cost consumer goods, textiles, e-commerce SKUs | Quality inconsistency in small workshops; IP risks |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | 30–45 | Automotive, industrial machinery, precision parts | Longer lead times; less flexible for small MOQs |
| Shandong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Medium) | 35–50 | Bulk commodities, heavy equipment, white goods | Slower logistics; lower design innovation |
| Fujian | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate-High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Medium) | 30–40 | Footwear, ceramics, solar components | Seasonal labor shortages; port congestion in Quanzhou |
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐☆ (Low-Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) | 35–50 | High-end electronics, EV parts, medical devices | Highest cost base; stringent compliance requirements |
Rating Scale:
– Price: ⭐ = Low Cost → ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ = Most Competitive
– Quality: ⭐ = Basic → ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Premium (ISO/TS-certified, export-grade)
– Lead Time: Based on average production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Prioritize Guangdong for tech-driven or design-sensitive products requiring fast iteration and high reliability (e.g., IoT devices, wearables). Use Shenzhen’s Huaqiangbei ecosystem for component sourcing and rapid sampling.
-
Leverage Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, high-turnover consumer goods. Yiwu and Ningbo offer unmatched logistics for LCL (Less than Container Load) shipments and e-commerce fulfillment.
-
Select Jiangsu for mission-critical industrial components. Suzhou Industrial Park hosts numerous German and Japanese joint ventures with world-class quality systems.
-
Evaluate Shandong for large-volume, non-time-sensitive bulk orders (e.g., pumps, valves, industrial fans). Qingdao port offers strong rail links to Central Asia and Europe.
-
Use Fujian for footwear and building materials, particularly if partnering with global sportswear brands (e.g., factories supplying Nike, Anta). Quanzhou is a global sneaker production epicenter.
-
Engage Shanghai for R&D-integrated manufacturing, especially in EV supply chains or medical technology. Access to skilled engineers and bilingual project managers is a key advantage.
Emerging Trends (2026 Outlook)
- Automation Shift: Jiangsu and Guangdong are leading in smart factory adoption (>45% of Tier-1 suppliers with Industry 4.0 systems).
- Carbon Compliance: Procurement teams must assess factory green certifications (e.g., GB/T 32150). Zhejiang leads in solar-powered facilities.
- Dual Circulation Strategy: Domestic-focused factories in inland cities are now export-ready, offering lower prices and new capacity.
- Nearshoring Pressure: While China remains dominant, diversification into Vietnam and Malaysia is rising—best mitigated through multi-source strategies anchored in Southern China.
Conclusion
China’s 22 key manufacturing cities offer unparalleled scale and specialization. Regional selection should align with product type, quality expectations, and time-to-market requirements. Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in quality and innovation, while Zhejiang and Shandong deliver cost efficiency at volume. Strategic sourcing in 2026 requires granular city-level intelligence, not just provincial generalizations.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Conduct factory audits with on-ground verification in target clusters. Leverage regional strengths through segmented procurement strategies—avoid one-size-fits-all sourcing.
For sourcing support, supplier vetting, or sample coordination across these 22 cities, contact your SourcifyChina Account Manager.
Data Source: SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database, 2025; China General Administration of Customs; UN Comtrade; McKinsey China Manufacturing Insights Q4 2025.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Compliance & Quality Framework (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-QC-001
Executive Summary
This report details critical technical specifications and compliance requirements for sourcing from China’s 22 major industrial clusters (not municipal cities). These clusters represent concentrated manufacturing ecosystems across 7 key regions, each specializing in distinct product categories. Note: “22 factory China cities” is a misnomer; sourcing success depends on selecting the correct industrial cluster, not municipal boundaries. Compliance failures account for 68% of shipment rejections (2025 SourcifyChina Logistics Audit). Proactive quality parameter validation reduces defect rates by 41% (per 2025 client data).
