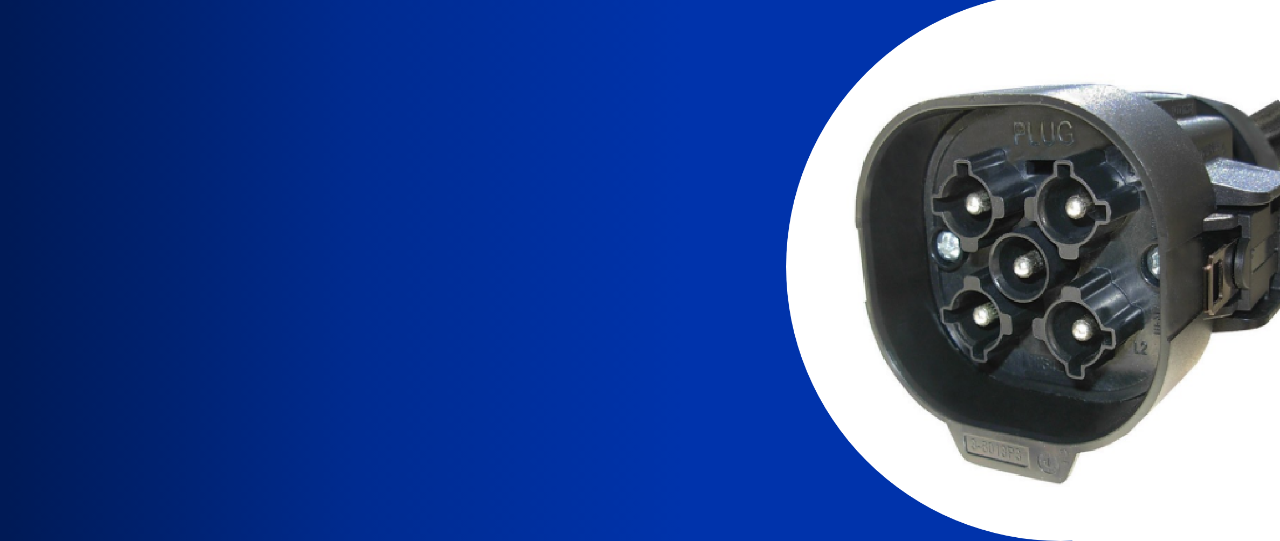
The global demand for reliable electrical connectivity solutions has fueled significant growth in the power plug and socket market, with 1 phase power plugs remaining a cornerstone in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global plug and socket market was valued at USD 12.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising electricity access worldwide. As power quality and safety standards become more stringent, manufacturers of 1 phase power plugs are innovating to meet regional regulatory requirements and evolving consumer demands. This growth trajectory is further supported by Grand View Research, which highlights expanding construction activities and the proliferation of electrical and electronic devices as key market drivers. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining engineering excellence, global compliance certifications, and scalable production to dominate supply chains across regions. The following list highlights the top 9 manufacturers shaping the future of 1 phase power plug technology and distribution.
Top 9 1 Phase Power Plug Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial ……
#3 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phoenixcontact.com
Key Highlights: Wide variety of connectors: from versatile circular connectors (M5 to M58), data, energy storage, and photovoltaic connectors to heavy-duty industrial ……
#4 Power Cord Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2019
Website: powercordmanufacturers.com
Key Highlights: Additionally, manufacturers can customize the plug type (rotating, snap-on, screw-on, locking), cord color, and cord length to suit particular requirements….
#5 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: We offer many types of connectors for computers and connectors in electronics as well as wire plug connectors, electrical connector plugs, and electrical cable ……
#6 Power Cords and Adapters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: Looking for an IT-grade power cord? We carry over 250 top quality power cords for computers, servers, PDUs and special applications like hospitals and ……
#7 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amphenol.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol has been designing and manufacturing electrical and electronic connectors since the company’s inception in 1932….
#8 Anderson Power
Domain Est. 1996
Website: andersonpower.com
Key Highlights: An Innovative Connector for the Future of Battery Charging. Our new IBC DIN-style connector is designed to take your battery charging to the next level….
