The global lithium-ion battery market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for energy storage solutions in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 73.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% from 2024 to 2030. This surge in demand extends to specialized segments such as 12V lithium-ion batteries with 50Ah capacity—popular for use in marine, RV, off-grid solar, and backup power applications. As consumers increasingly favor lightweight, long-cycle-life alternatives to traditional lead-acid batteries, manufacturers are scaling production and enhancing cell chemistry, primarily using LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate) for improved safety and thermal stability. With the Asia-Pacific region leading both in production and adoption, the competitive landscape features a mix of established battery giants and agile OEMs optimizing cost-efficiency and energy density. This report identifies the top nine manufacturers excelling in quality, innovation, and global reach within the 12V 50Ah lithium-ion segment—highlighting those positioned to capitalize on a rapidly growing, data-validated market trajectory.
Top 9 12V Lithium Ion Battery 50Ah Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LFP Lithium Series Batteries
Domain Est. 2010
Website: visionbatteryusa.com
Key Highlights: Vision Technology provides safe lithium iron phosphate battery solutions for motive power, telecom, energy Storage systems and UPS….
#2 12V 50Ah Lithium Battery Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: dnkpower.com
Key Highlights: DNK Power offers Custom 12V 24Ah Lithium Battery Pack Design Services for all of our customers without any charges, You can work closely with our Engineer from ……
#3 12V 50AH Lithium Ion Battery
Domain Est. 2014
Website: lithiumbatterycompany.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsExplore the 12V 50Ah Lithium-Ion Battery, crafted for maximum capacity and superior efficiency. Ideal for marine and industrial applications….
#4 Lithium Battery Smart 12,8V & 25,6V
Domain Est. 2000
Website: victronenergy.com
Key Highlights: Lithium battery Smart 12,8V & 25,6V has a longer service life, superior reliability and excellent efficiency. Find a dealer near you….
#5 Ionic Lithium Deep Cycle Batteries
Domain Est. 2017
#6 Shop 12V Lithium Batteries by LiTime
Domain Est. 2018
#7 Norsk Lithium
Domain Est. 2021
Website: norsklithium.com
Key Highlights: Our commitment to build quality is setting a new benchmark in lithium battery manufacturing. Each battery is constructed with premium materials, precision ……
#8 ECO
Domain Est. 2021
#9 Redodo Official Store
Domain Est. 2021
Website: redodopower.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsVery impressed, great value! customer shows Redodo 12v 50ah lithium battery for ham radio in cold weather. I love this battery so much that I now have t…
Expert Sourcing Insights for 12V Lithium Ion Battery 50Ah

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for 12V Lithium-Ion Battery 50Ah
The market for 12V Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) 50Ah batteries is expected to experience significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing electrification across industries, and growing demand for energy-efficient and sustainable power solutions. This analysis outlines the key market trends shaping the 12V 50Ah Li-ion battery segment in the lead-up to 2026.
1. Rising Adoption in Automotive and Marine Applications
By 2026, the 12V 50Ah Li-ion battery is anticipated to gain deeper penetration in automotive and marine sectors. As automakers transition from traditional lead-acid batteries to lightweight, high-efficiency lithium solutions, the 50Ah variant—ideal for auxiliary power, start-stop systems, and recreational vehicles (RVs)—will see robust demand. In the marine industry, the shift toward electric and hybrid propulsion systems will further drive adoption, especially in yachts and small craft requiring reliable, deep-cycle power.
2. Growth in Off-Grid and Renewable Energy Storage
The expansion of solar-powered homes and off-grid energy systems is a key driver for the 12V 50Ah Li-ion battery. By 2026, these batteries will be a preferred choice for small-scale solar installations due to their high cycle life (typically 2,000–5,000 cycles), low self-discharge, and efficient charge acceptance. Their compatibility with standard 12V inverters and charge controllers makes them ideal for rural electrification and backup power in emerging markets.