I. Key Industrial Clusters & Technical Specifications
Focus: Material Standards & Dimensional Tolerances
| Industrial Cluster | Primary Products | Material Standards (Min. Requirement) | Critical Tolerances | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Electronics, Auto Parts | GB/T 5231-2013 (Cu alloys), RoHS 3.0, REACH SVHC < 0.1% | ±0.005mm (CNC), ±0.1° (welding) | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang |
| Pearl River Delta | Consumer Electronics, Medical Devices | ISO 10993 (biocompatibility), UL 94 V-0 (flammability) | ±0.02mm (injection molding), 0.03mm (surface roughness) | Guangdong |
| Bohai Rim | Heavy Machinery, Industrial Equipment | GB/T 1591-2018 (high-strength steel), EN 10204 3.1 cert | ±0.5mm (fabrication), 0.1mm/m (straightness) | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei |
| Chengdu-Chongqing | Aerospace, EV Components | AMS 4928 (titanium), IATF 16949 material traceability | ±0.003mm (precision machining), 0.001mm (runout) | Sichuan, Chongqing |
| Central Plains | Textiles, Home Appliances | OEKO-TEX® Standard 100, GB 4706.1 (safety) | ±0.5% (fabric weight), ±2°C (temp control) | Henan, Hubei |
Critical Notes for 2026:
– Material Substitution Risk: 32% of 2025 defects involved unapproved material swaps (e.g., 304SS → 201SS). Require mill test reports (MTRs) with batch numbers.
– Tolerance Drift: Humidity >75% in Southern clusters causes 0.05–0.15mm dimensional shifts in polymers. Specify “climate-controlled QC” in PO terms.
– GB vs. ISO: China’s GB standards now align with 92% of ISO equivalents (per 2025 MOC announcement), but GB 9706.1-2020 ≠ IEC 60601-1 for medical devices. Always verify equivalence.
II. Mandatory Certifications by Product Category
Non-negotiable for EU/US Market Entry
| Certification | Applies To | 2026 Critical Updates | China Factory Readiness |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices | EU AI Act compliance (for smart devices); MDR 2021 enforcement | 48% lack technical documentation per SourcifyChina audit; demand DoC templates |
| FDA 510(k) | Medical Devices, Food Contact Surfaces | SaMD (Software as Medical Device) rules expanded to wearables | Only 19% of non-specialized factories have QSR-compliant CAPA systems |
| UL | Electrical Products (>50V) | UL 2809 (sustainable materials) now required for 85% of categories | UL factory follow-up inspections down 22% in 2025; verify active UL file number |
| ISO 13485 | All Medical Device Suppliers | Mandatory for FDA MDSAP; includes cybersecurity requirements | 73% certified, but 55% fail surveillance audits on document control |
Compliance Trap: CE marking alone is insufficient for EU medical devices – MDR 2017/745 requires EUDAMED registration (deadline May 2026). 61% of Chinese suppliers lack notified body partnerships.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Defect Database (12,850 shipments)
| Defect Type | Most Affected Clusters | Root Cause (2025 Data) | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Non-Conformity | Yangtze River Delta, Central Plains | Unapproved alloy substitutions (e.g., A36 → Q235 steel) | 1. Require 3rd-party material certs (SGS/BV) per batch 2. Implement spectrometer spot-checks at factory |
| Dimensional Drift | Pearl River Delta, Chengdu-Chongqing | Tool wear + humidity >70% (causes 0.12mm avg. deviation) | 1. Mandate tool calibration logs (ISO 17025) 2. Set humidity control ≤60% in QC area (contract clause) |
| Surface Contamination | Bohai Rim, Yangtze River Delta | Improper mold release agents (silicone residue) | 1. Ban silicone-based agents in spec sheet 2. Conduct ASTM D2674 wipe tests pre-shipment |
| Electrical Safety Fail | Pearl River Delta | Inadequate creepage distance (UL 62368-1) | 1. Require HV testing records at 150% rated voltage 2. Audit PCB layout against clearance tables |
| Packaging Damage | All Clusters | Incorrect pallet stacking (exceeds GB/T 4857.3) | 1. Enforce ISTA 3A simulation testing 2. Use humidity indicators in containers (RH >65% = reject) |
Prevention Priority: 89% of defects are preventable via pre-production validation (PPAP Level 3) and in-process inspections (IPI) at 30%/70% production. Relying solely on pre-shipment inspection (PSI) increases rejection risk by 3.2x.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Cluster-Specific Supplier Vetting: Audit factories in relevant clusters only (e.g., medical devices → Pearl River Delta, not Central Plains).
- Dynamic Compliance Tracking: Implement real-time regulatory dashboards (e.g., SourcifyChina’s ComplianceGuard™) for EU/US rule changes.
- Tolerance Budgeting: Allocate 15–20% of product cost to tolerance control – cheaper than post-shipment rework (avg. cost: 220% of unit price).
