The global fastener market, including manufacturers specializing in 2.56 mm bolts—often referenced in precision engineering and electronics assembly—is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries. According to Grand View Research, the global fasteners market was valued at USD 98.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing industrial automation, miniaturization of electronic components, and stricter performance standards in manufacturing. As demand for high-precision small-diameter bolts like the 2.56 mm variant intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in quality, innovation, and scalability. Based on production capacity, global reach, compliance with ISO standards, and R&D investment, here are the top 7 manufacturers dominating the 2.56 mm bolt segment.
Top 7 2 56 Bolt Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
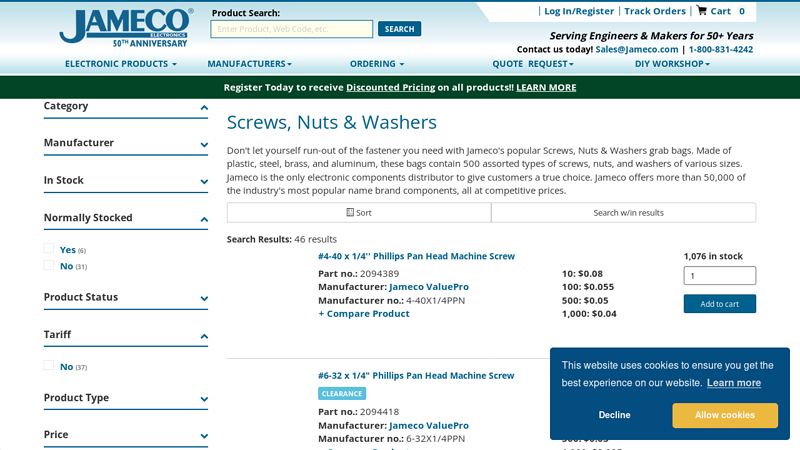
#1 Screws, Nuts & Washers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jameco.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 · 30-day returns#2-56 x 1/4” Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw. Clearance. Part no.: 2094354; Manufacturer: Jameco ValuePro; Manufacturer no.: 2-56X1/4PPN. +…
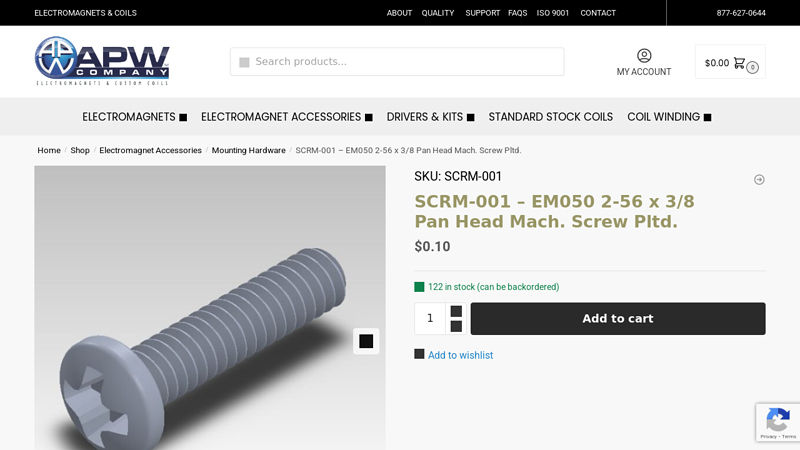
#2 SCRM
Domain Est. 2007
Website: apwcompany.com
Key Highlights: In stock $23.24 deliverySCRM-001 – EM050 2-56 x 3/8 Pan Head Mach. Screw Pltd. $0.10. 122 in stock (can be backordered). SCRM-001 – EM050 2-56 x 3/8 Pan Head Mach.Missing: bolt ma…
#3 Global Leader in Fastening Technology
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stanleyengineeredfastening.com
Key Highlights: Lightweight, durable, and cost-effective, our plastic fasteners are designed for modern applications across automotive, electronics, and consumer goods….