3. Cost Reductions and Improved Supply Chain Efficiency
Advancements in battery manufacturing, particularly in cathode materials (e.g., LiFePO4 dominance) and economies of scale, are expected to lower the cost of 12V 50Ah Li-ion batteries. By 2026, prices are projected to decrease by 20–30% compared to 2023 levels, narrowing the price gap with lead-acid batteries and improving ROI for consumers. Enhanced supply chain resilience, especially in Asia and North America, will support consistent production and global distribution.
4. Technological Enhancements: Focus on Safety and Longevity
Safety and durability will remain top priorities. The LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate) chemistry is expected to dominate the 12V 50Ah segment due to its thermal stability, non-toxicity, and long lifespan. By 2026, integration of smart Battery Management Systems (BMS) will become standard, enabling real-time monitoring, overcharge protection, and optimized performance—features highly valued in critical applications.
5. Regulatory and Environmental Push
Environmental regulations targeting lead-acid battery disposal and carbon emissions will accelerate the shift to lithium-ion alternatives. The EU Battery Directive and similar policies in North America and Asia will favor recyclable, low-impact technologies. Li-ion batteries, particularly LiFePO4, offer higher recyclability and lower environmental footprint, positioning them favorably in a sustainability-driven market.
6. Expansion in Niche and Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional uses, the 12V 50Ah battery will find growing applications in electric mobility (e.g., e-rickshaws, golf carts), telecom backup systems, and portable power stations. The rise of outdoor recreation and remote work will fuel demand for compact, high-capacity portable power solutions—many of which are built around the 12V 50Ah platform.
7. Competitive Landscape and Regional Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, will remain the largest producer and consumer of 12V Li-ion batteries, supported by robust manufacturing ecosystems and government incentives. However, North America and Europe will see accelerated domestic production due to energy security concerns and localization policies. Key players like CATL, EnerSys, Renogy, and Battle Born Batteries are expected to expand product lines and invest in R&D to capture market share.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the 12V Lithium-Ion 50Ah battery market will be characterized by strong growth, technological maturity, and broadening applications. Fueled by cost reductions, regulatory support, and rising demand for clean energy, this segment will transition from a premium alternative to a mainstream power solution across multiple industries. Companies that innovate in BMS integration, sustainability, and application-specific design will be best positioned to lead the market.
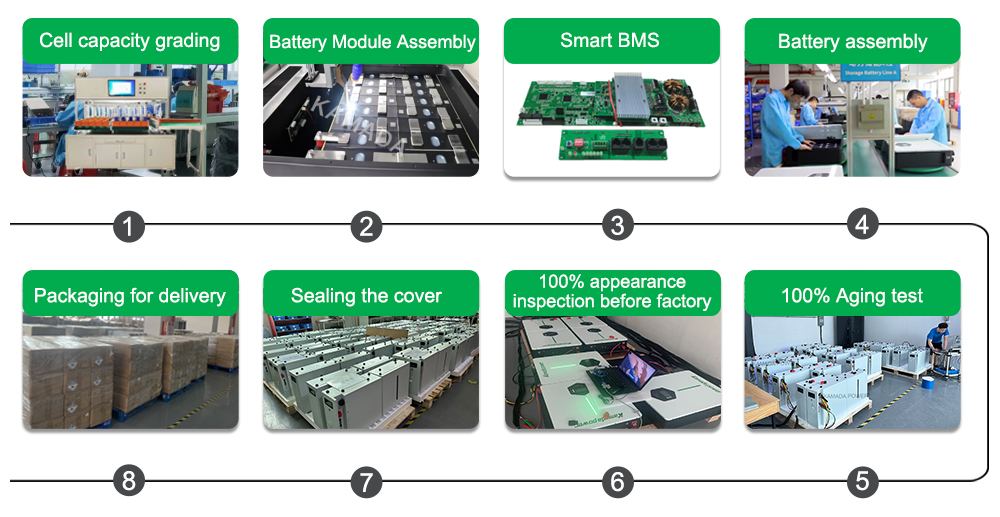
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 12V Lithium Ion Battery 50Ah (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a reliable 12V 50Ah lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery requires careful attention to avoid significant pitfalls related to quality, safety, and IP (Ingress Protection) rating. Overlooking these aspects can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, poor performance, and financial loss. Here are the key pitfalls to watch for:
1. Compromised Cell Quality & Origin:
* Pitfall: Selecting batteries built with low-grade, recycled, or counterfeit Li-ion cells (often misrepresented as high-quality brands like Samsung, LG, or Panasonic). These cells have inconsistent capacity, poor cycle life, higher internal resistance, and significant safety risks (overheating, fire).