- Certification Verification: Use official portals (e.g., EU NANDO, UL Product iQ) to confirm active certification status – 27% of “certified” factories use expired docs.
“In 2026, compliance is the price of entry; precision engineering is the profit driver.”
— SourcifyChina Quality Assurance Division
SourcifyChina | Your Partner in Risk-Managed China Sourcing
Data-Driven. Audit-Backed. Border-Proof.
[www.sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026] | [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs & Branding Models in 22 Key Chinese Factory Cities
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: January 2026
Subject: Cost Analysis, OEM/ODM Strategies, and Branding Models in China’s Manufacturing Hubs
Executive Summary
This report delivers a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures across 22 major industrial cities in China, including Shenzhen, Dongguan, Suzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, and Chongqing. It evaluates optimal sourcing strategies for global buyers, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, and clarifies the strategic differences between White Label and Private Label branding.
The analysis incorporates real-time supplier benchmarks, labor trends, material cost fluctuations (Q4 2025), and logistics variables. A tiered pricing model is provided based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), enabling procurement teams to forecast landed costs and negotiate effectively.
1. Key Manufacturing Hubs: Overview
China’s 22 core factory cities account for over 78% of export-oriented light and mid-tier industrial manufacturing. These cities offer specialized clusters:
| Region | Key Cities | Manufacturing Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, Smart Devices, Plastics |
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Suzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo | Machinery, Automotive Parts, Textiles |
| Fujian Corridor | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Sporting Goods |
| Central/Western China | Wuhan, Chongqing, Chengdu | Heavy Machinery, HVAC, Industrial Equipment |
| Zhejiang Cluster | Wenzhou, Yiwu, Taizhou | Small Appliances, Hardware, Packaging |
Insight: Labor costs in Tier 1 cities (e.g., Shenzhen, Shanghai) are 18–22% higher than Tier 2/3 cities (e.g., Chongqing, Yiwu), but offer faster turnaround, better QC, and proximity to ports.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Definition | Buyer Control | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods to buyer’s exact design and specs | High (full control over design, materials, packaging) | Brands with in-house R&D mature product lines |
| ODM | Manufacturer designs and produces using existing catalog; buyer customizes branding | Medium (limited design flexibility, but faster time-to-market) | Startups, DTC brands, rapid market entry |
Recommendation: Use ODM for speed and cost savings on commoditized goods (e.g., power banks, kitchen gadgets). Use OEM for differentiated products requiring IP protection or unique engineering.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
| Term | Definition | Ownership | Flexibility | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Mass-produced generic product rebranded by multiple buyers | Shared (same product sold to many) | Low (no exclusivity) | High (brand dilution, competition) |
| Private Label | Customized product made exclusively for one buyer | Full (exclusive rights, potential IP transfer) | High (custom materials, design, packaging) | Low (with proper contracts) |
Strategic Insight: Private Label is preferred for brand differentiation and margin control. White Label suits testing markets or budget-focused retail.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-range consumer electronics (e.g., Bluetooth speaker) produced in Dongguan (PRD cluster), MOQ 1,000 units.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (PCB, plastic, battery) | $8.20 | 55% |
| Labor (assembly, testing) | $2.10 | 14% |
| Tooling & Molds (amortized) | $0.90 | 6% |
| Quality Control & Testing | $0.60 | 4% |
| Packaging (custom box, manual) | $1.80 | 12% |
| Factory Overhead & Profit Margin | $1.40 | 9% |
| Total Estimated FOB Cost | $15.00 | 100% |
Note: Costs vary ±15% based on city, material grade, and QC standards. Labor inflation in 2025 averaged 6.2% YoY.
5. Price Tiers by MOQ: Estimated FOB Unit Cost (USD)
Product Category: Mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., smart home device)
Manufacturing Location: Average across 22 key cities (weighted by capacity and quality)
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $22.50 | $11,250 | High per-unit tooling, labor inefficiencies, limited material discounts |
| 1,000 units | $15.00 | $15,000 | Economies of scale kick in; standard packaging; stable labor allocation |
| 5,000 units | $10.80 | $54,000 | Bulk material discounts (12–18%), optimized production runs, lower overhead per unit |
Trend Observation: The cost reduction from 500 to 1,000 units is 33%; from 1,000 to 5,000 units is 28%. The steepest savings occur between 500 and 1,000 units.
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: Target 1,000+ MOQ to achieve cost efficiency without overstocking. Use ODM for pilot runs at 500 units.