#4 McMaster
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mcmaster.com
Key Highlights: McMaster-Carr is the complete source for your plant with over 700000 products. 98% of products ordered ship from stock and deliver same or next day.Missing: 2 56…
#5 2
Domain Est. 1996
#6 Metric Hex Bolt Dimensions
Domain Est. 2006
Website: atlrod.com
Key Highlights: Metric Hex Bolt Dimensions | Atlanta Rod and Manufacturing | Manufacturing of Bolts, Concrete Embeds, Construction Fasteners, and Stainless Steel Bolts ……
#7 Alloy Socket Set Screw Stock
Domain Est. 2014
Website: setscrewmfg.com
Key Highlights: #2-56 X 3/8 CUP POINT ALLOY HEX SOCKET SET SCREW BLACK OXIDE, 19,000. H08560500CPX, #2-56 X 1/2 CUP POINT ALLOY HEX SOCKET SET SCREW BLACK OXIDE, 10,000….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 2 56 Bolt

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 2-56 Bolts
As we approach 2026, the market for 2-56 bolts—small-diameter, 56-thread-per-inch machine screws commonly used in precision applications—continues to evolve in response to advancements in manufacturing, shifts in industrial demand, and global supply chain dynamics. These miniature fasteners, while seemingly minor components, play a critical role in high-precision industries such as electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
1. Rising Demand in Electronics and IoT Devices
The proliferation of compact electronic devices, wearables, and Internet of Things (IoT) hardware is driving increased demand for 2-56 bolts. Their small size and reliable thread engagement make them ideal for securing circuit boards, sensors, and internal chassis components. As smart devices become more miniaturized, the need for standardized, precision-engineered fasteners like the 2-56 bolt is expected to grow steadily through 2026.
2. Growth in Medical and Dental Equipment Manufacturing
The medical device sector is a significant consumer of 2-56 bolts, particularly in surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and dental tools. With continued innovation in minimally invasive devices and portable medical technology, demand for corrosion-resistant, high-strength variants (such as those made from stainless steel or titanium) is projected to rise. Regulatory emphasis on reliability and traceability will further influence material and quality standards.
3. Aerospace and Defense Applications
In aerospace, where weight reduction and precision are paramount, 2-56 bolts are frequently used in avionics and internal assemblies. The ongoing modernization of defense systems and increased satellite deployment (including small satellites and CubeSats) are expected to maintain steady demand. Specialized coatings and strict compliance with MIL-SPEC standards will remain key differentiators in this high-reliability sector.
4. Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Post-pandemic supply chain challenges and geopolitical tensions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing and inventory resilience. In North America and Europe, there is growing interest in reshoring fastener production, which could benefit domestic suppliers of 2-56 bolts. This trend is likely to accelerate through 2026, driven by the need for shorter lead times and greater supply chain transparency.
5. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and processes. Recyclable alloys, reduced carbon footprint production methods, and non-toxic coatings (e.g., alternatives to cadmium plating) are becoming more prevalent. These factors will influence the design and sourcing decisions for 2-56 bolts, especially in regulated industries.
6. Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
As smart factories expand, the demand for standardized, machine-readable components increases. While the 2-56 bolt itself is passive, its integration into automated assembly lines—especially in electronics and robotics—requires consistent dimensional tolerances and packaging optimized for pick-and-place systems. This is driving tighter quality control and customized packaging solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 2-56 bolt market will remain a niche but strategically important segment of the fastener industry. Driven by technological miniaturization, supply chain adaptation, and material innovation, demand is expected to grow modestly but steadily, particularly in high-tech and regulated sectors. Manufacturers who invest in precision engineering, sustainability, and responsive distribution will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing M5x0.8 56mm Bolts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing industrial fasteners like M5x0.8x56mm bolts (commonly written as M5-56 or M5x56) requires attention to detail to avoid performance, safety, and compliance issues. Here are key pitfalls to avoid, particularly concerning quality and IP (Ingress Protection) considerations:
1. Assuming Grade Equivalency Without Verification
A frequent error is assuming international bolt grades (e.g., ISO 898-1 Class 8.8 or 10.9) are interchangeable with regional standards (like ASTM A325 or SAE J429 Grade 5). Using a lower-grade bolt than required—especially in structural or safety-critical applications—can lead to premature failure. Always verify the mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, hardness) and ensure compliance with the project’s technical specifications.
2. Overlooking Material Compatibility for IP Environments
In applications requiring IP ratings (e.g., enclosures rated IP65, IP67), the bolt material must resist corrosion in specific environments. Using standard carbon steel bolts in high-humidity or outdoor settings can lead to rust, compromising both structural integrity and the enclosure’s seal. Opt for stainless steel (e.g., A2-70 or A4-80) or zinc-plated variants where appropriate, ensuring they meet environmental and longevity requirements.
3. Ignoring Thread Quality and Tolerance
Poor thread accuracy (e.g., incorrect pitch, thread damage, or out-of-tolerance fit) can result in cross-threading, reduced clamping force, or difficulty during assembly. This is especially critical in automated assembly lines or high-vibration environments. Specify bolts meeting ISO 965 (medium tolerance, 6g for external threads) and source from reputable manufacturers with consistent quality control.
