The global laser welding equipment market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, energy-efficient manufacturing solutions across automotive, electronics, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 5.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of high-power laser systems, particularly those in the 1,500 W range, which offer optimal balance between processing speed and material penetration for mid-to-heavy-duty applications. As of 2024, manufacturers offering 1500 W laser welders are at the forefront of innovation, integrating automation, real-time monitoring, and fiber laser efficiency to meet evolving industry standards. The following list highlights the top eight manufacturers leading this segment, selected based on production capacity, technological advancement, global market reach, and customer reviews—reflecting their pivotal role in shaping the future of industrial laser welding.
Top 8 1500 W Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 1500w laser welder Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Website: laserdmk.com
Key Highlights: The 1500w laser welder of DMK has advantages over antique welding implies. Very initial, it creates a lot cleanser and weld that’s precise creating specific ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
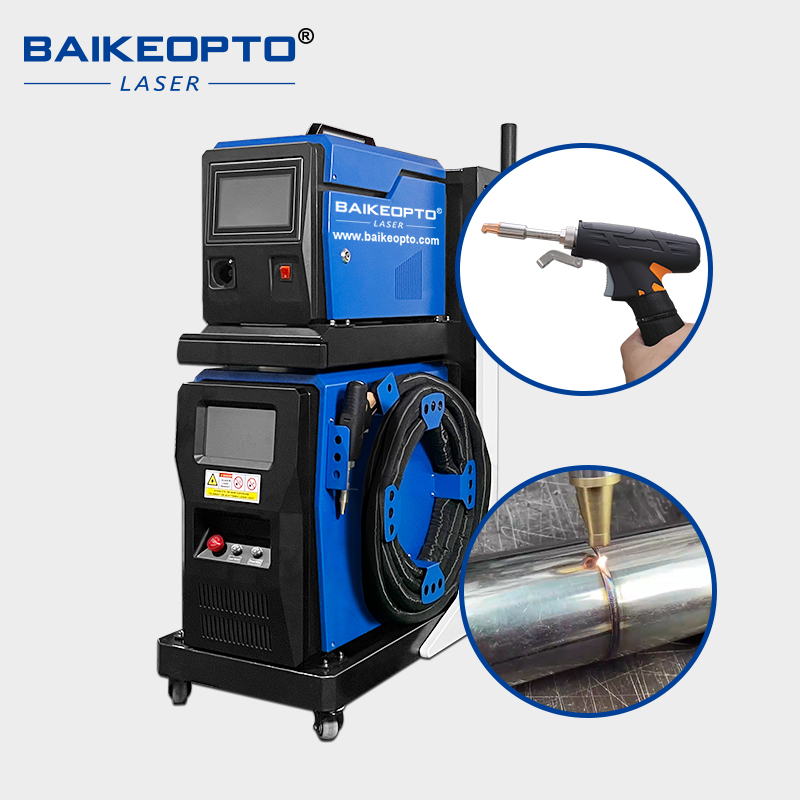
#3 BK
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: In stockBK-WD1500N 1500W Automatic Energy-Saving Fiber Laser Welder Machine for Mold & Sheet Metal Applications ; Cantilever size, L800*W800*1600mm,Arm length1300….
#4 Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Website: omtech.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery1500W Laser Power: Tackle both thick and thin metals with ease using OMTech’s 1500W fiber laser welder. Enjoy fast, precise welding with minimal material ……
#5 Laser Welder 1500W Handheld Laser Welding Equipment HT
Website: heltec-energy.com
Key Highlights: This is a Lithium Battery Special Handheld Galvanometer-Type Laser Welding Machine, supporting welding 0.3mm-2.5mm copper/aluminum….