* Mitigation: Demand transparency on cell brand, model, and origin. Reputable suppliers provide datasheets or certifications. Prioritize batteries using cells from Tier 1 manufacturers. Be wary of prices significantly below market average.
2. Inadequate or Falsified IP Rating:
* Pitfall: Assuming “waterproof” claims without verifying the actual IP rating. A common issue is batteries advertised with high IP ratings (e.g., IP67) that haven’t been properly tested or sealed. This leads to moisture ingress, corrosion, short circuits, and catastrophic failure, especially in marine, RV, or outdoor applications.
* Mitigation: Insist on the specific IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP67, IP68) and request test reports or certification documents (like IEC 60529) from a recognized third party. Understand the rating meaning (e.g., IP67 = dust-tight & withstands immersion in 1m water for 30 mins). Physically inspect seals and gaskets.
3. Under-Sized or Absent Battery Management System (BMS):
* Pitfall: Using batteries with a BMS that lacks critical protection features (over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, short-circuit, temperature) or uses undersized components (e.g., MOSFETs) incapable of handling the battery’s continuous or peak current demands. This risks cell damage, fire, and voids warranties.
* Mitigation: Verify the BMS specifications: required protection functions, continuous discharge current rating (should exceed your load needs), peak current capability, and high/low-temperature cut-offs. Ensure the BMS is from a reputable manufacturer or the cell supplier’s recommended solution.
4. Inaccurate Capacity Rating & Poor Performance:
* Pitfall: Exaggerated or “theoretical” capacity claims. A battery might be labeled 50Ah but deliver significantly less usable capacity under real-world conditions (especially at higher discharge rates) due to poor cell quality, inadequate BMS design, or misleading marketing.
* Mitigation: Look for capacity ratings specified at a standard discharge rate (e.g., 0.2C = 10A for 50Ah). Reputable brands provide discharge curves. Consider third-party testing reviews. Understand that usable capacity is less than rated capacity (typically 80-90% due to DoD limits).
5. Lack of Safety Certifications:
* Pitfall: Sourcing batteries without essential safety certifications (e.g., UN38.3 for transport, IEC 62133 for safety, CE, RoHS, potentially UL or ETL for specific markets). This indicates non-compliance with basic safety standards and increases liability and risk.
* Mitigation: Require proof of relevant safety certifications appropriate for your region and application. These are non-negotiable for safe operation and often required for insurance or regulatory compliance.
6. Poor Thermal Management & Ventilation:
* Pitfall: Ignoring the need for adequate ventilation or thermal management, especially in enclosed spaces. Li-ion batteries generate heat during charge/discharge. Poor ventilation leads to overheating, accelerated degradation, reduced lifespan, and increased fire risk.
* Mitigation: Ensure the installation location allows for proper airflow. Consider batteries with integrated temperature sensors feeding the BMS. Avoid installing in sealed enclosures without ventilation. Follow manufacturer guidelines for operating temperature ranges.
7. Insufficient Cycle Life & Warranty Mismatch:
* Pitfall: Overlooking the specified cycle life (e.g., 2000+ cycles to 80% capacity is common for quality LFP) or accepting a warranty that doesn’t cover realistic degradation or usage patterns. A short warranty often reflects low confidence in long-term quality.
* Mitigation: Compare cycle life ratings at a standard Depth of Discharge (DoD), typically 80%. Scrutinize warranty terms: duration, what’s covered (capacity fade, defects), and conditions (temperature, usage). A longer warranty (e.g., 3-5 years) from a reputable brand is preferable.
