The global fastener manufacturing market has experienced steady expansion, driven by growing demand from automotive, construction, aerospace, and electronics industries. According to Grand View Research, the global fastener market was valued at USD 115.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this market includes precision screws such as the #1-8 size, widely used in small-scale assemblies and electronic enclosures due to their optimal balance of strength and compactness. Mordor Intelligence further underscores this trend, noting increased production volumes in Asia-Pacific—particularly in China and India—due to rising industrialization and infrastructure development. As demand for high-precision, standardized screw sizes grows, manufacturers specializing in #1-8 screws are scaling production, enhancing quality control, and expanding global distribution. The following list highlights the top eight manufacturers leading innovation and market share in the #1-8 screw size segment.
Top 8 1 8 Screw Size Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Global Leader in Fastening Technology
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stanleyengineeredfastening.com
Key Highlights: As the world’s #1 fastening systems provider, Stanley® Engineered Fastening builds on over 100 years of experience and the strength of legacy brands like ……
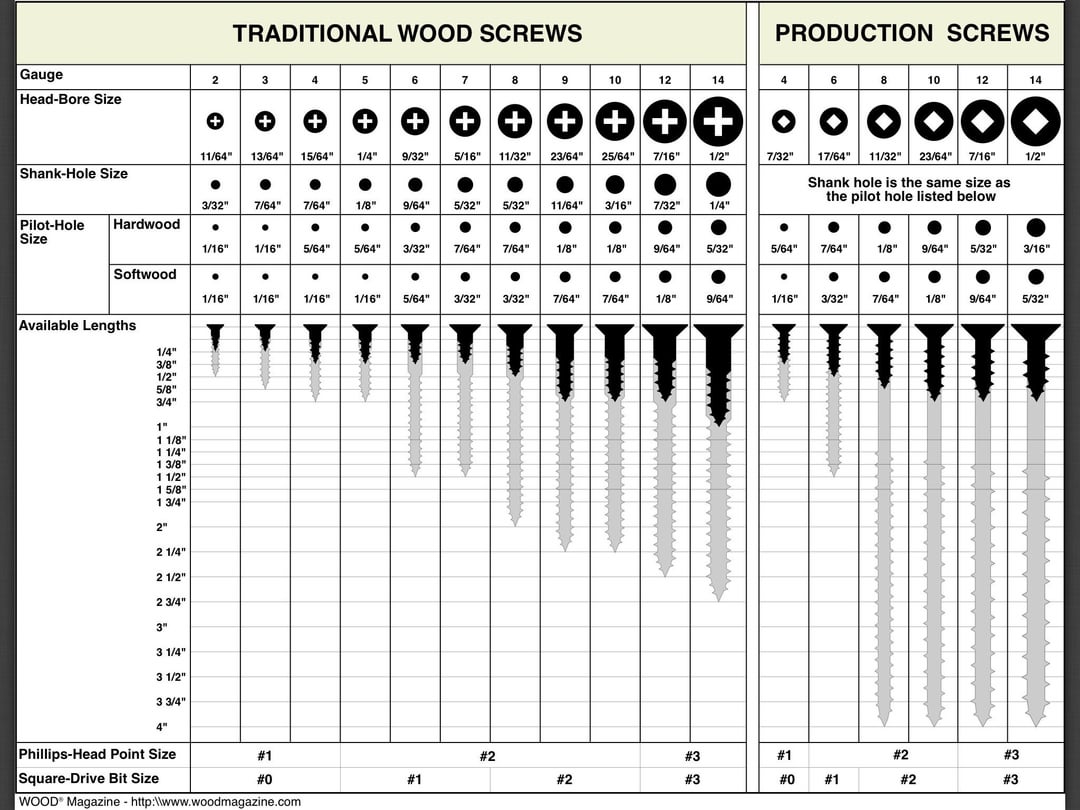
#2 Screw Size Charts
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mcmaster.com
Key Highlights: Choose from our selection of screw size identifiers, screw, bolt, and nut size identifiers, reference charts, and more. Same and Next Day Delivery….