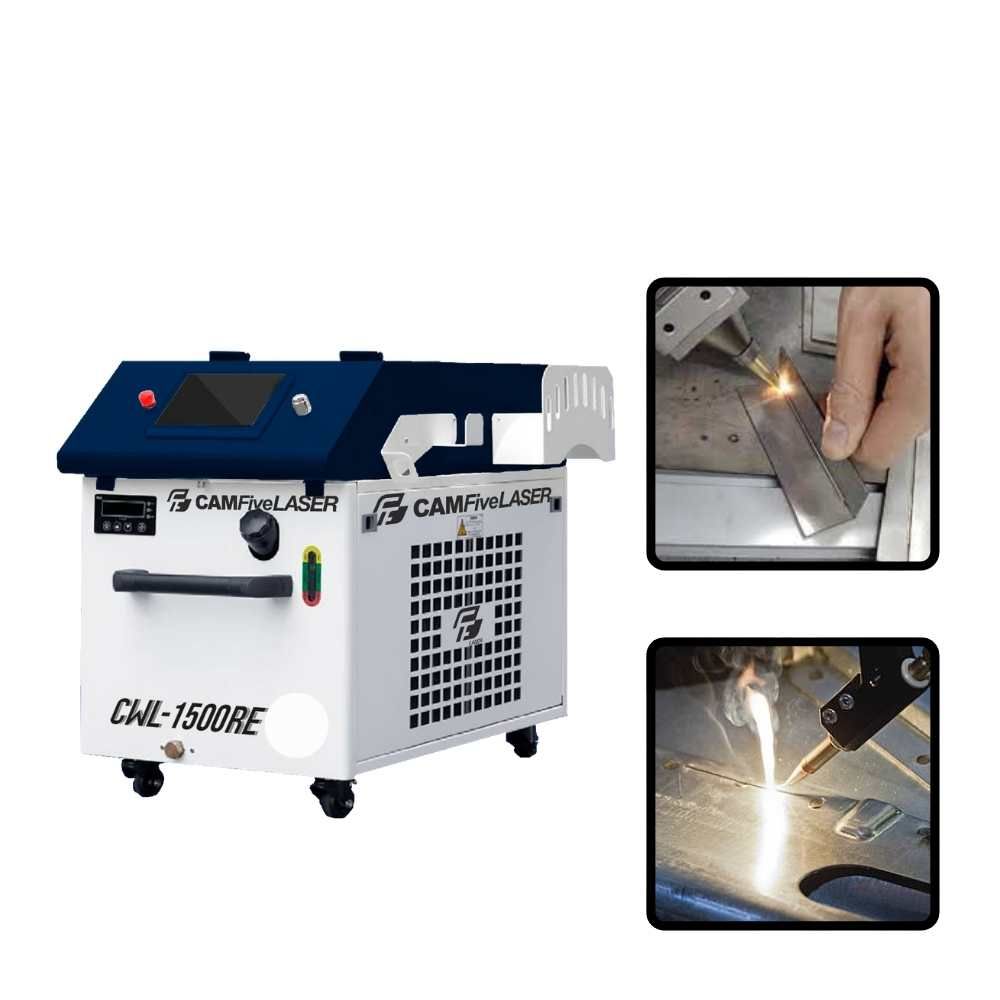
#6 1500W Handheld Fiber Laser Welder CAMFive CWL
Website: camfivelaser.com
Key Highlights: In stock 30-day returnsFIBER SOURCE: 1500W. ☑️ Increases efficiency between 3 to 10 times. Save 2 welders. ☑️ Up to 8 times faster than argon arc welder….
#7 Mini handheld laser welding machine, 1500W laser welder
Website: triumphlaser.com
Key Highlights: Mini laser welding machine is designed to be lightweight and compact, making them easy to carry to different job sites or within a workshop….
#8 HWA Series Best Air
Website: hg-star.com
Key Highlights: Model: SMART HWA Series. Category: Air-cooled laser welding machines. Brand Name: HG Laser. Laser power: 1500W. Application: cabinet kitchen, staircase ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1500 W Laser Welder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 1500 W Laser Welders
The global market for 1500 W laser welders is poised for substantial growth and transformation by 2026, driven by increasing automation, advancements in fiber laser technology, and rising demand across key industrial sectors. This analysis explores the primary trends shaping the adoption, innovation, and competitive landscape of 1500 W laser welding systems in the coming years.