By proactively addressing these common pitfalls—focusing on verifiable cell quality, genuine IP ratings, robust BMS, accurate specifications, and proper certifications—you significantly increase the chances of sourcing a safe, reliable, and high-performing 12V 50Ah lithium-ion battery that meets your application’s demands.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 12V Lithium-Ion Battery 50Ah (UN 3480, Class 9 Hazardous Material)
Based on IATA DGR, IMDG Code, and 49 CFR Regulations (Hazard Class 2 Not Applicable – Correction: Lithium Batteries are Class 9)
Note on “H2”: There appears to be a misunderstanding in the request. H2 typically refers to Hydrogen (UN 1049/UN 3074), which is Hazard Class 2 (Gases). However, a 12V Lithium-Ion Battery 50Ah is not an H2 (hydrogen) product. It is a Class 9 hazardous material under UN 3480.
This guide assumes you meant hazardous materials in general (HazMat) or possibly mislabeled “H2” as a placeholder. Below is the correct logistics and compliance guide for lithium-ion batteries, not hydrogen.
✅ Product Overview
- Item: 12V Lithium-Ion Battery
- Capacity: 50Ah
- Energy: 12V × 50Ah = 600Wh
- Classification: Lithium-ion battery, UN 3480, Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods)
- Packing Instructions: IATA PI 965, Section IB (for standalone batteries shipped separately from equipment)
🔍 Regulatory Basis
- IATA DGR (Air): 65th Edition (2024)
- IMDG Code (Sea): Amendment 42-24 (2024)
- 49 CFR (Ground/USA): Department of Transportation (DOT)
- UN Manual of Tests and Criteria: Required for classification
📦 Classification & Identification
| Parameter | Value |
|——–|——-|
| UN Number | UN 3480 |
| Proper Shipping Name | “Lithium ion batteries, not contained in equipment, not packed with equipment” |
| Hazard Class | Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods) |
| Packing Group | Not assigned (PG varies based on test results, but generally treated as PG II if applicable) |
| Hazard Labels | Class 9 label (diamond-shaped, black and white with “9” and “Class 9”) + Lithium Battery Handling Mark |
| Tunnel Code | D/E (check based on configuration and quantity) |
✈️ AIR TRANSPORT (IATA DGR)
Applicable Section: PI 965, Section IB
Requirements:
-
State of Charge (SoC): Batteries must not exceed 30% SoC unless approved by the operator.
Exception: Batteries packed with/contained in equipment (PI 966/967) may be at higher SoC if powering the equipment.
-
Packing:
- Protected from short circuits (terminals insulated or enclosed).
- Packed in strong outer packaging.
- Prevent movement inside package.
-
Non-conductive inner packaging.
-
Marking & Labeling:
- Proper Shipping Name: “Lithium ion batteries, not contained in equipment”
- UN Number: UN 3480
- Class 9 Hazard Label
- Lithium Battery Handling Mark (rectangular, 120 × 110 mm):
- “LITHIUM ION BATTERIES – FORBIDDEN FOR TRANSPORT ABOARD AIRCRAFT UNLESS APPROVED”
- Battery type, quantity, watt-hour rating (max 600Wh/unit)
- Phone number of responsible party
-
Shipper/Consignee addresses
-
Documentation:
- Dangerous Goods Declaration (DGD): Required
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (signed by certified individual)
-
Air Waybill with “Dangerous Goods” notation
-
Quantity Limits (PI 965 IB):
- Max 35 kg gross weight per package
- No limit per aircraft if compliant (but airlines may impose restrictions)
🚢 SEA TRANSPORT (IMDG Code)
Packing Instruction: P908 (equivalent to IATA PI 965 IB)
Requirements:
- UN 3480, Class 9, PG II (if applicable)
- Cargo Transport Unit (CTU) Stowage: Stow “on deck” or “under deck” depending on packing and quantity; follow segregation rules.
