The global demand for efficient power conversion solutions has fueled significant growth in the transformer market, particularly for devices enabling single-phase to three-phase power transformation—critical in industrial, commercial, and renewable energy applications. According to Grand View Research, the global transformer market size was valued at USD 58.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by rising investments in grid modernization, increasing electrification in emerging economies, and the integration of renewable energy sources requiring advanced power conditioning. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trend, forecasting a CAGR of over 7.2% for the transformer market through 2028, with particular demand surge in industrial automation and electric motor applications where 1-phase to 3-phase transformers play a pivotal role. As industries shift toward more reliable and energy-efficient power systems, manufacturers leading in innovation, efficiency, and global reach are emerging as key players in meeting this expanding need. The following list highlights the top nine manufacturers at the forefront of this transformation.
Top 9 1 Phase To 3 Phase Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Virginia Transformer Corp
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1971
Website: vatransformer.com
Key Highlights: The largest U.S.-owned custom power transformer manufacturer since 1971, with six advanced facilities across the U.S. and Mexico….
#2
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ermco-eci.com
Key Highlights: As the leading US manufacturer of oil-filled distribution transformers, we customize solutions to tackle your challenges — and meet your goals ……
#3 Transformer Manufacturer
Website: prolec.energy
Key Highlights: Prolec manufactures 1200MVA, 345kV transformers top rated and manufactured to the latest IEEE, ANSI, NEMA & ISO 9001:2015 quality standards….
#4 Transformers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: Single Phase or combine to create three-phase autotransformers, ranging from 0.05 kVA to 3 kVA. Type QMS – Single Phase 5 kVA – 25kVA ABB Transformer. Type QMS ……
#5 Dry type transformer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton types DS-3 (single-phase) and DT-3 (three-phase) general purpose ventilated dry-type transformers are two-winding, self-cooled, and available in a wide ……
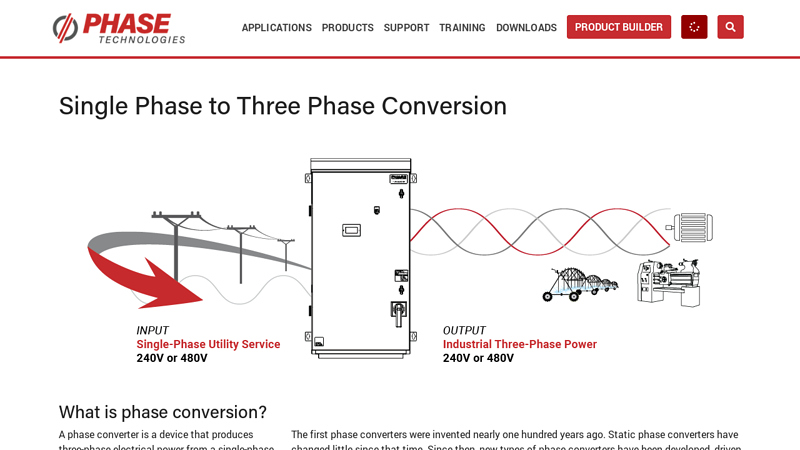
#6 Single Phase to Three Phase Conversion
Domain Est. 2003
Website: phasetechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Phase Technologies manufactures modern and highly efficient digital phase converters and variable frequency drives (VFD’s) for virtually any application….
#7 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#8 Single Phase to Three (3) Phase Power Converter Transformers
Domain Est. 2011
Website: northamericaphaseconverters.com
Key Highlights: 5-day delivery 30-day returns…
#9 Meta Power Solutions
Domain Est. 2021
Website: metapowersolutions.com
Key Highlights: Our company designs, manufactures, and supplies transformers up to 200 MVA and voltage levels of 138kV, 66kV, 33kV, 11kV, 6.6kV, 3.3kV, 433V, 415V, etc….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1 Phase To 3 Phase Transformer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 1 Phase to 3 Phase Transformers
The global market for 1 phase to 3 phase transformers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy demands, technological advancements, and regional infrastructure development. These transformers, which convert single-phase input power to three-phase output for industrial and commercial applications, are gaining traction due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness in decentralized power systems.
1. Rising Demand in Renewable Energy Integration
A key trend shaping the 2026 market is the integration of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, into distributed grids. Many off-grid and hybrid solar installations operate on single-phase supply but require three-phase power for motors and machinery. This drives demand for compact and efficient 1 phase to 3 phase transformers, especially in rural and remote areas where three-phase grid access is limited.