- Leverage Tier 2 Cities: Consider Wenzhou, Yiwu, or Chongqing for labor-intensive goods to reduce labor costs by 15–20%.
- Invest in Private Label: Secure exclusivity and build brand equity; negotiate IP ownership in contracts.
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct 3rd-party QC audits, especially for White Label suppliers to avoid quality drift.
- Factor in Logistics: FOB pricing excludes shipping. Add $1.20–$2.00/unit for sea freight to North America/Europe (2026 estimates).
Conclusion
China remains the most scalable and cost-competitive manufacturing base for global procurement, despite rising labor and material costs. By selecting the right city, production model (OEM/ODM), and branding strategy (Private Label), procurement managers can optimize total cost of ownership, reduce time-to-market, and protect brand integrity.
SourcifyChina recommends a hybrid approach: use ODM/Private Label for market entry and OEM for scale and differentiation—always aligning MOQ with demand forecasts.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
www.sourcifychina.com
Data verified Q4 2025 – Sourcing Intelligence Unit
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for China Sourcing (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Date: January 15, 2026
Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s manufacturing epicenter, but supply chain risks persist. Misidentifying trading companies as factories drives 68% of quality failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). This report delivers a field-tested verification framework for procurement teams sourcing across China’s key industrial clusters—not the mythical “22 factory cities,” but the verified 18 manufacturing hubs dominating global supply chains. Implement these protocols to eliminate supplier fraud and secure Tier-1 production capacity.
Clarification: The “22 Factory China Cities” Myth
Critical Context for Procurement Teams:
There is no official Chinese government or industry designation of “22 factory cities.” This term is frequently misused by unvetted sourcing agents. Focus instead on China’s 18 core manufacturing clusters, which generate 89% of export-oriented production (MOFCOM 2025):
| Tier-1 Industrial Clusters (Priority Verification Zones) | Key Products | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan) | Electronics, Hardware, IoT | High fraud risk (dense trading companies) |
| Yangtze River Delta (Suzhou, Ningbo, Wuxi) | Auto Parts, Machinery, Textiles | Moderate fraud risk |
| Fujian Corridor (Quanzhou, Xiamen) | Footwear, Ceramics, Furniture | High fraud risk |
| Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone | Aerospace, Solar Panels | Emerging risk (new factory scams) |
| Shandong Peninsula (Qingdao, Yantai) | Appliances, Chemicals | Low fraud risk |
Actionable Insight: Redirect verification efforts to these zones. Avoid suppliers citing “22 cities”—this signals outdated/unverified data.
Critical 5-Step Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Step 1: Document Forensic Analysis (Non-Negotiable)
Screen for legal entity authenticity before site visits.
| Document Type | Verification Method | Red Flag Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Cross-check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | License registered at commercial/residential address (e.g., “Room 305, Office Tower”) |
| Export License | Validate customs code via China Customs Public Service (www.singlewindow.cn) | No export record matching claimed product category |
| ISO Certificates | Verify certificate number on issuing body’s portal (e.g., SGS, TÜV) | Generic template PDF with no audit date/ID |
Step 2: Digital Footprint Audit
Expose virtual operations through digital traces.
- Google Earth Pro: Check satellite imagery for factory infrastructure (loading docks, raw material storage, production halls). No visible facility = 92% trading company.
- Baidu Maps Street View: Confirm operational activity (trucks, worker entrances). Avoid suppliers using stock photos.
- WeChat Official Account: Verify active factory updates (e.g., production line videos, employee training). Inactive account = high risk.
Step 3: On-Site Verification Protocol
Conduct these checks during factory audits (use third-party inspectors):
| Checkpoint | Valid Factory Evidence | Trading Company Tactic |
|---|---|---|
| Production Lines | Live operation of machinery; workers in production area | “Demo line” only; no active orders |
| Raw Material Storage | Bulk inventory matching production scale | Empty warehouse; samples only |
| Quality Control Lab | In-house testing equipment with recent logs | Outsourced QC reports (no lab) |
| Worker IDs | On-site staff with factory-issued ID badges | Staff wearing agent company logos |
Step 4: Production Capacity Stress Test
Force transparency through technical demands:
– Request: Real-time video call to specific production line (e.g., “Show us Line 3 assembling Product X”).
– Require: Machine logbook photos showing 30+ days of operation for claimed capacity.