- Marking & Placarding:
- Class 9 label on package
- UN number and proper shipping name
- CTU placarded if aggregate gross weight > 882 lbs (~400 kg) of Class 9
- Documentation:
- Dangerous Goods Manifest
- Container Packing Certificate (if containerized)
- Declaration of Dangerous Goods
🚚 GROUND TRANSPORT (USA – 49 CFR)
Regulations: 49 CFR Parts 100–185 (DOT)
Requirements:
- Classification: UN 3480, Class 9
- Packaging: Strong, securely closed, protection from short circuits
- Marking:
- UN 3480
- “Lithium ion batteries, not contained in equipment”
- Shipper/consignee info
- Labeling: Class 9 hazard label required on packages > 30 kg
- Shipping Paper: Required with proper description:
“Lithium ion batteries, 9, UN 3480, PG II, (30% SoC), PI 965, IB”
- Placarding: Not required unless >1,001 lbs aggregate gross weight of Class 9 materials
- Training: Personnel must be hazmat-trained and certified (49 CFR 172.704)
🔋 Safety & Testing Requirements
- UN 38.3 Test Summary: Required for all lithium batteries shipped after January 1, 2020.
- Must include test results for:
- Altitude simulation
- Thermal cycling
- Vibration, shock, impact, external short circuit, etc.
- Document must be available upon request.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Must be functional to prevent overcharge, over-discharge, and thermal runaway.
🌍 Special Considerations
- Airline Approval: Some carriers require prior approval for PI 965 Section IB shipments.
- E-commerce Restrictions: Major carriers (e.g., FedEx, UPS, DHL) may restrict or prohibit standalone lithium-ion battery shipments by air.
- State/Local Laws: California (e.g., Cal OSHA), EU (CLP), and others may have additional labeling or reporting requirements.
- Recycling/Disposal: Follow local regulations (e.g., EPA, WEEE) for end-of-life handling.
✅ Best Practices
- Use certified packaging tested to UN standards.
- Train staff in hazmat handling and documentation.
- Verify SoC before packing (≤30% for air).
- Keep UN 38.3 test summary on file.
- Label clearly – avoid rejection at checkpoints.
- Review carrier-specific rules (e.g., IATA airline restrictions).
❌ Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Shipping at full charge (violates air regulations)
- Omitting the Lithium Battery Handling Mark
- Failing to insulate terminals
- Not including a completed DGD
- Misclassifying as non-hazardous
📞 Key Contacts
- IATA: https://www.iata.org
- IMDG Code: International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- DOT Hazmat: https://www.phmsa.dot.gov
- UN Manual of Tests and Criteria: Available via UN Publishing
Final Note
⚠️ This battery (600Wh) exceeds the 100Wh limit for consumer carry-on exceptions and is a regulated hazardous material in all transport modes.
Do not ship without proper classification, packaging, labeling, and documentation.
If you were actually referring to hydrogen (H2) systems incorporating lithium batteries, please clarify for a combined compliance guide.
Let me know if you need templates for:
– Shipping labels
– DG Declaration
– UN 38.3 Summary Format
– Training checklist
Conclusion for Sourcing a 12V Lithium-Ion Battery 50Ah
Sourcing a 12V 50Ah lithium-ion battery requires a balanced evaluation of performance, safety, cost, and supplier reliability. Lithium-ion technology offers significant advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries, including higher energy density, longer cycle life, faster charging, and lower maintenance. When selecting a supplier, key factors such as battery chemistry (typically LiFePO4 for stability and safety), build quality (BMS integration, certifications), warranty, and customer support must be prioritized.
After assessing multiple suppliers and product options, it is recommended to partner with a reputable manufacturer or distributor that provides UL, CE, or UN38.3 certifications, transparent data sheets, and proven track records in reliability and after-sales service. While initial costs may be higher than conventional alternatives, the long-term savings in lifespan and efficiency justify the investment—especially for solar energy systems, marine applications, RVs, or off-grid power solutions.
In conclusion, sourcing a high-quality 12V 50Ah lithium-ion battery involves due diligence in vetting suppliers and verifying technical specifications. Opting for a trusted brand with safety certifications and strong customer reviews ensures optimal performance, durability, and peace of mind for your power needs.