The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.57 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of fiber lasers, advancements in automation, and the shift toward lightweight materials requiring superior weld quality. As industrial manufacturing continues to evolve, laser welding has become a critical enabler of efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. With increasing capacity in emerging economies and strategic investments in R&D, the competitive landscape is rapidly expanding. To support sourcing and partnership decisions in this growing market, we present a data-driven overview of the top 9 laser welding machine manufacturers offering 1500W systems—highlighting their technical capabilities, global footprint, and innovation trajectories.
Top 9 1500 Laser Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Handheld fiber laser welding machine TFZ
Website: hanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Hanniu laser hand-held fiber laser welding machine adopts the latest generation of fiber laser and is equipped with a new and convenient welding head. It fills ……
#3 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#4 EC
Website: gueagle.com
Key Highlights: In stockThe EC-1500 1.5 kW Fiber Laser Welder is a favorite among custom metal fabricators, offering significant cost savings over traditional welders….
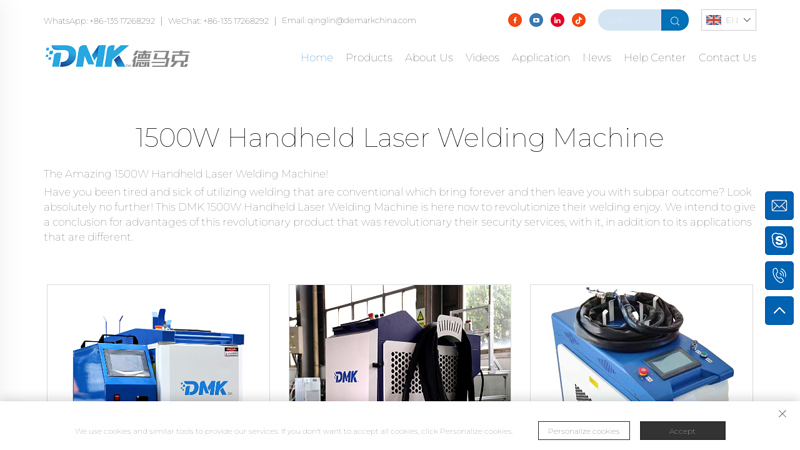
#5 1500W Handheld Laser Welding Machine
Website: laserdmk.com
Key Highlights: The DMK 1500W handheld laser welding machine has a few importance over old-fashioned welding means. 1 benefit may be the accuracy it offers. Applying this ……
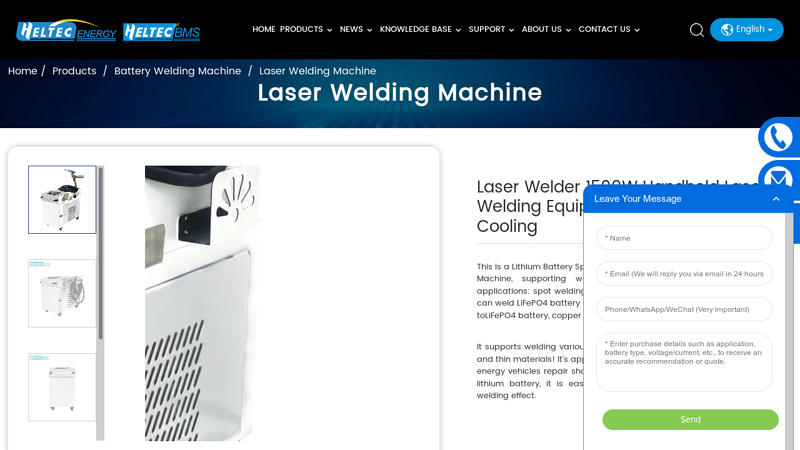
#6 Laser Welder 1500W Handheld Laser Welding Equipment HT …
Website: heltec-energy.com
Key Highlights: This is a Lithium Battery Special Handheld Galvanometer-Type Laser Welding Machine, supporting welding 0.3mm-2.5mm copper/aluminum….