4. Failing to Confirm Dimensional Accuracy
While the nominal length is 56mm, variations in underhead length, thread length, or head diameter can affect fit, especially in blind holes or tight spaces. Bolts that are too long may interfere with internal components; too short may not engage enough threads. Confirm full dimensional specs, including thread length (often ~22–25mm for M5x56), and request certifications (e.g., test reports) when precision is critical.
5. Sourcing from Unverified Suppliers
Procuring bolts from uncertified or low-cost suppliers risks receiving counterfeit or substandard products. These may appear correct but fail under load or corrode prematurely. Always source from reputable suppliers with traceability, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and the ability to provide material test reports (MTRs) or conformity declarations.
6. Neglecting Surface Finish and Coating Specifications
The surface treatment impacts both corrosion resistance and IP rating compliance. Inadequate or inconsistent plating (e.g., thin zinc coating) may not withstand environmental exposure, leading to galvanic corrosion—especially when mated with dissimilar metals. Specify required finishes (e.g., zinc-nickel, Geomet, or duplex coatings) and ensure they align with environmental conditions and IP sealing requirements.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures the selected M5x56 bolts meet performance, durability, and safety standards—critical for maintaining system integrity in demanding industrial applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 2.56 Bolt
Overview
The 2.56 Bolt is a high-performance electric vehicle developed by Bolt Motor Company. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transportation, handling, import/export, and operation of the 2.56 Bolt model.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all 2.56 Bolt units meet regional safety and emissions standards. Key regulations include:
– United States: DOT (Department of Transportation) and NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) compliance, including FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards).
– European Union: Compliance with UNECE regulations and EU Whole Vehicle Type Approval ( WVTA ), including CO₂ emissions and battery safety standards.
– China: CCC (China Compulsory Certification) and NEV (New Energy Vehicle) registration requirements.
– Other Regions: Confirm local EV certification (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, R155/R156 for cybersecurity and software updates in applicable markets).
Transportation & Handling
- Inbound Logistics: Coordinate containerized or Ro-Ro (Roll-on/Roll-off) shipping for international delivery. Use EV-certified carriers with climate-controlled options if storing long-term.
- Battery Safety: Lithium-ion batteries must comply with UN 38.3 testing requirements. Vehicles should be shipped at ≤30% state of charge to reduce risk.
- Packaging & Protection: Use anti-corrosion film and protective coverings during transit. Secure vehicles to prevent movement in transport.
- On-Site Handling: Use EV-safe towing equipment and non-conductive tools. Avoid lifting by undercarriage components unless specified.
Import & Export Documentation
Mandatory documentation includes:
– Commercial Invoice and Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and Conformity Certificate (CoC)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Battery Test Reports (UN 38.3, MSDS)
– Import permits (if required by destination country)
Customs Clearance
- Classify under correct HS Code (e.g., 8703.80 for electric passenger vehicles).
- Declare battery capacity (kWh) and voltage for tariff and duty assessment.
- Prepare for potential EV-specific duties or incentives (e.g., reduced tariffs under green vehicle programs).
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
- Adhere to battery recycling regulations (e.g., EU Battery Directive, US state-level requirements).
- Maintain records for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs.
- Report carbon footprint data if required by market (e.g., EU PEF methodology).
After-Sales & Service Logistics
- Distribute service parts via temperature-monitored supply chains where applicable.
- Train service centers on high-voltage system handling (ISO 26262 and IEC 61010 standards).
- Ensure software update compliance with UNECE R155 (cybersecurity) and R156 (software updates).
Incident Reporting & Recall Management
- Establish protocols for reporting safety defects to regulatory bodies (e.g., NHTSA Defect Petition, EU Rapid Exchange System).
- Maintain traceability via VIN and production batch records.
- Execute recalls in accordance with local laws and timelines.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for the 2.56 Bolt ensures legal operation, safety, and customer satisfaction across global markets. Always verify region-specific requirements and maintain up-to-date documentation throughout the vehicle lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing 2-56 Bolts
In conclusion, sourcing 2-56 bolts requires careful consideration of material, length, drive type, finish, and application requirements. These small but critical fasteners are commonly used in electronics, aerospace, automotive, and precision instrumentation due to their standardized thread size (1/4″-56 UNC) and reliable performance in light-duty applications.
After evaluating various suppliers, availability, cost, quality standards (such as ASTM, ISO, or MIL-SPEC), and lead times, it is recommended to source 2-56 bolts from reputable industrial hardware suppliers or specialized fastener distributors. Ensuring the correct specifications—such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance or nylon for insulation—will enhance performance and longevity in the intended application.
Bulk purchasing from certified vendors can also provide cost savings and consistent quality. Ultimately, selecting the appropriate 2-56 bolt variant based on environmental conditions and mechanical demands ensures reliable assembly and optimal functionality across projects.