2. Growth in Small-Scale Industrial and Agricultural Applications
With the expansion of micro-industries and smart farming technologies, especially in developing economies, there is increased need for affordable three-phase power solutions. 1 phase to 3 phase transformers enable farmers and small manufacturers to operate three-phase equipment—such as pumps, compressors, and CNC machines—using existing single-phase infrastructure, fueling market growth.
3. Technological Advancements in Solid-State and VFD-Based Systems
By 2026, solid-state transformers and variable frequency drive (VFD)-based phase converters are expected to dominate the market. These systems offer superior efficiency, reduced harmonic distortion, and better voltage regulation compared to traditional rotary or static converters. Manufacturers are focusing on compact, low-maintenance designs with digital monitoring and IoT integration for predictive maintenance.
4. Regional Infrastructure Development in Asia-Pacific and Africa
Countries such as India, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Kenya are investing heavily in rural electrification. As single-phase distribution remains prevalent in these regions, demand for phase-converting transformers is rising to support agro-processing units, small workshops, and telecom towers. Government initiatives and public-private partnerships are accelerating deployment.
5. Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Standards
Stricter energy efficiency regulations in regions like the EU and North America are prompting manufacturers to develop transformers with lower losses and higher power quality. By 2026, compliance with standards such as IEC 60076 and DOE Level 3 efficiency requirements will become a competitive necessity.
6. Market Consolidation and Competitive Landscape
Leading players—including ABB, Siemens, Schneider Electric, and regional manufacturers—are expanding product portfolios and investing in R&D. Strategic partnerships with solar inverter companies and smart grid solution providers are expected to strengthen market presence. Meanwhile, cost-effective offerings from Chinese and Indian suppliers are increasing competition in the mid-to-low power segment.
In summary, the 2026 market for 1 phase to 3 phase transformers will be shaped by digitalization, sustainability goals, and the need for flexible power solutions in decentralized energy systems. The convergence of renewable energy, smart technology, and infrastructure growth will position these transformers as critical components in the modern energy landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a single-phase to three-phase transformer involves critical considerations beyond basic specifications. Overlooking quality and ingress protection (IP) can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Assessment
Many buyers focus solely on price and basic electrical ratings, neglecting deeper quality indicators that impact longevity and performance:
- Choosing Unverified Manufacturers: Selecting suppliers without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IEC standards) or verifiable track records increases the risk of substandard materials and workmanship.
- Poor Core and Winding Materials: Low-grade silicon steel cores increase core losses and heat, while inferior copper or aluminum windings lead to higher resistance, inefficiency, and potential hotspots.
- Insufficient Testing and Compliance: Transformers lacking proper factory acceptance tests (FAT)—such as insulation resistance, turns ratio, and no-load/load loss tests—may harbor hidden defects.
- Inadequate Thermal Management: Poor design or undersized cooling systems (e.g., insufficient surface area or cooling fins) can cause overheating, especially under continuous load.
Misjudging Ingress Protection (IP) Rating Needs
The IP rating defines protection against solids and liquids—critical for transformers installed in harsh environments. Common mistakes include:
- Underestimating Environmental Exposure: Deploying an IP20-rated transformer (basic finger protection) in dusty, humid, or outdoor settings invites contamination, short circuits, and corrosion.
- Over-Specifying IP Ratings Unnecessarily: Choosing IP65 or higher for a clean, indoor environment increases cost without benefit. Balance protection with practicality.
- Ignoring Installation Context: Failing to consider nearby water sources, airborne contaminants, or washdown procedures can lead to inadequate protection, even with a seemingly high IP rating.
- Neglecting Sealing and Gland Quality: Even with a high IP rating, poor cable entry seals or substandard enclosures compromise protection over time.
Overlooking Long-Term Reliability and Support
- Lack of Warranty and Service Support: Choosing suppliers with short or vague warranties and poor after-sales service can leave you stranded during failures.
- No Spare Parts Availability: Critical spares (e.g., fuses, terminations, fans) may be unavailable if the manufacturer is obscure or unsupported locally.
- Insufficient Documentation: Missing or unclear technical manuals, wiring diagrams, and maintenance guides hinder safe operation and troubleshooting.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence: verify certifications, demand test reports, match IP ratings to the environment, and choose reputable suppliers with proven reliability and support.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1 Phase To 3 Phase Transformer
This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and regulatory compliance involved in transporting, handling, and deploying a 1 Phase to 3 Phase transformer. These transformers are used to convert single-phase input power into three-phase output power, commonly for industrial, commercial, or remote applications where three-phase power is required but only single-phase supply is available.