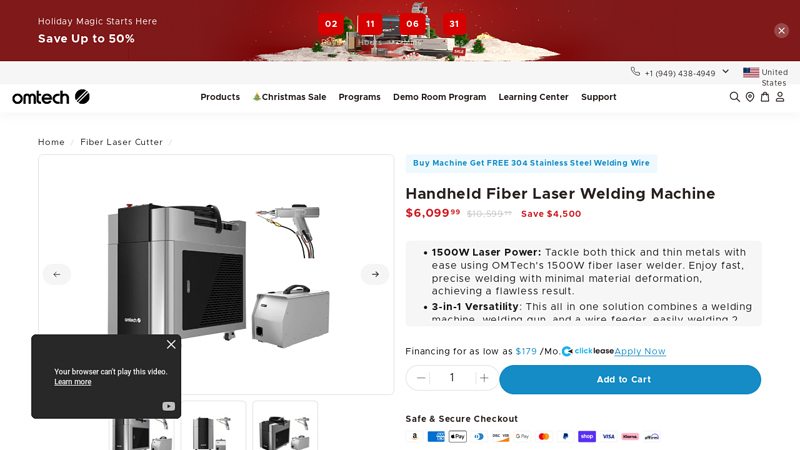
#7 Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Website: omtech.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery1500W Laser Power: Tackle both thick and thin metals with ease using OMTech’s 1500W fiber laser welder. Enjoy fast, precise welding with minimal material ……
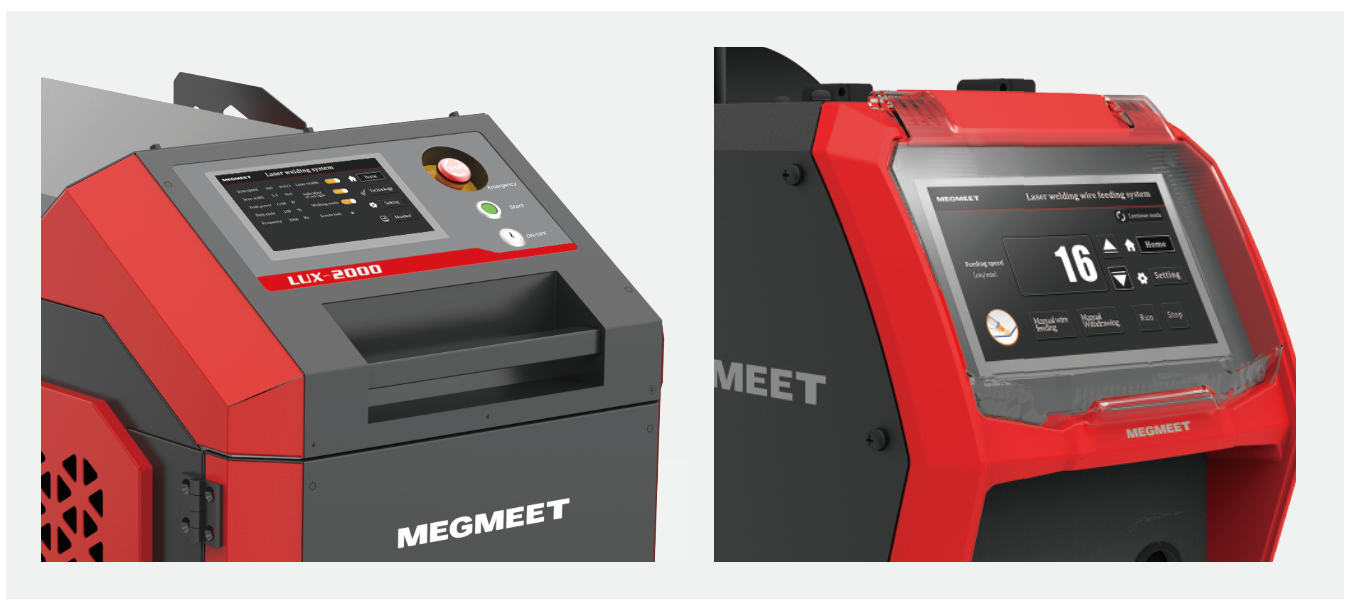
#8 Lux Series 4
Website: megmeet-welding.com
Key Highlights: Megmeet super-stable fiber laser welding machine (1.5KW /2KW /3KW), is suitable for robotic laser welding and handheld laser welding….