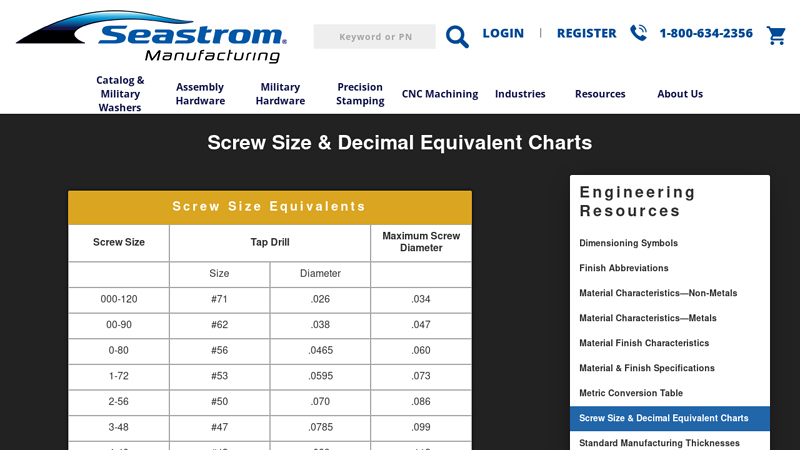
#3 Screw Size & Decimal Equivalent Charts
Domain Est. 1997
Website: seastrom-mfg.com
Key Highlights: Screw Size & Decimal Equivalent Charts. Screw Size Equivalents. Screw Size Tap Drill Maximum Screw Diameter. Size Diameter. 000-120 #71 .026 .034….
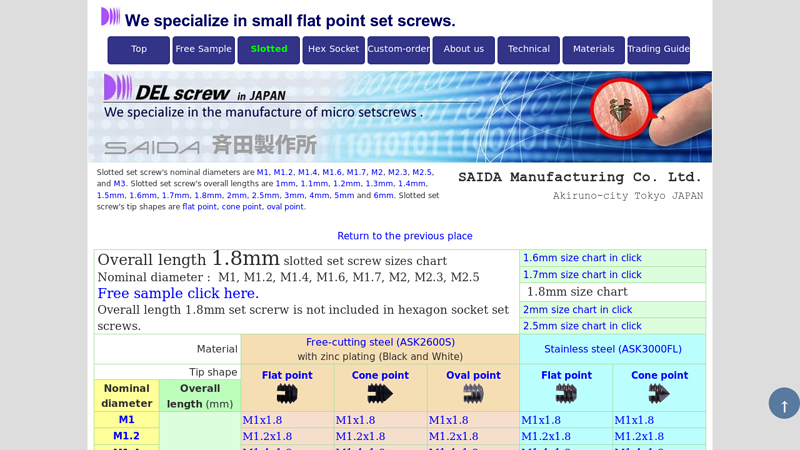
#4 Overall Length 1.8mm set screw sizes chart
Domain Est. 2004
Website: del-screw.com
Key Highlights: Overall length 1.8mm slotted set screw sizes chart. Nominal diameter : M1, M1.2, M1.4, M1.6, M1.7, M2, M2.3, M2.5. Free sample click here….
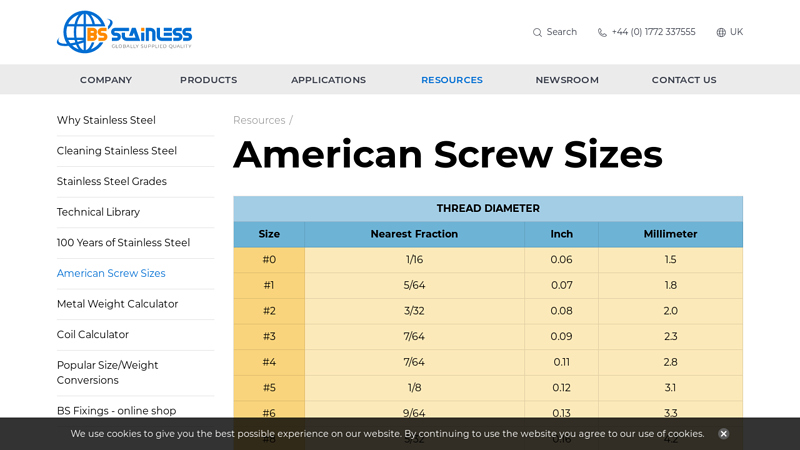
#5 American Screw Sizes
Domain Est. 2008
Website: bsstainless.com
Key Highlights: American Screw Sizes: Thread Diameter, Sizes, Nearest Fraction. … 1/8, 0.12, 3.1. #6, 9/64, 0.13, 3.3. #8, 5/32, 0.16, 4.2. #10, 3/16, 0.19, 4.8….