#9 Plugs and sockets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: catalogue.bals.com
Key Highlights: A large selection of Bals connectors. We manufacture plugs and sockets in different variants and thus cover all your needs for different connection solutions ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1 Phase Power Plug
2026 Market Trends for 1 Phase Power Plug
The global market for 1 phase power plugs is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy demands, regulatory standards, and technological advancements. As one of the foundational components in residential, commercial, and light industrial electrical systems, the 1 phase power plug market is adapting to a rapidly changing energy landscape. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the market through 2026, including standardization efforts, smart technology integration, sustainability demands, regional growth dynamics, and the impact of electrification trends.
Increasing Standardization and Regulatory Compliance
A major trend influencing the 1 phase power plug market in 2026 is the push toward greater international standardization and stricter regulatory compliance. Governments and international bodies are focusing on harmonizing plug and socket designs to improve safety, interoperability, and cross-border product compatibility. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, particularly IEC 60884 and IEC 60309, are increasingly being adopted globally. By 2026, countries that previously used legacy or region-specific plug types (e.g., Type C, G, or I) are expected to accelerate the adoption of universal or regionally harmonized standards, especially in emerging markets.
Additionally, safety regulations are becoming more stringent, requiring features such as shutters, insulation sleeves, and overload protection. These mandates will influence plug design and manufacturing, leading to a shift toward higher-quality, safer products and phasing out non-compliant variants.
Growth in Smart and Connected Power Plugs
The integration of smart technology is one of the most transformative trends in the 1 phase power plug sector. By 2026, the demand for smart plugs—capable of remote control, energy monitoring, and integration with home automation systems—is expected to surge. Enabled by the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home ecosystems (e.g., Google Home, Amazon Alexa, Apple HomeKit), smart 1 phase power plugs are becoming mainstream.
Manufacturers are increasingly embedding Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee connectivity into standard plugs, allowing users to monitor and manage energy consumption via smartphone apps. These smart plugs also support automation routines, voice control, and energy-saving features such as auto-shutdown during idle periods. The market for smart 1 phase plugs is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 15% from 2022 to 2026, with strong adoption in North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are reshaping the design and production of 1 phase power plugs. By 2026, sustainability will be a key differentiator in the market. Manufacturers are shifting toward using recyclable, halogen-free, and biodegradable materials in plug housings and components. The European Union’s RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations are driving this trend, with similar policies emerging in other regions.
Additionally, energy efficiency is influencing plug design. Even though the plug itself consumes minimal power, smart variants are being optimized for low standby power draw. Manufacturers are also focusing on extending product lifespans and designing for disassembly and recycling, aligning with circular economy principles.
Regional Market Dynamics and Electrification Growth
Regional demand for 1 phase power plugs varies significantly, but overall growth is being fueled by urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising electrification rates. In Asia-Pacific—particularly in India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa—millions of new households are gaining access to electricity, creating strong demand for affordable yet safe 1 phase plugs. These markets are witnessing a transition from rudimentary electrical fittings to standardized, safety-certified plugs.
In contrast, mature markets such as North America and Western Europe are focused on retrofitting existing infrastructure with smart and energy-efficient solutions. Renovation of older buildings and compliance with new electrical codes are driving demand for modern plug designs. Latin America and the Middle East are experiencing steady growth, supported by government-led electrification programs and investments in residential construction.
Impact of Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging and Renewable Integration
Although 1 phase power plugs are not typically used for high-power EV charging, they remain relevant in Level 1 EV charging systems, especially in residential settings. By 2026, as EV adoption grows globally, the demand for reliable, durable 1 phase plugs (such as the IEC 60309 or Type F/G for home charging) will rise. Consumers are increasingly installing dedicated 1 phase EV outlets in homes and garages, creating a niche but growing segment within the plug market.
