The global medical needle manufacturing market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for minimally invasive procedures, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and expanding vaccination programs worldwide. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global hypodermic needles market was valued at approximately USD 13.8 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth trajectory underscores the critical importance of reliable, high-quality needle production—particularly in commonly used gauges such as 16 gauge, which are essential in surgical settings, blood donation, and critical care applications. With increasing emphasis on precision, safety-engineered designs, and infection control, manufacturers are investing heavily in innovation and compliance with international standards. As demand surges, a select group of global leaders have emerged in the 16 gauge needle segment, combining advanced manufacturing capabilities, stringent quality control, and global distribution networks to meet evolving healthcare needs. These top eight manufacturers represent the forefront of performance, scalability, and technological advancement in one of the most vital components of modern medicine.
Top 8 16 Guage Needle Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
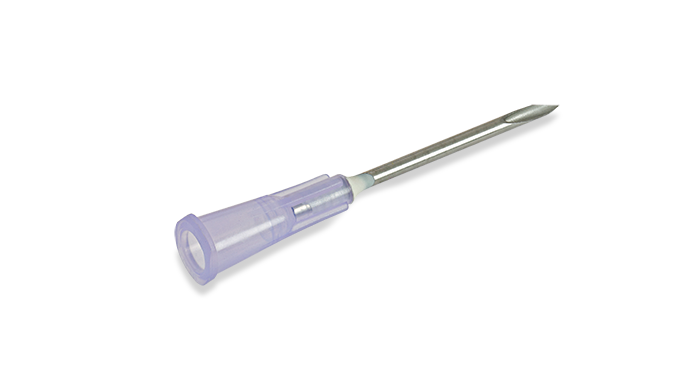
#1 16 G x 1 in. BD PrecisionGlide™ Needle
Domain Est. 1990
Website: bd.com
Key Highlights: BD PrecisionGlide™ Needle technology incorporates a thin wall, tri-bevel tip and a proprietary lubricant which is designed to provide ease of penetration….
#2 Small Diameter Tubing & Cannula Needle Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: vitaneedle.com
Key Highlights: Vita Needle is a small diameter tubing and cannula needle manufacturer, and our company provides tube products for a wide range of industries….
#3 16 Gauge x 4″, 100/Pkg
Domain Est. 2005
Website: pattersonvet.com
Key Highlights: AirTite Vet Premium Hypodermic Needle, 16 Gauge x 4″, 100/Pkg, AIR-TITE PRODUCTS CO INC, Manufacturer Item #:N164, Patterson Item #:07-856-4789….
#4 Shop 16 Gauge Hypodermic Needles
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mms.mckesson.com
Key Highlights: Order Hypodermic Needles and other in-stock supplies and products. We deliver to your care setting….
#5 Blunt
Domain Est. 1994
Website: stemcell.com
Key Highlights: These sterile 16 gauge needles are ideal for safe & accurate handling of methylcellulose-based media. Blunt end reduces risk of needle stick injuries….
#6 16 gauge, Metal Hub Needle (N), PN: 91016
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hamiltoncompany.com
Key Highlights: In stock $10 deliveryHamilton’s 16 gauge Metal Hub Needle (PN: 91016) is designed for reliable liquid dispensing in labs. Featuring a stainless steel shaft and nickel-plated ……
#7 16 gauge needles
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sigmaaldrich.com
Key Highlights: 1–3 day deliveryFind 16 gauge needles and related products for scientific research at MilliporeSigma….
#8 NEEDLES
Domain Est. 2008
Website: cadencescience.com
Key Highlights: Cadence specializes in needle manufacturing of Reusable and Specialty Needles for a variety of applications. … Pipetting Needles 16g x 6″, MM 316Stainless Steel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 16 Guage Needle

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 16 Gauge Needles
The global market for 16 gauge needles is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in medical technology, rising demand for critical care procedures, and evolving healthcare infrastructure. The 16 gauge needle—commonly used in high-volume intravenous (IV) access, emergency medicine, blood transfusions, and surgical settings—remains a vital component in clinical environments. Below are the key trends expected to shape the 16 gauge needle market by 2026:
1. Rising Demand in Emergency and Critical Care Settings
With the increasing incidence of trauma cases, surgical interventions, and emergency hospitalizations globally, there is a growing reliance on large-bore IV access. The 16 gauge needle facilitates rapid fluid resuscitation and blood product administration, making it indispensable in emergency departments and intensive care units (ICUs). The expansion of emergency medical services (EMS) and trauma centers, especially in emerging economies, will amplify demand.