Regulatory Compliance
Electrical Safety Standards
Ensure the transformer complies with relevant national and international electrical safety standards. Common certifications include:
– IEC 60076 (Power Transformers)
– IEEE C57.12.00 (Standard for Liquid-Immersed Distribution, Power, and Regulating Transformers)
– UL 1561 or UL 5085 (for dry-type transformers in North America)
– CSA C22.2 No. 66 (Canada)
Verify that the unit bears appropriate certification marks (e.g., CE, UKCA, EAC, or UL Listed) as required by the destination country.
Energy Efficiency Regulations
Check compliance with energy efficiency standards such as:
– DOE 2016 Rule (U.S. Department of Energy – applicable to distribution transformers)
– EU Ecodesign Directive (Lot 20) – for energy-related products in Europe
Non-compliant units may be restricted from import or sale.
EMC and Environmental Regulations
Ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance per:
– IEC 61000-6-2 (Industrial Immunity)
– FCC Part 18 (U.S. – for industrial, scientific, and medical equipment)
Additionally, comply with environmental directives like:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals)
– WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) – for end-of-life handling
Customs and Import Compliance
– Obtain Harmonized System (HS) code for accurate customs classification (e.g., 8504.23 or 8504.31 depending on type and rating).
– Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, and certificate of origin.
– Some countries require a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) or SASO (Saudi Arabia), SONCAP (Nigeria), or other local certification.
– Check for import duties, taxes, and any import restrictions on electrical equipment.
Logistics Planning
Packaging and Handling
– Transformers must be securely packed in wooden crates or pallets with moisture barriers and shock-absorbing materials.
– Use lifting points as specified by the manufacturer; never lift by terminals or bushings.
– Include “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” labels.
– For oil-filled units, ensure seals are leak-proof and include oil preservation documentation.
Transportation Mode Selection
– Road: Suitable for regional delivery; confirm axle weight limits and route clearance (height, width).
– Rail: Cost-effective for long distances; requires compatible loading gauges.
– Sea: Ideal for international shipments; use ISO containers with proper ventilation and moisture control.
– Air: Fast but expensive; verify weight and dimensional constraints with airline.
Weight and Dimensions
– Confirm the transformer’s gross weight, dimensions, and center of gravity.
– Heavy units (>3 tons) may require special permits, escort vehicles, or rigging equipment.
– Coordinate site access: gate width, crane availability, and foundation readiness.
Storage Requirements
– Store in a dry, indoor, temperature-controlled environment.
– Protect from dust, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres.
– If stored long-term, perform periodic inspections and, for oil-filled units, check oil quality and preservation (e.g., nitrogen padding).
Installation and Site Compliance
Site Preparation
– Ensure foundation or mounting structure meets manufacturer specifications for load-bearing and alignment.
– Verify clearance for ventilation, maintenance, and safety per NFPA 70 (NEC) or IEC 61936.
Electrical Installation
– Installation must be performed by licensed electricians.
– Follow grounding and bonding requirements per local codes.
– Confirm input (1Φ) and output (3Φ) voltage, frequency, and load compatibility.
Commissioning and Documentation
– Conduct insulation resistance, turns ratio, and polarity tests before energizing.
– Retain all compliance documents (test reports, certificates, manuals) for audit and warranty purposes.
– Register the transformer with local utility or regulatory body if required.
Safety and Training
- Provide personnel with safety training on high-voltage equipment.
- Use appropriate PPE during handling and installation.
- Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines, stakeholders can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient deployment of 1 Phase to 3 Phase transformers across global markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Single-Phase to Three-Phase Transformer
Sourcing a single-phase to three-phase transformer requires careful consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, and operational constraints. While such transformers do not inherently convert phase systems directly—since true phase conversion typically requires additional components like phase converters or variable frequency drives (VFDs)—they can be part of a broader solution when used in conjunction with appropriate equipment.
When selecting a transformer in this context, it is essential to clarify whether the goal is voltage transformation within a multi-phase system or actual phase conversion for powering three-phase machinery from a single-phase supply. In most cases, standalone transformers cannot convert single-phase to three-phase power; instead, phase conversion must be achieved using rotary or solid-state phase converters, with the transformer serving only to adjust voltage levels.
Key factors in sourcing include load requirements, efficiency, compatibility with existing infrastructure, regulatory standards, and total cost of ownership. It is recommended to consult with qualified electrical engineers or suppliers to ensure the chosen solution meets performance, safety, and reliability standards.
In summary, while a single-phase to three-phase transformer isn’t feasible in the conventional sense, a properly designed system incorporating phase conversion technology and appropriately rated transformers can effectively deliver three-phase power from a single-phase source. Proper assessment and expert guidance are critical to implementing a safe and efficient solution.