-
Growing Demand in Manufacturing and Automotive Industries
By 2026, the automotive and general manufacturing sectors are expected to be the largest consumers of 1500 W laser welders. The push toward electric vehicles (EVs) has intensified the need for high-precision, high-speed welding of battery components, motor housings, and lightweight chassis structures. A 1500 W laser offers an optimal balance between power and precision for thin-to-medium thickness materials, making it ideal for EV production lines. Automation integration with robotics further enhances throughput, supporting Industry 4.0 initiatives. -
Advancements in Fiber Laser Efficiency and Reliability
Fiber laser technology continues to evolve, with manufacturers focusing on improving wall-plug efficiency, beam quality, and system longevity. By 2026, 1500 W fiber laser welders are expected to deliver enhanced energy efficiency (up to 40–45%), reduced cooling requirements, and lower operational costs. These improvements make the systems more attractive for small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking cost-effective yet high-performance welding solutions. -
Expansion into New Application Areas
Beyond traditional industries, 1500 W laser welders are gaining traction in emerging sectors such as aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and renewable energy. For example, solar panel frame production and drone component fabrication increasingly rely on the consistent weld quality and minimal heat distortion offered by 1500 W systems. The versatility of these lasers in handling various metals—steel, aluminum, copper, and dissimilar metal joints—broadens their applicability. -
Increased Adoption in Asia-Pacific Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and South Korea, will lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and expanding EV supply chains. Local production of laser systems is reducing costs and improving accessibility. Chinese manufacturers such as Raycus, Max Photonics, and JPT are offering competitive 1500 W laser sources, enabling domestic integration into welding machines at lower price points. -
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and IoT
Laser welders are becoming smarter, with real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance features. By 2026, most 1500 W systems will likely include IoT-enabled sensors and cloud connectivity, allowing manufacturers to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent weld quality through data analytics. AI-driven process optimization is expected to become a standard differentiator among premium systems. -
Intensifying Competition and Price Pressure
As more players enter the market, competition is heating up, leading to price reductions and faster innovation cycles. Established brands like IPG Photonics, TRUMPF, and nLIGHT face growing competition from Asian suppliers offering comparable performance at lower costs. This trend is accelerating global adoption but also pressuring profit margins, pushing companies to focus on value-added services and customized solutions. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency as Key Drivers
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing purchasing decisions. The energy-efficient design of modern 1500 W laser welders—especially when replacing traditional arc welding—helps reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, the minimal need for consumables and lower material waste enhance the eco-friendliness of laser welding processes. -
Rise of Hybrid and Modular Systems
Modular laser welding platforms that allow power scalability (e.g., combining multiple 1500 W units) are gaining popularity. Hybrid systems integrating laser welding with other processes like cleaning or cutting in a single workstation improve workflow efficiency. These flexible configurations are particularly appealing for job shops and contract manufacturers serving diverse clients.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 1500 W laser welder market will be characterized by technological maturity, wider industrial adoption, and strong regional growth—especially in Asia. While competition will drive pricing downward, innovation in intelligence, integration, and efficiency will define market leadership. Companies investing in smart, adaptable, and sustainable laser welding solutions are best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 1500 W Laser Welder (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a 1500 W laser welder involves significant investment and technical complexity, making it crucial to avoid common pitfalls related to both quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these areas can lead to performance issues, safety risks, legal exposure, and financial losses.
Quality Pitfalls
Overestimating Power Output Claims
Many suppliers advertise “1500 W” peak or burst power, but actual stable continuous output may be significantly lower (e.g., 1200–1300 W). This discrepancy reduces welding penetration and speed. Always demand third-party test reports (e.g., from TÜV or SGS) verifying sustained output under industrial conditions.
Compromised Optical Components
Low-cost systems may use inferior lenses, fiber optics, or collimators that degrade quickly under high power, leading to beam distortion, reduced efficiency, and frequent replacements. Insist on specifications detailing component materials (e.g., fused silica lenses) and expected lifespan.
Inadequate Cooling Systems
A 1500 W laser generates substantial heat. Units with undersized or poorly designed cooling (e.g., insufficient chiller capacity or airflow) risk thermal shutdowns or permanent damage. Verify chiller specs (e.g., ≥ 3 kW cooling capacity) and ask for thermal stress test data.
Poor Beam Quality (M² Value)
Beam quality directly affects focusability and weld precision. Some vendors omit M² values or provide inflated numbers. For industrial welding, M² < 1.3 is ideal. Request beam profiler reports to confirm actual performance.