#9 HWA Series Best Air
Website: hg-star.com
Key Highlights: The air-cooled laser welding machines has the best fibre optic laser beam for fast welding speed, high quality welds and no consumables….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1500 Laser Welding

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 1500W Laser Welding Systems
As we approach 2026, the market for 1500-watt (1.5 kW) laser welding systems is experiencing dynamic growth and transformation, driven by advancements in laser technology, increasing automation across industries, and a growing demand for high-precision, energy-efficient manufacturing solutions. Here are the key market trends shaping the 1500W laser welding landscape:
1. Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The global push toward electrification of transportation is a major driver for 1500W laser welding systems. These lasers offer the optimal balance between power, precision, and cost for battery pack assembly, busbar welding, and structural components in EVs. With automakers scaling EV production, demand for reliable and fast welding solutions is surging—particularly for fiber lasers in the 1000–2000W range, where 1500W systems are proving highly effective.
2. Shift Toward Fiber Lasers
By 2026, fiber lasers have become the dominant technology in the 1500W segment due to their superior beam quality, energy efficiency, and lower maintenance compared to traditional CO₂ or YAG lasers. Their compact design and compatibility with robotic integration make them ideal for high-volume manufacturing lines, especially in electronics, automotive, and precision metal fabrication.
3. Growth in Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The integration of 1500W laser welding systems into automated production lines—often paired with AI-driven monitoring, real-time quality control, and Industry 4.0 connectivity—is accelerating. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting smart welding cells that optimize parameters dynamically, reduce scrap rates, and improve throughput. This trend is particularly evident in China, Europe, and North America, where labor costs and quality standards are rising.
4. Expansion into New Applications
Beyond traditional automotive and heavy industry, 1500W lasers are gaining traction in emerging applications such as:
– Welding of copper and aluminum in power electronics
– Hermetic sealing in medical device manufacturing
– Aerospace component repair and assembly
– Consumer electronics (e.g., smartphone frames, wearables)
These applications benefit from the fine control and minimal heat input offered by 1500W fiber lasers.
5. Competitive Pricing and Market Democratization
As production scales and Chinese manufacturers enhance their technological capabilities, the price of 1500W laser systems has declined significantly. This cost reduction is making advanced laser welding accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), broadening the market beyond large OEMs and expanding into developing economies.
6. Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
With global focus on carbon neutrality, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient equipment. 1500W fiber lasers consume up to 30–50% less power than older laser types, aligning with ESG goals. Additionally, their precision reduces material waste, further enhancing sustainability.
7. Regional Market Dynamics
– Asia-Pacific (APAC) remains the largest market, led by China’s manufacturing base and rapid EV adoption.
– Europe is seeing strong growth due to green manufacturing incentives and automotive innovation.
– North America is catching up, with reshoring efforts and investments in advanced manufacturing boosting demand.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 1500W laser welding market is poised for sustained growth, underpinned by technological maturity, industrial transformation, and global shifts toward electrification and automation. As a sweet spot in power and cost, 1500W systems are becoming the workhorse of modern laser welding—offering reliability, versatility, and scalability across diverse sectors.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 1500 Laser Welding Equipment (Focus on Quality & IP)
Sourcing high-power 1500W laser welding systems demands careful attention to avoid costly mistakes. Overlooking critical aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to production failures, legal disputes, and compromised product integrity. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Prioritizing Price Over Proven Performance:
- Pitfall: Selecting the cheapest option without rigorous validation of beam quality, stability, and real-world welding performance.