Moreover, the integration of solar power and home energy storage systems often relies on standard 1 phase outlets for inverters and monitoring devices. As distributed energy resources become more common, the need for compatible and robust power plugs will continue to expand.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 1 phase power plug market will be characterized by a convergence of safety, intelligence, sustainability, and global standardization. While the basic function of the plug remains unchanged, its role within modern electrical ecosystems is evolving. Smart connectivity, regulatory alignment, and environmental responsibility will define product innovation and market leadership. Companies that invest in R&D, comply with international standards, and anticipate regional electrification needs will be best positioned to capture growth in this essential yet dynamic segment of the electrical infrastructure market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 1-Phase Power Plugs (Quality, IP Rating)
Sourcing 1-phase power plugs may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to safety hazards, equipment damage, and compliance issues. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Choosing Plugs with Inadequate IP Ratings for the Environment
A frequent mistake is selecting power plugs with an IP rating too low for their intended environment. For example, using an IP20-rated plug (basic touch protection only) in outdoor, industrial, or wet areas exposes connections to dust and moisture, increasing the risk of short circuits, corrosion, and electric shock. Always match the IP rating to the application—IP44 or higher is typically required for outdoor or washdown environments.
Ignoring Material Quality and Construction Standards
Low-cost plugs often use substandard plastics and poor metal contacts that degrade quickly under heat or mechanical stress. Inferior materials can lead to overheating, arcing, and fire hazards. Ensure plugs are made from flame-retardant, high-temperature-resistant materials and comply with international standards such as IEC 60309, UL 498, or national equivalents.
Assuming All Plugs Meet Certification Requirements
Not all products labeled as compliant actually meet safety certifications. Counterfeit or non-certified plugs may bypass rigorous testing, posing serious safety risks. Always verify authentic certifications (e.g., CE, UL, CCC) through documentation and reputable suppliers—do not rely solely on product markings.
Overlooking Mechanical Durability and Insertion Cycles
In industrial or high-usage settings, plugs undergo frequent mating and unmating. Low-quality connectors may fail after only a few dozen cycles due to worn contacts or broken housings. Check manufacturer specifications for rated insertion cycles (e.g., 5,000+ cycles) and robust strain relief to ensure longevity.
Mismatching Voltage and Current Ratings
Using a plug rated below the circuit’s voltage or current demand causes overheating and potential failure. Always confirm the plug’s rating (e.g., 250V, 16A) exceeds the application’s requirements, with a safety margin for surges or continuous loads.
Neglecting Environmental and Chemical Resistance
In industrial or chemical environments, standard plugs may degrade due to exposure to oils, solvents, or UV radiation. Select plugs with chemically resistant housings and UV-stabilized materials when deploying in harsh conditions.
Failing to Verify Compatibility with Cables and Connectors
Poor cable gland design or mismatched connector systems can result in insecure fits, cable pull-out, or compromised IP ratings. Ensure the plug is compatible with the cable diameter and connector series to maintain environmental sealing and mechanical integrity.
By addressing these pitfalls early in the sourcing process, you ensure reliable, safe, and compliant power connections tailored to your specific operational needs.
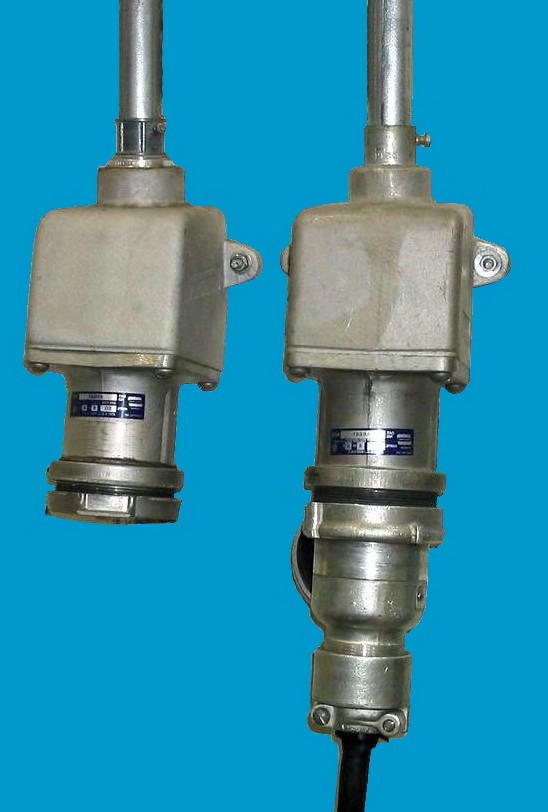

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1-Phase Power Plug
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the import, distribution, and use of 1-phase power plugs across international markets. Adherence to these standards ensures safety, legal conformity, and seamless supply chain operations.