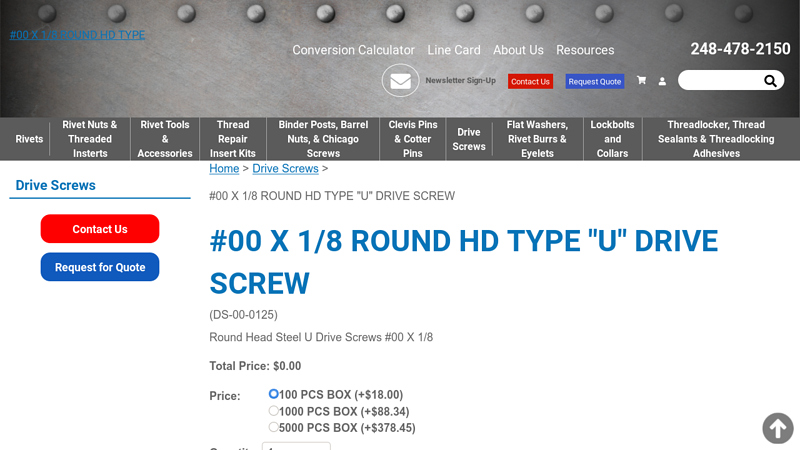
#6 #00 X 1/8 ROUND HD TYPE “U” DRIVE SCREW
Domain Est. 2009
Website: rivetsonline.com
Key Highlights: #00 X 1/8 ROUND HD TYPE “U” DRIVE SCREW · Size: #00 · Length: 1/8 · Head Style: Round · Material: Steel Zinc Plated….
#7 MS21318
Domain Est. 2013
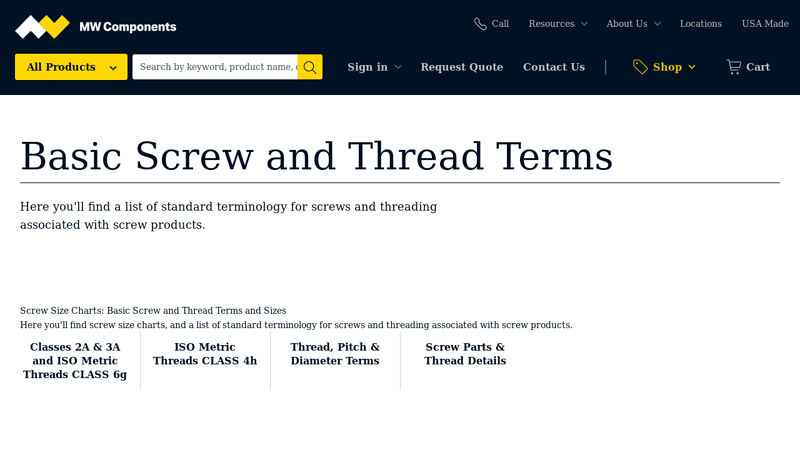
#8 Screw Size Charts: Basic Screw & Thread Terms
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: Review our screw size chart and our list of screw and thread terms including pitch, angles, thread thickness, engagement depth. Shop for your screws today….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1 8 Screw Size
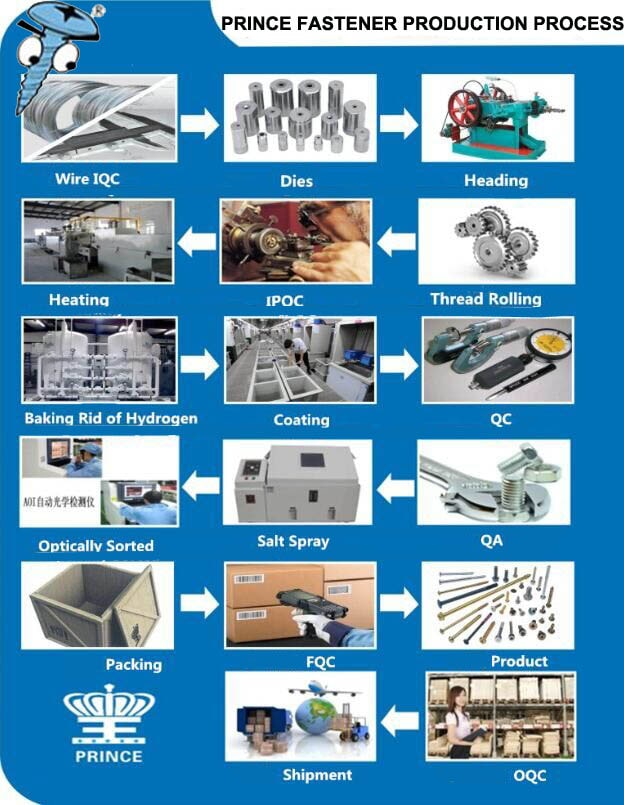
H2: 2026 Market Trends for 1/8″ Screw Size
The global market for 1/8″ screw size is expected to experience steady growth and notable shifts by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements in fastening systems, and increased automation across key end-use sectors. As one of the most commonly used small-diameter screws, the 1/8″ size serves critical applications in electronics, automotive assembly, aerospace components, medical devices, and consumer goods manufacturing.
A major trend shaping the 2026 outlook is the rising demand for precision-engineered fasteners in compact and lightweight products. With the proliferation of miniaturized electronics—such as wearables, IoT devices, and smartphones—there is an increasing reliance on small, reliable screws like the 1/8″ size that offer strong holding power without adding bulk. Manufacturers are responding by enhancing screw materials (e.g., stainless steel, titanium, and high-strength alloys) and surface treatments for improved corrosion resistance and durability.
Another key driver is the automation of assembly processes in industries such as automotive and electronics. The 1/8″ screw is highly compatible with automated screw-driving systems, which are becoming standard in high-volume production environments. This trend is pushing suppliers to standardize thread types (e.g., #6-32, 8-32, or metric equivalents) and head designs (Phillips, Torx, hex) to ensure seamless integration with robotic equipment.
Sustainability is also emerging as a significant influence. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are prompting fastener producers to adopt eco-friendly manufacturing practices, including energy-efficient cold-forming techniques and recyclable packaging. Additionally, reusable or demountable designs using 1/8″ screws are gaining traction in modular electronics and repairable appliances, aligning with the circular economy.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the 1/8″ screw market by 2026, fueled by robust electronics manufacturing in China, Vietnam, and India. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, particularly in aerospace and medical device sectors where regulatory compliance and quality standards favor high-performance small fasteners.
In summary, the 1/8″ screw size is poised for sustained relevance in 2026, supported by trends in miniaturization, automation, material innovation, and sustainability. Market players that invest in precision manufacturing, supply chain resilience, and environmentally responsible practices are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this evolving landscape.