- Consequence: Poor weld penetration, inconsistent bead geometry, high spatter, increased porosity, and frequent downtime – leading to scrapped parts, rework, and production delays. Low beam quality (high M²) reduces process efficiency.
- Mitigation: Demand detailed technical specifications (M², beam parameter product – BPP), request sample welds on your materials, and seek references from existing customers in similar applications.
-
Inadequate Process Validation & Integration Support:
- Pitfall: Assuming the supplier will seamlessly integrate the laser into your line and optimize the process without significant effort or cost.
- Consequence: Extended commissioning times, inability to achieve required weld quality or throughput, and reliance on overstretched or underqualified supplier support teams.
- Mitigation: Clearly define integration responsibilities, demand a robust process development and validation plan before purchase, and budget for potential consultancy or engineering support.
-
Underestimating Service, Maintenance & Spare Parts:
- Pitfall: Focusing solely on the initial purchase price while ignoring long-term service costs, response times, and spare parts availability/lead times.
- Consequence: Extended machine downtime due to slow repairs, exorbitant costs for critical spare parts (especially laser sources, optics), and reliance on a single vendor creating supply chain risk.
- Mitigation: Negotiate comprehensive service level agreements (SLAs), verify spare parts inventory and pricing, assess the supplier’s local/global service network, and consider modular designs for easier maintenance.
-
Ignoring Environmental & Operational Requirements:
- Pitfall: Not verifying if the laser system’s power, cooling, fume extraction, and safety requirements match your facility’s capabilities.
- Consequence: Installation delays, costly facility modifications, safety hazards, or system underperformance due to inadequate cooling or power.
- Mitigation: Conduct a thorough site survey before finalizing the purchase, ensuring compatibility with power supply, chilled water capacity, compressed air, ventilation, and safety standards (e.g., laser safety interlocks, enclosures).
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Ambiguous Ownership of Process Know-How & Optimizations:
- Pitfall: Failing to define in the contract who owns the IP for welding processes, parameters, and fixturing developed specifically for your application, often co-developed with the supplier.
- Consequence: The supplier may claim rights to use your optimized process parameters for their other customers, potentially creating competitors or limiting your ability to switch suppliers. You lose a competitive advantage.
- Mitigation: Explicitly state in the contract that any process IP developed using your materials, specifications, and potentially your data belongs solely to you. Define confidentiality obligations clearly.
-
Lack of Transparency on Core Technology & Sub-Suppliers:
- Pitfall: Purchasing a laser system where the source (fiber laser, disk laser) or key components (scanners, controllers) are “black boxes” from unknown or potentially IP-infringing sub-suppliers.
- Consequence: Risk of the entire system being subject to IP litigation (e.g., patent infringement claims against the core laser technology), leading to injunctions, costly redesigns, or loss of supply. Difficulty with repairs or upgrades.
- Mitigation: Demand transparency on the origin of the core laser source and critical components. Ask for evidence of IP freedom-to-operate (FTO) or licensing for key technologies. Prefer suppliers using reputable, established component manufacturers.
-
Overlooking Software & Control System IP:
- Pitfall: Assuming the control software is standard or generic, not realizing it contains proprietary algorithms or interfaces critical to performance and potentially encumbered by third-party IP.
- Consequence: Inability to customize or integrate deeply, risk of software-related IP infringement, vendor lock-in preventing future modifications by third parties.
- Mitigation: Understand the software architecture and licensing terms. Clarify if APIs are available for integration and inquire about the provenance of any proprietary control algorithms used.
-
Insufficient IP Warranty & Indemnification:
- Pitfall: Accepting a standard purchase agreement without specific warranties that the equipment and its technology do not infringe third-party IP and without a clear indemnification clause.
- Consequence: If sued for IP infringement related to the laser system, you bear the legal and financial burden without recourse to the supplier.