Regulatory Standards & Certifications
1-phase power plugs must comply with regional electrical safety and compatibility standards. Key certifications include:
- IEC 60884: International standard for plugs and socket-outlets for household and similar purposes.
- UL 498 (North America): Standard for attachment plugs and receptacles; products typically require UL or CSA listing.
- BS 1363 (UK): Specifies 3-pin plugs with fuse; requires UKCA or CE marking (post-Brexit).
- AS/NZS 3112 (Australia/New Zealand): Governs plug design and safety; requires RCM marking.
- CEE 7/16 (Europlug), CEE 7/7 (Schuko/French): Common in Europe; CE marking with compliance to Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and RoHS is mandatory.
- CCC (China): Required for plugs sold in China under the China Compulsory Certification system.
Always verify plug configuration (pin size, shape, voltage, current rating) matches the destination country’s grid specifications (e.g., 120V/60Hz in North America, 230V/50Hz in Europe).
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for compliance and end-user safety:
- Include voltage, current, frequency, and manufacturer details on the product and packaging.
- Use multilingual labels where applicable (e.g., EU, Canada).
- Clearly display certification marks (e.g., CE, UL, CCC) as required by jurisdiction.
- Include safety warnings (e.g., “Do not use with wet hands”, “For indoor use only”).
- Ensure packaging is durable and protects against moisture, impact, and electrostatic discharge during transit.
Import & Customs Compliance
When shipping internationally, ensure:
- Accurate HS (Harmonized System) code classification (e.g., 8536.69 for electrical plug connectors).
- Provide certificates of conformity (CoC), test reports, and declaration of conformity (DoC) upon request.
- Comply with import restrictions or bans on non-certified electrical products (e.g., UK, EU, Australia).
- Account for tariffs, VAT, and import duties based on destination country regulations.
Transportation & Handling
- Ship via carriers compliant with IATA/IMDG regulations if applicable (mainly relevant for large-scale or hazardous material combinations).
- Avoid extreme temperatures and humidity during storage and transit.
- Use anti-static packaging where necessary to protect internal components.
- Segregate incompatible goods (e.g., flammable materials) during warehousing.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
- Adhere to RoHS (EU), REACH, and similar regulations restricting hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, phthalates).
- Comply with WEEE (EU) or equivalent e-waste directives requiring take-back and recycling programs.
- Ensure flame-retardant materials meet UL 94 flammability ratings.
- Provide user instructions in local language, including disposal guidelines.
Quality Assurance & Documentation
- Maintain up-to-date test reports from accredited laboratories (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek).
- Conduct regular audits of manufacturing facilities to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Retain technical files and conformity documentation for a minimum of 10 years (per EU requirements).
Conclusion
Successfully managing logistics and compliance for 1-phase power plugs requires proactive adherence to technical, safety, and regulatory standards in each target market. Partnering with certified manufacturers and experienced customs brokers can mitigate risks and ensure smooth market access. Always consult local regulatory authorities or compliance experts when entering new regions.
In conclusion, sourcing a single-phase power plug requires careful consideration of technical specifications, regional standards, safety certifications, and application requirements. It is essential to select a plug that is compatible with the local voltage, frequency, and socket types, while also meeting recognized safety standards such as UL, CE, or IEC. Additionally, factors like current rating, material quality, durability, and environmental conditions should guide the selection process. By evaluating suppliers based on reliability, compliance, and cost-effectiveness, organizations can ensure a safe, efficient, and sustainable power connection. Proper sourcing not only enhances operational safety but also minimizes downtime and maintenance costs in the long term.