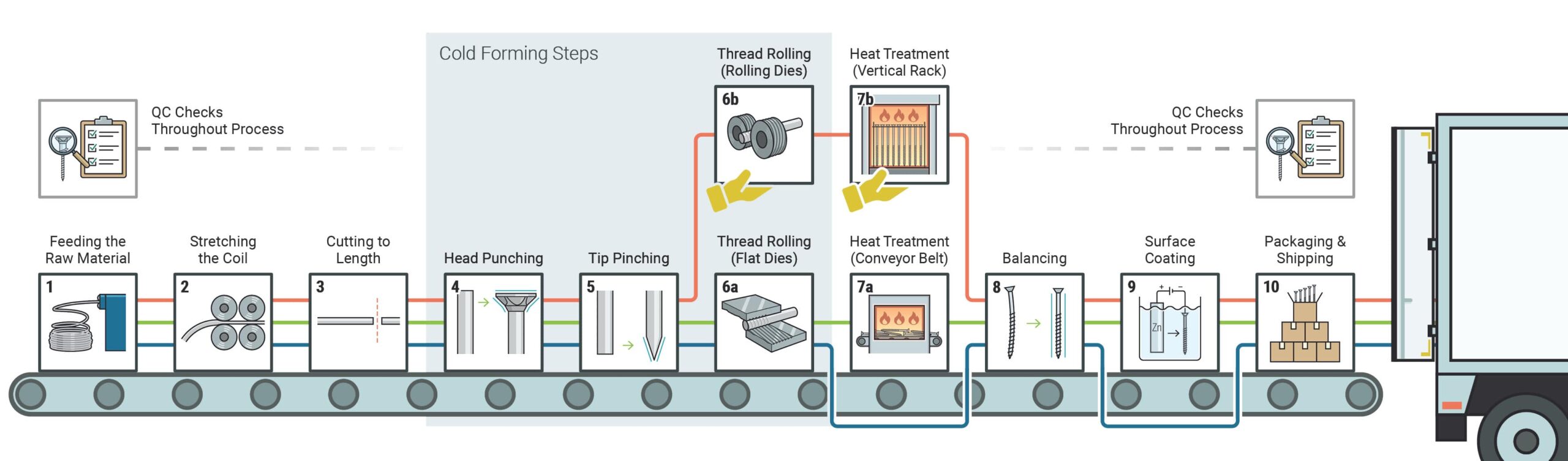
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 1/8″ Screw Size (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing 1/8″ screws—especially for precision applications—can present several challenges related to quality inconsistencies and incorrect interpretation of Inch-Pound (IP) measurements. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Confusing 1/8″ as the Screw Diameter
A frequent error is assuming “1/8″” refers to the major diameter of the screw. In reality, 1/8″ is a nominal size and may not precisely match actual thread dimensions. For example, a #8 screw has a major diameter of approximately 0.164″, not 0.125″ (which is exactly 1/8″). This misunderstanding leads to improper fit, assembly failures, or incompatibility with pre-tapped holes.
2. Overlooking Thread Series (UNC vs. UNF)
Even if the diameter is correctly interpreted, sourcing the wrong thread pitch (e.g., UNC instead of UNF) can compromise joint integrity. For 1/8″ nominal screws, ensure you specify the correct thread series (e.g., 1/8″-27 NPT for tapered pipe threads or confirm if machine screw standards apply), as mismatched threads affect torque, sealing, and load capacity.
3. Assuming All 1/8″ Screws Are Identical Across Standards
Different standards (ASME, SAE, ISO inch equivalents) may define “1/8″” screws differently. A lack of adherence to specified standards can result in poor quality, non-compliance, or failure in critical environments. Always verify the applicable specification (e.g., ASME B18.2.1).
