The global fastener market, valued at approximately USD 109.2 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030, according to Grand View Research. A critical component within this expansive industry is the 1/4-inch screw segment, widely used across automotive, construction, electronics, and industrial manufacturing sectors. The rising demand for high-precision, corrosion-resistant, and lightweight fasteners—driven by advancements in electric vehicles and modular construction—has intensified competition among manufacturers. In parallel, Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady growth in industrial automation and infrastructure development, particularly in the Asia-Pacific and North American regions, further bolstering demand for standardized screws, including 1/4-inch variants. As supply chains become more globalized and quality standards more stringent, identifying leading 1/4 screw manufacturers is essential for procurement teams and OEMs seeking reliability, scalability, and compliance. The following analysis highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping this space, evaluated on production capacity, innovation, geographic reach, and market reputation.
Top 10 1 4 Screws Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Star Drive Wood Screws – Screw Products, Inc.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: screw-products.com
Key Highlights: Screw Products Inc. specializes in star drive stainless steel and heat treated wood screws for decks, log homes, remodeling, kitchen cabinets, docks, ……
#2 Chrome Bolts, Stainless Steel Bolts, Metric Bolts, Socket Head Cap …
Domain Est. 2002
Website: allensfasteners.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsFasteners & Industrial Supply ; Machine Screws · Electrical Connectors · Sheet Metal Screws ; Brass Fittings ; We carry hex head, socket head, button head and flat …..
#3 Pro-Twist
Domain Est. 2003
Website: pro-twist.com
Key Highlights: Pro-Twist is an industry-leading manufacturer of professional-grade fasteners that are used for a wide variety of applications. Get started with us today!…
#4 Fasco Fastener & Industrial Supply Corp
Domain Est. 2012
Website: fascofas.com
Key Highlights: Fasco Fastener & Industrial Supply is your one stop shop for durable, high-quality fasteners for many types of construction projects….
#5 See all Screws
Domain Est. 1991
Website: us.sfs.com
Key Highlights: Product Type. Wood screw (1) ; Diameter. #10 (1) ; Material. Stainless Steel A2 (1) ; Head Style. Dome head (3) ; Drill Capacity Max [Inches]. 0.197″ Aluminum (2)….
#6 Fastening Systems — Screws & Nails
Domain Est. 1995
Website: strongtie.com
Key Highlights: Information about our wide variety of nail types and screw styles designed for every project including our Strong-Drive® and Deck-Drive™ product lines….
#7 Specialty Fastening Solutions for the Commercial Construction …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: itwbuildex.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture self-drilling and tapping screws, anchors, toggles, and other fastening systems under the Teks, Sammys, Dec-King, EZ Ancor, and Rock-On-brands….
#8 PEM – PennEngineering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: PEM offers innovative fastening solutions for a variety of applications across industries like Automotive Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Datacom and more….
#9 SPAX US
Domain Est. 2004
Website: spax.us
Key Highlights: Our Engineered Screws & Fasteners are manufactured and rigorously tested right here in the heart of America. Rely on us to help you drive the highest quality….