2. Technological Innovations and Safety Enhancements
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize safety-engineered 16 gauge needles featuring retractable mechanisms, passive shielding, and needle-free connectors to reduce needlestick injuries. Regulatory pressures from agencies such as the FDA and OSHA continue to push adoption of safer devices. These innovations not only improve clinician safety but also align with global healthcare worker protection standards.
3. Growth in Home Healthcare and Ambulatory Surgery Centers
As healthcare delivery shifts toward outpatient and home-based care, the use of 16 gauge needles in ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) and mobile emergency units is on the rise. While typically reserved for in-hospital use, the need for rapid access during certain outpatient procedures (e.g., rapid hydration or contrast administration in imaging) supports moderate growth in non-traditional settings.
4. Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America
Healthcare infrastructure development in countries like India, China, Brazil, and Mexico will drive market growth. Increased hospital admissions, rising surgical volumes, and government investments in public health systems are expected to boost procurement of IV access devices, including 16 gauge needles. Local manufacturing and cost-effective product variants will further support accessibility.
5. Impact of Material and Sustainability Trends
Sustainability initiatives are influencing product design. By 2026, major suppliers may shift to recyclable packaging and bio-based plastics in needle hubs and catheters. Additionally, efforts to reduce single-use plastic waste may prompt innovations in reusable or sterilizable components, though sterility requirements will likely limit full reusability of needles.
6. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market remains dominated by key players such as Becton Dickinson (BD), B. Braun, Smiths Medical (ICU Medical), and Terumo Corporation. Continued mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are expected to enhance product portfolios and expand geographic reach. Differentiation through smart IV systems—where 16 gauge catheters integrate with flow-monitoring devices—may emerge as a competitive edge.
7. Influence of Pandemic Preparedness and Blood Donation Programs
Lessons from recent global health crises have emphasized the need for rapid IV access and blood transfusion capabilities. National stockpiling of critical medical supplies, including large-bore needles, is likely to continue. Additionally, expanding blood donation and plasma therapy programs will sustain steady demand for 16 gauge needles used in apheresis and rapid collection procedures.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 16 gauge needle market will be shaped by a confluence of clinical necessity, safety regulations, and regional healthcare development. While the product segment remains mature, innovation in safety features, materials, and integration with digital health tools will ensure continued relevance and moderate growth. Stakeholders should focus on emerging markets, safety compliance, and sustainable manufacturing to capitalize on evolving opportunities.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing 16 Gauge Needles (Quality, IP)
Sourcing 16 gauge needles—especially for medical or laboratory applications—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, regulatory non-compliance, and legal risks. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Manufacturing Standards
One of the most significant risks is sourcing needles made from substandard materials or produced in facilities lacking proper certifications. Low-quality stainless steel can lead to needle dullness, increased patient discomfort, or even breakage during use. Additionally, inconsistent manufacturing processes may result in defects such as burrs, inconsistent bevel angles, or wall thickness variations.
Key Risks:
– Use of non-medical-grade stainless steel (e.g., not ASTM F899 compliant)
– Lack of ISO 13485 certification in manufacturing facilities
– Inadequate quality control leading to batch inconsistencies
Mitigation: Always verify material specifications, request certificates of conformance (CoC), and conduct third-party audits or inspections of supplier facilities.
Non-Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Medical-grade needles must comply with regional and international regulations such as FDA 510(k) clearance (U.S.), CE marking (EU), or compliance with ISO 7864 (sterile hypodermic needles). Sourcing from suppliers who lack these certifications can result in shipment delays, product recalls, or legal liabilities.
Key Risks:
– Distributing needles without proper regulatory clearance
– Incomplete or falsified documentation
– Non-sterile products being marketed as sterile
Mitigation: Confirm regulatory status directly with the supplier and verify listings in official databases (e.g., FDA’s 510(k) database). Include compliance clauses in procurement contracts.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing needles from unauthorized or counterfeit manufacturers can lead to IP violations, especially if the design or branding mimics patented or trademarked products from established medical device companies (e.g., Becton Dickinson, Terumo). Even minor design similarities may trigger legal disputes.
Key Risks:
– Replication of patented needle hub designs, bevel configurations, or safety mechanisms
– Unauthorized use of brand names or logos
– Exposure to litigation or customs seizures
Mitigation: Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP rights. Require written assurance of freedom to operate (FTO) and avoid suppliers offering “equivalent” products that closely mimic branded devices.
Inadequate Packaging and Sterility Assurance
Improper packaging compromises sterility, which is critical for medical use. Sourcing needles with poor packaging design—such as non-integral seals or non-validated sterilization processes—can expose end users to infection risks.