4. Compromising on Material and Coating Quality
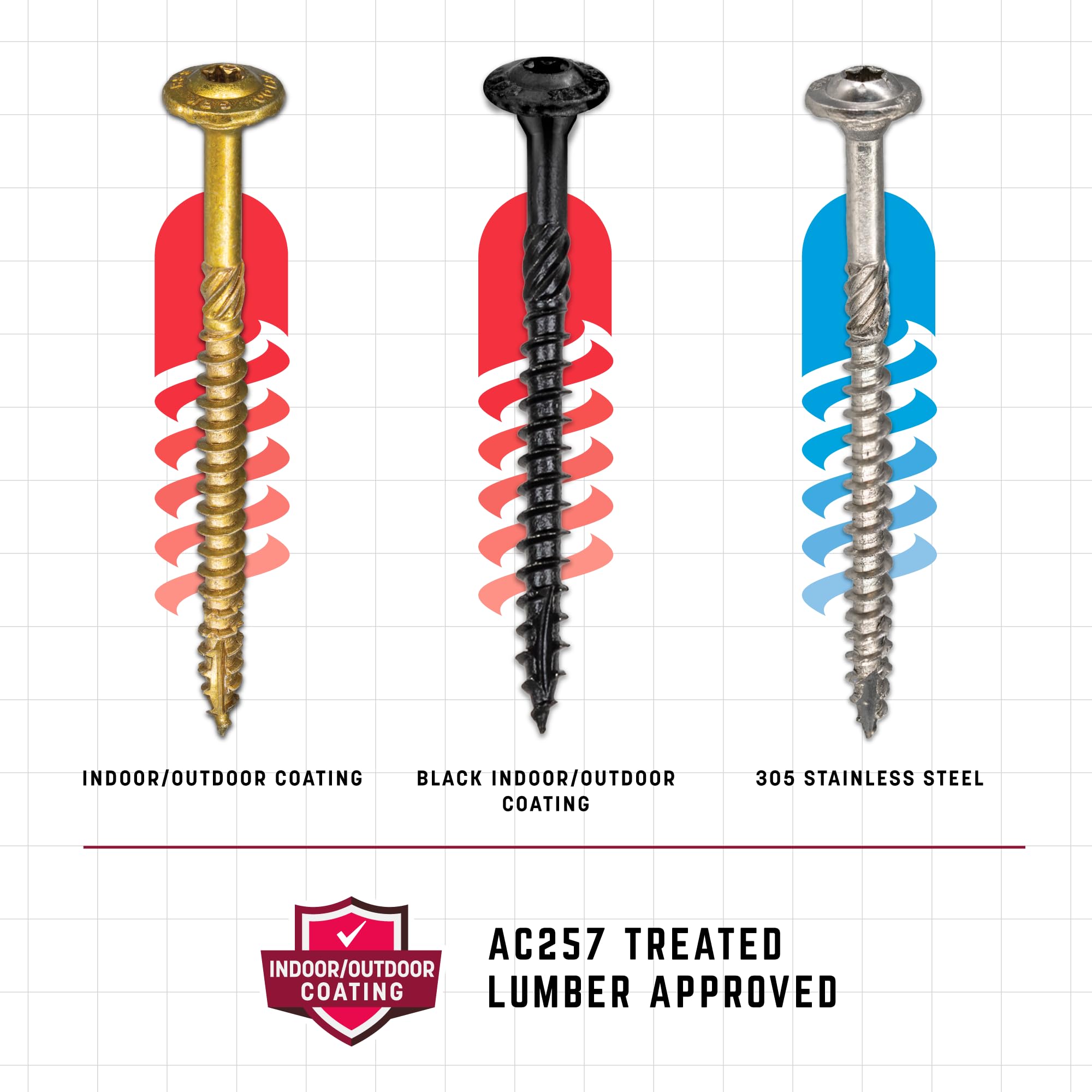
Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials (e.g., low-grade steel) or inadequate coatings, leading to corrosion, stripping, or reduced strength. For applications requiring durability or resistance to environmental factors, specify material grades (e.g., 18-8 stainless steel) and coatings (e.g., zinc plating, Dacromet).
5. Ignoring Tolerance and Fit Requirements
Precision applications demand tight tolerances. Screws sourced without attention to class of fit (e.g., Class 2A/2B) may result in loose joints or excessive assembly force. Poorly controlled manufacturing tolerances in low-cost batches can lead to high rejection rates during assembly.
6. Misinterpreting IP (Inch-Pound) Units in Specifications
Inch-Pound (IP) units govern torque values, thread dimensions, and mechanical properties in imperial systems. Misreading torque specs (e.g., in-lb vs. ft-lb) or failing to use IP-compatible tools can lead to under-torquing (loose joints) or over-torquing (damaged threads or fasteners).