#10 Big Timber
Domain Est. 2018
Website: bigtimberfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Choose from one of our many fastening solutions. At Big Timber Construction Fasteners, we believe that using the right tool will make or break your project’s ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1 4 Screws
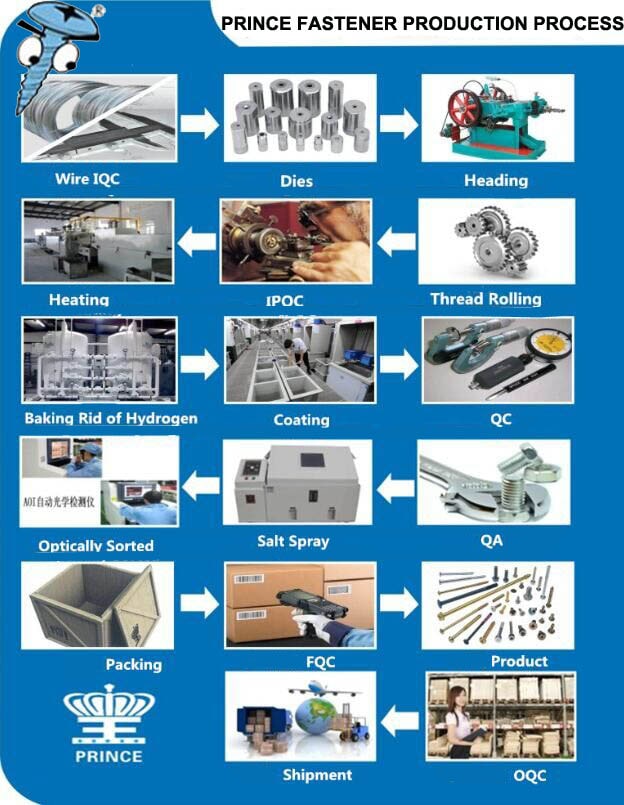
H2: Market Trends for 1/4-Inch Screws in 2026
The global market for 1/4-inch screws is expected to experience steady growth and transformation in 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing, shifts in construction and industrial demand, and evolving sustainability standards. As a standard fastener size widely used across multiple sectors—including construction, automotive, furniture, and DIY applications—the 1/4-inch screw segment will reflect broader macroeconomic and technological trends.
1. Rising Demand in Construction and Infrastructure
With governments worldwide investing in infrastructure modernization—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia—the construction sector will remain a primary driver of demand for 1/4-inch screws. These screws are commonly used in structural framing, decking, and heavy-duty installations. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and similar initiatives in Europe are expected to sustain high activity levels through 2026, boosting fastener consumption.
2. Growth in Industrial Automation and Manufacturing
The expansion of automated manufacturing processes will increase the need for standardized, high-quality fasteners. 1/4-inch screws are frequently used in machinery assembly, robotics, and production line equipment. As industries adopt Industry 4.0 technologies, demand for precision-engineered screws with consistent threading and durability will rise, favoring manufacturers offering high-tolerance products.
3. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and processes. In 2026, there will be growing demand for 1/4-inch screws made from recycled steel, zinc-coated alternatives with reduced environmental impact, and corrosion-resistant coatings that extend product life. Biodegradable or recyclable packaging for fasteners is also expected to become standard among leading suppliers.
4. E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Channels
The DIY and home improvement market continues to expand, fueled by online platforms like Amazon, Home Depot, and specialized industrial suppliers. In 2026, convenience, fast delivery, and detailed product information will drive consumer preference. Pre-packaged kits of 1/4-inch screws tailored for specific applications (e.g., deck building, furniture assembly) will gain popularity, especially in North America and Western Europe.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Regional Sourcing
Following disruptions in recent years, companies are reshoring or nearshoring fastener production. In 2026, regional manufacturing hubs in Mexico, Eastern Europe, and Southeast Asia will play a key role in supplying 1/4-inch screws, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers. This shift will improve delivery times and reduce logistics costs, especially for large-scale construction and industrial clients.
6. Price Volatility and Raw Material Costs
Steel and zinc prices will remain influential cost factors. While efforts to stabilize supply chains may mitigate some volatility, geopolitical tensions and energy costs could lead to moderate price fluctuations in 2026. Companies that lock in long-term material contracts or invest in alternative alloys may gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
The 1/4-inch screw market in 2026 will be shaped by infrastructure growth, industrial automation, sustainability demands, and digital retail expansion. Manufacturers and suppliers who innovate in materials, streamline distribution, and adapt to regional market needs will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends. As a foundational component in countless applications, the 1/4-inch screw will remain a small but critical element of global industrial and consumer activity.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 1/4 Screws (Quality, IP)
Sourcing 1/4 screws—especially in industrial, construction, or precision applications—requires careful attention to specifications and quality standards. Two critical factors often overlooked are material quality and adherence to Ingress Protection (IP) ratings where applicable. Below are common pitfalls to avoid.