Key Risks:
– Use of non-validated sterilization methods (e.g., unverified EtO or gamma irradiation)
– Packaging that fails integrity tests (e.g., leak-prone blister packs)
– Lack of traceability (e.g., missing lot numbers or expiration dates)
Mitigation: Require validation reports for sterilization and packaging. Perform sterility and packaging integrity testing during quality checks.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability Gaps
Many low-cost suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, lack transparent supply chains. This opacity increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or diverted products and complicates root cause analysis during quality incidents.
Key Risks:
– Unknown or subcontracted manufacturing sources
– Incomplete documentation for traceability
– Difficulty in recalling defective batches
Mitigation: Insist on full supply chain mapping and batch traceability. Use suppliers who maintain robust documentation and comply with UDI (Unique Device Identification) requirements where applicable.
Conclusion
To avoid common pitfalls when sourcing 16 gauge needles, prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality systems, regulatory compliance, and clear IP standing. Conduct thorough audits, demand comprehensive documentation, and build contracts that enforce accountability—ensuring both product safety and legal protection.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 16 Gauge Needle
Product Overview
The 16 gauge needle is a medical device commonly used for intravenous (IV) access, blood transfusions, and the administration of fluids or medications requiring rapid infusion due to its larger internal diameter. Proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure patient safety, maintain sterility, and meet legal requirements.
Regulatory Classification
The 16 gauge needle is classified as a medical device under regulatory frameworks including:
– U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Classified as a Class II medical device under 21 CFR 880.5580 (Intravascular catheter needle). Requires 510(k) premarket notification.
– European Union: Must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745. Typically classified as Class IIa, requiring conformity assessment by a Notified Body.
– Other Regions: Compliance with local regulations such as Health Canada, TGA (Australia), and PMDA (Japan) is required for distribution.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Sterile Packaging: Must be individually sealed in sterile, tamper-evident packaging.
- Labeling: Labels must include:
- Product name and gauge size (16G)
- Sterility statement
- Single-use only warning
- Lot number and expiration date
- Manufacturer name and address
- UDI (Unique Device Identifier) in compliance with FDA and EU MDR
- Regulatory markings (e.g., CE mark, FDA registration number)
Storage Conditions
- Store in a clean, dry environment at temperatures between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
- Keep away from chemicals or substances that may compromise packaging integrity.
Transportation and Shipping
- Use validated shipping containers that maintain environmental conditions during transit.
- Follow UN 3373 (Biological Substance, Category B) guidelines if transporting contaminated devices; sterile needles typically do not fall under hazardous transport unless soiled.
- Ensure temperature-controlled logistics if required by manufacturer specifications.
- Maintain chain of custody documentation for traceability.
Import/Export Compliance
- Export Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, Certificate of Free Sale, and Certificate of Conformity may be required.
- Import Regulations: Verify import licenses, customs tariffs (HS Code: typically 9018.39), and regulatory approvals in destination country.
- Dual-use Considerations: Confirm that needles are not subject to controlled substance equipment regulations in certain jurisdictions.
Handling and Distribution
- Only authorized medical or logistics personnel should handle the product.
- Distributors must be licensed medical device wholesalers and comply with local Good Distribution Practice (GDP) guidelines.
- Maintain traceability via lot tracking and UDI integration in inventory systems.
Quality and Compliance Audits
- Conduct regular audits of manufacturing, packaging, and distribution partners.
- Maintain Quality Management System (QMS) compliant with ISO 13485.
- Report adverse events or device malfunctions to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED).
Disposal and Environmental Compliance
- Unused sterile needles: Dispose of per municipal or healthcare waste regulations.
- Used needles: Must be discarded in FDA-cleared sharps containers and treated as biohazardous waste per OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030).
- Recycling: Not applicable—single-use devices must not be reprocessed unless validated and legally approved.
Training and Documentation
- Train staff on proper handling, storage, and emergency response procedures.
- Maintain records of training, shipping, quality checks, and regulatory submissions for a minimum of 5 years (or as required locally).
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for 16 gauge needles require adherence to global medical device regulations, proper storage and transport practices, accurate labeling, and robust quality systems. Ensuring compliance protects public health and supports uninterrupted supply chain operations.
In conclusion, sourcing a 16-gauge needle requires careful consideration of several key factors including intended medical application, quality standards, material composition (typically medical-grade stainless steel), regulatory compliance (such as FDA or ISO certifications), and supplier reliability. Due to its relatively large diameter, the 16-gauge needle is commonly used in high-flow situations such as blood transfusions, rapid fluid administration, or apheresis procedures. Ensuring compatibility with existing medical devices and adherence to sterility requirements is essential. It is recommended to procure from reputable, certified suppliers who provide consistent quality, proper documentation, and timely delivery to maintain clinical safety and operational efficiency. Conducting due diligence during the sourcing process helps safeguard patient outcomes and ensures compliance with healthcare standards.