7. Sourcing from Unqualified Suppliers
Procuring from vendors without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100 for aerospace) increases the risk of receiving non-conforming parts. Always verify supplier credentials, request material test reports (MTRs), and conduct incoming inspections.
8. Not Verifying Application Context
A 1/8″ screw in a high-vibration environment (e.g., automotive or aerospace) requires different features (e.g., locking mechanisms, higher tensile strength) than one used in static assemblies. Failing to consider the operational environment leads to premature failure.
By carefully addressing these pitfalls—particularly clarifying dimensional standards, ensuring material integrity, and validating supplier quality—procurement teams can avoid costly mistakes when sourcing 1/8″ screws in IP units.
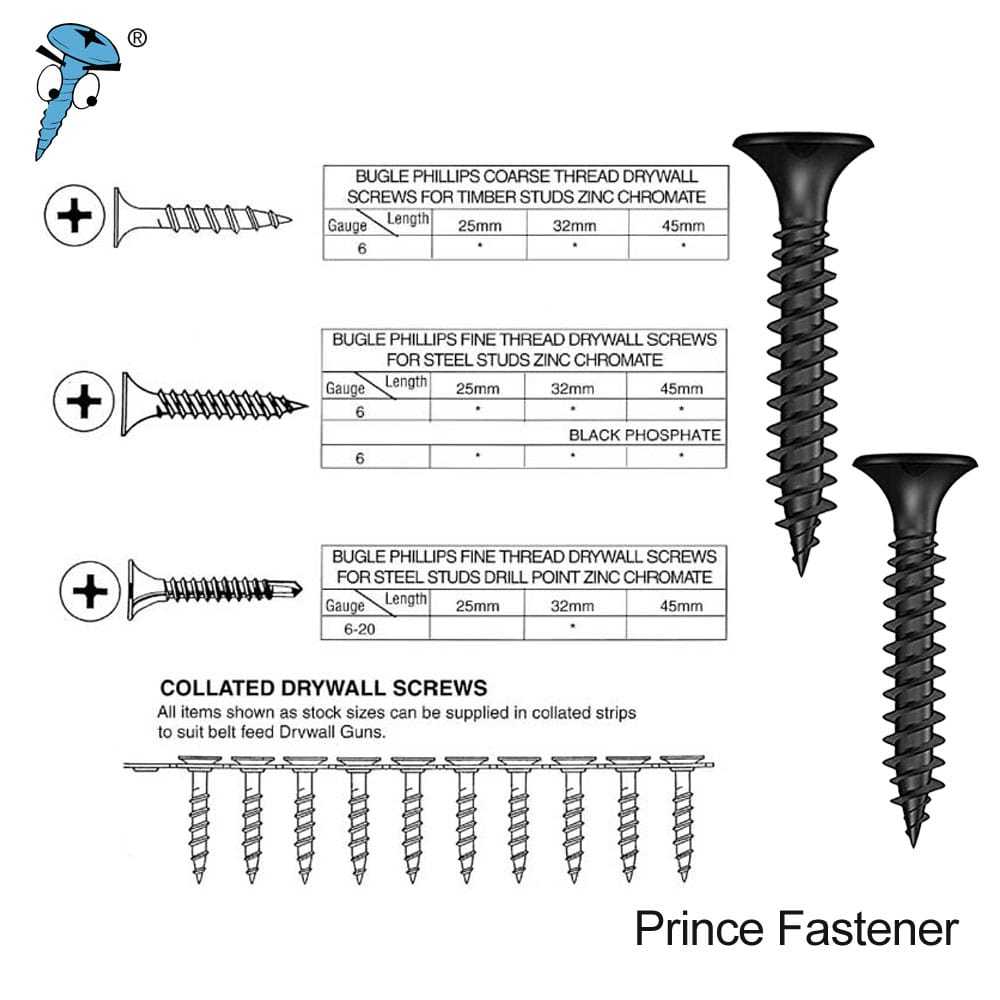
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for #8 Screw Size
When handling, transporting, or importing/exporting products containing #8 screws, adherence to logistics best practices and regulatory compliance is essential. This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and compliance aspects related to the common #8 screw size.