1. Assuming All 1/4 Screws Are the Same
One of the most frequent mistakes is treating all 1/4 screws as interchangeable. The designation “1/4” refers only to the nominal diameter and does not specify thread pitch, length, material, strength grade, or head type. Using an incorrect variant can lead to mechanical failure or incompatibility.
Tip: Always specify full thread dimensions (e.g., 1/4″-20 UNC x 1″) and required standards (e.g., ASTM A449, ISO 898-1).
2. Overlooking Material Quality and Corrosion Resistance
Many low-cost suppliers use substandard materials, such as low-grade carbon steel or improperly plated metals, leading to rust, thread stripping, or premature failure—especially in humid or outdoor environments.
Pitfall: Screws labeled “stainless steel” may be low-quality 201-grade instead of corrosion-resistant 304 or 316.
Tip: Request material certifications and verify compliance with standards like ASTM A320 or ISO 3506.
3. Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Requirements
While IP ratings typically apply to enclosures and electrical housings, the screws used in such assemblies contribute to overall environmental sealing. Poorly selected screws can compromise IP integrity.
Pitfall: Using standard screws instead of sealed or gasketed variants in IP65 or higher-rated enclosures, leading to moisture or dust ingress.
Tip: For high IP-rated systems, use screws with integrated O-rings, proper sealing washers, or ensure tight thread fit (e.g., fine threads or thread-locking compounds).
4. Failing to Verify Thread Fit and Tolerance
Improper thread tolerances—especially in coarse vs. fine thread systems—can result in cross-threading, galling, or insufficient clamping force.
Pitfall: Mixing 1/4″-20 (coarse) and 1/4″-28 (fine) threads, which may appear to fit initially but fail under load.
Tip: Confirm thread pitch and tolerance class (e.g., 2A/2B) with the supplier and perform fit checks during quality inspection.
5. Skipping Supplier Qualification and Traceability
Procuring screws from unverified suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant products. Traceability is essential for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Pitfall: Receiving screws without lot numbers, material test reports, or certification documents.
Tip: Only source from reputable, audited suppliers who provide full traceability and compliance documentation.
6. Neglecting Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
In certain industries (e.g., marine, medical, food processing), screws must meet environmental regulations like RoHS, REACH, or FDA standards.
Pitfall: Using cadmium-plated screws in food-grade equipment, which may violate safety regulations.
Tip: Clearly specify required compliance standards in procurement contracts.
By addressing these common pitfalls, you can ensure the reliability, safety, and longevity of assemblies using 1/4 screws—especially in applications where quality and IP ratings are mission-critical.
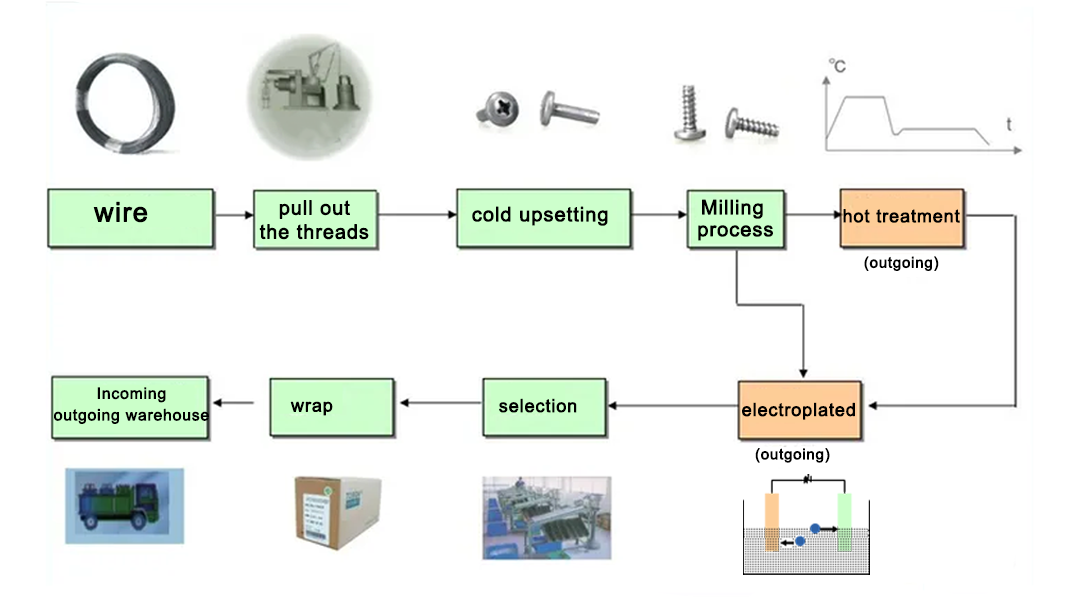
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1/4 Screws
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to 1/4-inch screws. Whether used in construction, manufacturing, or retail, proper management ensures safety, efficiency, and legal compliance.