Lack of Safety Certification
Non-compliant systems may lack essential safety features (e.g., interlocks, emergency stops, or proper laser shielding), violating OSHA/IEC 60825-1 standards. Confirm the unit has valid CE, FDA, or equivalent certification with test documentation.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unlicensed Core Technology
Some manufacturers use proprietary laser sources, control software, or scanning heads without proper licensing. Purchasing such systems risks legal action against you as the end user for IP infringement, especially in regulated markets like the EU or U.S.
Proprietary Software Lock-in
Suppliers may embed closed-source firmware that restricts maintenance, upgrades, or integration with existing systems. This creates dependency and increases long-term costs. Demand SDKs, open communication protocols (e.g., Modbus), or proof of software licensing.
Counterfeit or Gray-Market Components
Units may incorporate unlicensed or cloned control boards, drivers, or software derived from legitimate brands (e.g., copied from IPG or Raycus systems). These lack support, updates, and void warranties. Audit supply chains and require component origin documentation.
Inadequate IP Warranty
Standard contracts often omit indemnification clauses for IP disputes. If sued for using infringing technology, you may bear full liability. Negotiate explicit IP warranties in the purchase agreement, requiring the supplier to cover legal costs.
Data and Process Ownership Ambiguity
Cloud-connected welders may transmit operational data to the vendor. Unclear terms could allow the supplier to claim ownership of your welding parameters or production data. Review data policies and ensure contractual rights to your process IP.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct Factory Audits: Visit the manufacturer to verify production standards and component sourcing.
- Demand Third-Party Validation: Require test reports for power, beam quality, and safety compliance.
- Engage Legal Counsel: Review contracts for IP indemnification and data rights.
- Pilot Testing: Run a trial with your materials to validate performance claims before full procurement.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP risks, you ensure a reliable, compliant, and legally secure investment in your laser welding capability.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1500 W Laser Welder
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe transportation, handling, import/export, and operation of a 1500 W fiber laser welder. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, personnel safety, and equipment integrity.
- Regulatory Classification & Documentation
1.1 Harmonized System (HS) Code
– Typical HS Code: 8515.31.00 (Electrode or laser welding machines)
– Confirm with local customs authority; variations may apply by country.
– Required for import/export declarations, duty assessment, and customs clearance.
1.2 Technical Documentation
– Include with shipment:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Technical Specifications Sheet
– CE or IEC/EN 60825-1 Compliance Certificate (laser safety)
– RoHS and REACH Compliance Declaration
– User Manual (including safety instructions)
- Safety & Hazard Compliance
2.1 Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1)
– The 1500 W laser is Class 4—highest hazard level.
– Equipment must have:
– Interlock systems
– Emergency stop
– Laser emission indicator
– Protective housing
– Warning labels (DANGER: Laser Radiation)
– Mandatory compliance with local laser safety regulations (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the U.S., Health Canada, EU directives).
2.2 Electrical Safety
– Complies with IEC 60204-1 (Safety of machinery – Electrical equipment).
– Voltage compatibility: Confirm supply voltage (e.g., 200–240 V AC, 3-phase).
– Power requirements: ~8–10 kVA depending on configuration.
2.3 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
– Must meet IEC/EN 61326-1 for industrial environments.
– Ensure proper grounding and shielding during operation.
- Packaging & Transportation
3.1 Packaging Requirements
– Use robust, shock-absorbent wooden crate with internal foam or custom foam inserts.
– Protect optical components and motion systems with protective caps and immobilization.
– Include desiccant packs to prevent moisture damage.
3.2 Handling Instructions
– Label crate: “FRAGILE,” “THIS SIDE UP,” “DO NOT STACK,” “LASER EQUIPMENT”
– Use forklift or crane for loading/unloading; avoid tilting beyond ±10°.
– Avoid exposure to rain, snow, or extreme temperatures during transit.
3.3 Transport Modes
– Air Freight: Subject to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (not classified as hazardous if no batteries).
– Sea Freight: Standard container (20’ or 40’). Secure crate to prevent shifting.
– Road Freight: Use padded suspension and covered trailers.