H2: Packaging & Storage
- Proper Containment: Store #8 screws in sealed plastic bags, anti-static packaging (if applicable), or bulk bins to prevent contamination, loss, or damage.
- Labeling: Clearly label containers with:
- Screw specification (e.g., #8-32 UNC, material type, length)
- Quantity per unit
- Lot or batch number
- Date of packaging
- Moisture Control: Use desiccants in packaging if storing in humid environments, especially for carbon steel screws to prevent rust.
- Stacking & Handling: Use sturdy cartons or totes. Avoid overstacking to prevent crushing packaging and damaging screws.
H2: Transportation & Handling
- Domestic Shipping (e.g., US, EU):
- Use appropriate parcel or freight services based on volume.
- Ensure packages meet carrier requirements (e.g., weight, dimensions, labeling).
- Consider vibration and shock protection when shipping loose screws.
- International Shipping:
- Declare accurate commodity codes (HS Code – see below).
- Provide detailed commercial invoices specifying:
- Description: “Steel Machine Screws, Size #8”
- Quantity, Net/Gross Weight
- Country of Origin
- Material composition (e.g., stainless steel, zinc-plated steel)
- Comply with import/export documentation (e.g., Certificate of Origin, Packing List).
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- HS Code Classification:
- Typical HS Code: 7318.15 (Screws, bolts, and nuts, of iron or steel)
- Subcategory may vary by material:
- Stainless steel: Often still under 7318.15, but verify with customs
- Coated or plated: May affect tariff treatment
- Note: Confirm exact HS code based on material, finish, and country-specific tariff schedules.
- RoHS Compliance (EU, UK, and others):
- Ensure screws meet Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) limits for lead, cadmium, etc., especially if used in electrical/electronic equipment.
- Provide RoHS compliance documentation upon request.
- REACH Regulation (EU):
- Declare compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals), particularly for substances like nickel or chromium in plated or stainless steel screws.
- Conflict Minerals (US Dodd-Frank Act):
- If screws contain tin, tungsten, tantalum, or gold (unlikely but possible in coatings), conduct due diligence if supplying to electronics manufacturers.
H2: Material & Environmental Compliance
- Material Certification:
- Provide Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Certificates of Conformance (CoC) when required, especially in aerospace, automotive, or medical applications.
- Recycling & Disposal:
- Metal screws are recyclable. Follow local waste regulations for industrial scrap metal disposal.
- Avoid landfill disposal where recycling is available.
H2: Quality & Traceability
- Batch Traceability: Maintain records linking screw batches to production date, material source, and inspection reports.
- Inspection Standards: Follow ISO or ANSI standards (e.g., ASME B18.6.3 for slotted head screws) during quality checks.
- Documentation Retention: Keep logistics and compliance records for minimum of 5–7 years, depending on industry requirements.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure efficient handling, regulatory compliance, and smooth logistics operations when managing #8 screws across the supply chain. Always verify requirements with local authorities and industry standards applicable to your market.
Conclusion for Sourcing 1/8″ Screw Size:
After evaluating suppliers, material options, thread types, and cost considerations, sourcing 1/8″ screws has been determined to be both feasible and cost-effective. This standardized size is widely available from multiple domestic and international suppliers, ensuring reliable lead times and competitive pricing. Whether requiring machine screws, self-tapping, or wood screws in 1/8″ diameter, common materials such as stainless steel, steel with zinc plating, or brass are readily accessible to meet application-specific needs including corrosion resistance, strength, or aesthetic finish. Compatibility with commonly used tools and equipment further enhances usability. It is recommended to partner with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, adherence to specifications (such as ASTM or ISO standards), and documentation for traceability—especially for critical applications in industries like electronics, automotive, or construction. Overall, sourcing 1/8″ screws offers reliability, versatility, and scalability for both prototyping and bulk production needs.