Packaging Requirements
1/4-inch screws must be packaged securely to prevent damage and ensure accurate inventory control. Common packaging includes:
– Bulk packaging in moisture-resistant bags or containers
– Retail packaging with clear labeling (size, material, quantity)
– Industrial totes or sealed cartons for large-volume shipments
Ensure packaging complies with ISTA (International Safe Transit Association) standards for durability during transport.
Labeling & Marking
All packaging must include:
– Screw size (e.g., 1/4″-20 x 1″)
– Material type (e.g., stainless steel, zinc-plated steel)
– Quantity
– Manufacturer or supplier identification
– Batch/lot number for traceability
– Hazard symbols if applicable (e.g., sharp object warnings)
Ensure labels are durable and legible to meet OSHA and consumer safety standards.
Transportation & Handling
- Use palletized loads secured with stretch wrap or strapping for stability.
- Avoid exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures during transit.
- Follow standard freight regulations (e.g., FMCSA in the U.S.) for weight and load distribution.
- For international shipping, comply with IMDG Code if transported by sea or IATA regulations for air freight (though screws are typically non-hazardous).
Storage Conditions
Store 1/4-inch screws in a dry, climate-controlled environment to prevent rust and degradation.
– Keep off concrete floors using pallets or shelving to avoid moisture absorption.
– Organize by type and size to reduce handling errors.
– Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure screws are compliant with chemical restrictions, especially regarding lead, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium.
- ASTM/ASME Standards: Screws should meet relevant specifications (e.g., ASTM A307 for general-purpose bolts).
- Customs Documentation (International Shipments): Provide accurate HS Code (e.g., 7318.15 for steel screws), commercial invoice, and country of origin.
- DOT & OSHA (U.S.): Follow workplace safety standards for handling and storage.
Import & Export Considerations
- Verify tariff classifications and potential duties based on destination country.
- Confirm if screws fall under any trade restrictions or anti-dumping measures.
- Maintain certification documentation (e.g., material test reports) for customs clearance.
Sustainability & Disposal
- Recycle packaging materials where possible.
- Dispose of damaged or obsolete screws through certified metal recycling channels.
- Comply with local environmental regulations for industrial waste.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance practices for 1/4-inch screws ensure product integrity, regulatory adherence, and efficient operations. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to maintain standards across the supply chain.
Conclusion on Sourcing 1/4″ Screws
In conclusion, sourcing 1/4″ screws requires careful consideration of several key factors including thread type (e.g., coarse or fine), length, material (such as stainless steel, zinc-plated steel, or alloy), drive type (e.g., Phillips, slotted, or hex), and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, or SAE). Suppliers should be evaluated based on reliability, cost-effectiveness, minimum order quantities, and delivery timelines. Whether sourcing for industrial manufacturing, construction, or consumer applications, ensuring compatibility with the intended use and adherence to quality standards is essential. Utilizing reputable suppliers—both local distributors and online platforms—can streamline procurement and enhance supply chain efficiency. Ultimately, a thorough and strategic sourcing approach will ensure optimal performance, durability, and value for the application.