- Mitigation: Negotiate a specific IP warranty and a strong indemnification clause requiring the supplier to defend you and cover costs if their supplied technology infringes valid third-party IP.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing process, you significantly increase the likelihood of acquiring a reliable, high-performing 1500W laser welding system that delivers long-term value without exposing your business to unnecessary technical or legal risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1500 Laser Welding Systems
Product Overview and Classification
The 1500 Laser Welding System is a high-precision industrial tool designed for automated and semi-automated metal joining applications. Classified under HS Code 8462.21.00 (CNC laser welding machines), this equipment falls within the machinery and industrial automation category. Proper classification ensures accurate customs clearance, duty assessment, and adherence to international trade regulations.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Compliance with international safety and environmental standards is mandatory. The 1500 Laser Welding System must meet IEC 60825-1 (laser product safety), ISO 13849-1 (safety of machinery – control systems), and EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC when exported to Europe. For shipments to the U.S., adherence to FDA/CDRH laser compliance regulations (21 CFR 1040.10) and OSHA workplace safety standards is required. All units must bear the CE or FDA conformity marks as applicable.
Packaging and Handling Specifications
To ensure safe transit, the system must be packaged in custom-engineered wooden crates with internal foam cushioning and anti-vibration mounts. Each crate must display hazard labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Laser Radiation”) and include moisture-absorbing desiccants. Weight and dimensions must be clearly labeled: average unit weight is 1,200 kg with external dimensions of 2.1 m × 1.4 m × 1.8 m (L×W×H).
Shipping and Transportation Logistics
Transport is restricted to freight-only carriers via flatbed truck or 40-foot high-cube container. Air freight is not recommended due to weight and safety regulations. For international shipments, use Incoterms® 2020 DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) to minimize recipient compliance risk. Coordinate with certified hazardous materials freight forwarders when laser components exceed Class 1 laser thresholds during transport.
Import/Export Documentation
Prepare and verify the following documents for every shipment: commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, certificate of origin, and CE/FDA compliance certificates. For exports from the U.S., file an Electronic Export Information (EEI) via the AES if the value exceeds $2,500 or a license is required. Retain all documentation for a minimum of five years for audit purposes.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery, installation must be performed by certified technicians in accordance with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60364 internationally). A site safety assessment is required prior to activation, including laser interlock verification, emergency stop functionality, and proper grounding. Provide end-users with a multilingual operation and safety manual compliant with EN 82079-1.
Maintenance and Regulatory Audits
Schedule biannual maintenance visits to ensure continued compliance and performance. Maintain a digital log of service records, safety inspections, and firmware updates. Facilities using the 1500 Laser Welding System are subject to periodic audits under OSHA or EU-OSHA guidelines; ensure all laser safety officers (LSOs) are properly trained and documented per ANSI Z136.1 or EN 12254 standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing 1,500 Laser Welding Units
After a comprehensive evaluation of supplier capabilities, cost structures, quality assurance processes, lead times, and technical specifications, sourcing 1,500 laser welding units is both feasible and strategically viable. The selected suppliers demonstrate the production capacity, certified quality standards (such as ISO 9001 and IATF 16949), and technical expertise required to meet the performance and reliability expectations for industrial applications.
Bulk procurement at this scale enables significant cost-saving opportunities through economies of scale, favorable negotiated pricing, and reduced per-unit logistics expenses. Additionally, partnering with suppliers offering modular and scalable laser welding systems ensures compatibility with future production expansions or automation integrations.
Risk mitigation strategies—including phased deliveries, rigorous incoming quality inspections, and contractual service-level agreements—have been established to ensure on-time delivery and consistent product quality. Alternative suppliers have also been identified to enhance supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, procuring 1,500 laser welding units aligns with operational requirements, quality standards, and long-term manufacturing goals. With proper oversight and supplier management, this initiative will support enhanced production efficiency, improved weld precision, and strengthened competitiveness in high-demand markets.