- Import/Export Controls
4.1 Export Licensing
– No ITAR or EAR (U.S. Department of Commerce) controls typically apply to commercial laser welders under 3 kW, but verify with local export authority.
– Some countries may require end-user certificates or end-use statements.
4.2 Import Duties & Taxes
– Research destination country’s import tariffs, VAT, and customs clearance procedures.
– Possible import restrictions or licensing for high-power lasers in certain regions (e.g., China, Russia, India).
4.3 Customs Broker Engagement
– Use a licensed customs broker experienced in industrial machinery.
– Provide complete and accurate documentation to prevent delays.
- Installation & Site Requirements
5.1 Facility Preparation
– Floor loading capacity: ≥500 kg/m² (verify machine weight—typically 300–600 kg).
– Climate control: 10–35°C ambient, humidity <80% non-condensing.
– Clean, dust-free environment recommended.
5.2 Utilities
– Electrical: 3-phase, 200–240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, dedicated circuit with surge protection.
– Cooling: Chiller unit required (integrated or external), 20–25°C water temperature.
– Compressed air: 0.5–0.7 MPa, oil- and moisture-free (if used for nozzle shielding or cleaning).
5.3 Safety Infrastructure
– Laser-safe enclosure or light-tight cabin with interlocks.
– Laser protective windows (OD 5+ for 1070 nm wavelength).
– Fume extraction system compliant with OSHA or local air quality standards.
- Operator Training & Compliance
6.1 Mandatory Training
– Operators must complete laser safety training per ANSI Z136.1 or equivalent.
– Training includes: hazard awareness, emergency procedures, PPE use, and system operation.
6.2 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
– Required: Laser safety goggles (OD 6+ at 1060–1080 nm), flame-resistant clothing, face shield.
– Hearing protection if auxiliary equipment (e.g., chiller, fume extractor) exceeds 85 dB.
6.3 Documentation & Recordkeeping
– Maintain:
– Equipment maintenance logs
– Laser safety program documentation
– Operator training records
– Incident reports (if applicable)
- Environmental & Disposal Compliance
7.1 Waste Management
– Dispose of failed laser components (e.g., fiber modules, optics) per local e-waste regulations.
– Used coolant and lubricants: handle as hazardous waste if applicable.
7.2 End-of-Life Disposal
– Follow WEEE Directive (EU) or equivalent for electronic waste recycling.
– Return components to manufacturer if a take-back program exists.
- Country-Specific Compliance (Examples)
| Country | Key Requirements |
|——–|——————|
| USA | FDA/CDRH laser product reporting (variance may apply); OSHA workplace safety |
| EU | CE Marking; Annex I of Machinery Regulation (EU) 2023/1230; Laser Safety Directive |
| China | CCC Mark may be required; SAB licensing for import; GB/T standards compliance |
| Canada | Health Canada laser product registration; CSA C22.2 No. 77 |
| Australia | RCM mark; AS/NZS IEC 60825.1 compliance; ARTG registration if applicable |
Conclusion
The 1500 W laser welder requires careful attention to international and local compliance standards throughout its lifecycle—from shipping and customs to installation and operation. Always consult with legal, safety, and technical experts in the destination country to ensure full regulatory adherence.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 1500 W Laser Welder
After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, cost considerations, supplier reliability, and long-term operational needs, sourcing a 1500 W fiber laser welder presents a strategic investment for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and weld quality. This power range offers an optimal balance between performance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for a wide range of applications including automotive components, precision fabrication, and thin to medium-thickness metal welding.
Key advantages include high precision, minimal heat distortion, reduced post-processing requirements, and increased production speed compared to traditional welding methods. Additionally, modern 1500 W systems often come with integrated safety features, user-friendly controls, and compatibility with automation, supporting scalability and workforce adaptability.
Potential suppliers have been assessed for technical support, warranty terms, delivery timelines, and training offerings. Selecting a reputable manufacturer with proven service networks ensures long-term reliability and minimizes downtime.
In conclusion, procuring a 1500 W laser welder aligns with goals of improving productivity, weld consistency, and competitiveness in the market. With proper operator training and maintenance planning, this equipment will deliver a strong return on investment and support future technological integration.