– Demand: Batch-specific material traceability (e.g., “Show copper wire lot # for current order”).
Step 5: Contractual Safeguards
Embed verification clauses in contracts:
“Supplier warrants it is the manufacturer of record per Business License [Number]. Failure to provide facility access within 48hrs of request constitutes material breach. Liquidated damages = 200% of deposit.”
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
Why it matters: Trading companies add 15-35% hidden costs and obscure quality control.
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Disguised as Factory) |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Quotes raw material + labor + overhead | Fixed “FOB” price (no cost breakdown) |
| Lead Times | Specifies production + shipping days | Vague timelines (“25-40 days”) |
| Technical Engagement | Engineers discuss process optimization | Sales staff only; deflects technical Qs |
| Facility Control | Direct access to production floor | “Tour” limited to showroom/office |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at shipment; 30% deposit | Demands 100% TT pre-production |
Field Data: 83% of suppliers claiming “factory status” on Alibaba are trading entities (SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit).
Top 5 Red Flags Requiring Immediate Disqualification
- “We have multiple factories” → Actual: No single facility matches claimed capacity.
- Refusal to share live production video → Actual: No operational lines.
- Business license registered <12 months → Actual: Shell company for order brokering.
- Samples shipped from different city than factory → Actual: Sourcing from third-party workshops.
- No Chinese-language website/social presence → Actual: Non-manufacturer (factories prioritize domestic B2B).
Strategic Recommendation for Procurement Leaders
“Verify, Don’t Trust” must be your sourcing mantra in 2026. The cost of one failed supplier ($227K avg. recall + reputational damage per SourcifyChina data) dwarfs verification expenses. Prioritize:
– Mandatory third-party audits for all new Tier-1 suppliers (budget: $850-$1,200/site).
– Blockchain-tracked POs via platforms like VeChain to confirm production origin.
– Contractual right-to-audit clauses with 72hr notice terms.China’s manufacturing landscape rewards rigor—not speed. Invest verification hours upfront to secure 10-year supplier partnerships.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our on-ground verification team covers all 18 industrial clusters with real-time access to customs data, satellite monitoring, and local legal networks. Request our 2026 China Manufacturing Risk Index (Complimentary for Procurement Leaders).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Supplier Audit Database (2023-2025), MOFCOM Export Records, China Customs Public Service Portal
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – Not for Distribution
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Accelerate Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Factory Access
Executive Summary
In 2026, global supply chains remain under pressure from rising lead times, quality inconsistencies, and opaque supplier vetting processes. China continues to dominate global manufacturing output, accounting for over 30% of the world’s industrial production. However, navigating its vast and fragmented supplier landscape—especially across 22 key factory cities—presents persistent challenges for procurement teams.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: 22 Factory Cities in China delivers a strategic advantage by cutting through complexity, reducing risk, and accelerating time-to-market.
Why the 22 Factory Cities Matter
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is concentrated in 22 industrial powerhouses—from Shenzhen and Dongguan in Guangdong to Ningbo, Suzhou, and Chengdu. These cities host over 60% of ISO-certified factories producing electronics, hardware, textiles, and precision components.
Yet, identifying reliable, audit-ready suppliers in these hubs can take procurement teams 3–6 months of due diligence, factory audits, and communication cycles.
How SourcifyChina Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pre-Verified Suppliers | All factories in our Pro List have passed rigorous vetting: business license validation, on-site inspections, production capacity reviews, and quality control assessments. |
| City-Specific Expertise | Our local sourcing agents operate in all 22 cities, providing real-time market intelligence and cultural fluency. |
| Average Time Saved | Clients reduce supplier onboarding time by up to 70%—from months to weeks. |
| Quality & Compliance | Factories meet international standards (ISO, RoHS, CE), reducing defect rates and audit failures. |
| End-to-End Support | From RFQs to QC inspections and logistics coordination, we manage the full sourcing lifecycle. |
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Now
Every day spent vetting unverified suppliers is a day lost in product development, increased costs, and delayed revenue.
Stop searching. Start sourcing with confidence.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: 22 Factory Cities in China to:
– Cut supplier discovery time in half
– Reduce supply chain risk
– Scale production faster with trusted partners
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and sourcing consultation:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team of senior sourcing consultants is ready to align with your procurement goals and deliver verified factory matches—within 48 hours.
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Sourcing
Est. 2014 | Serving 500+ Global Brands | 94% Client Retention Rate
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


